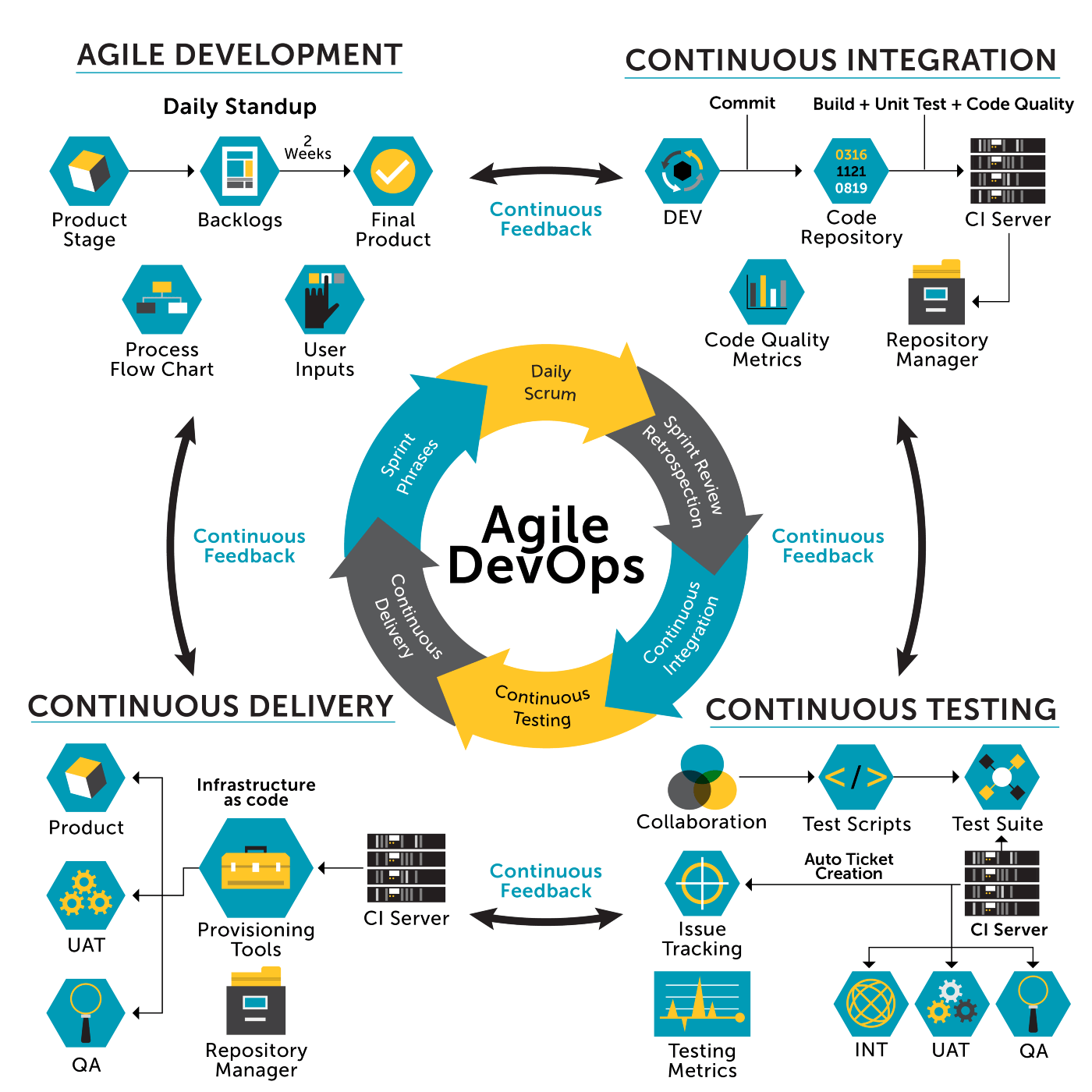
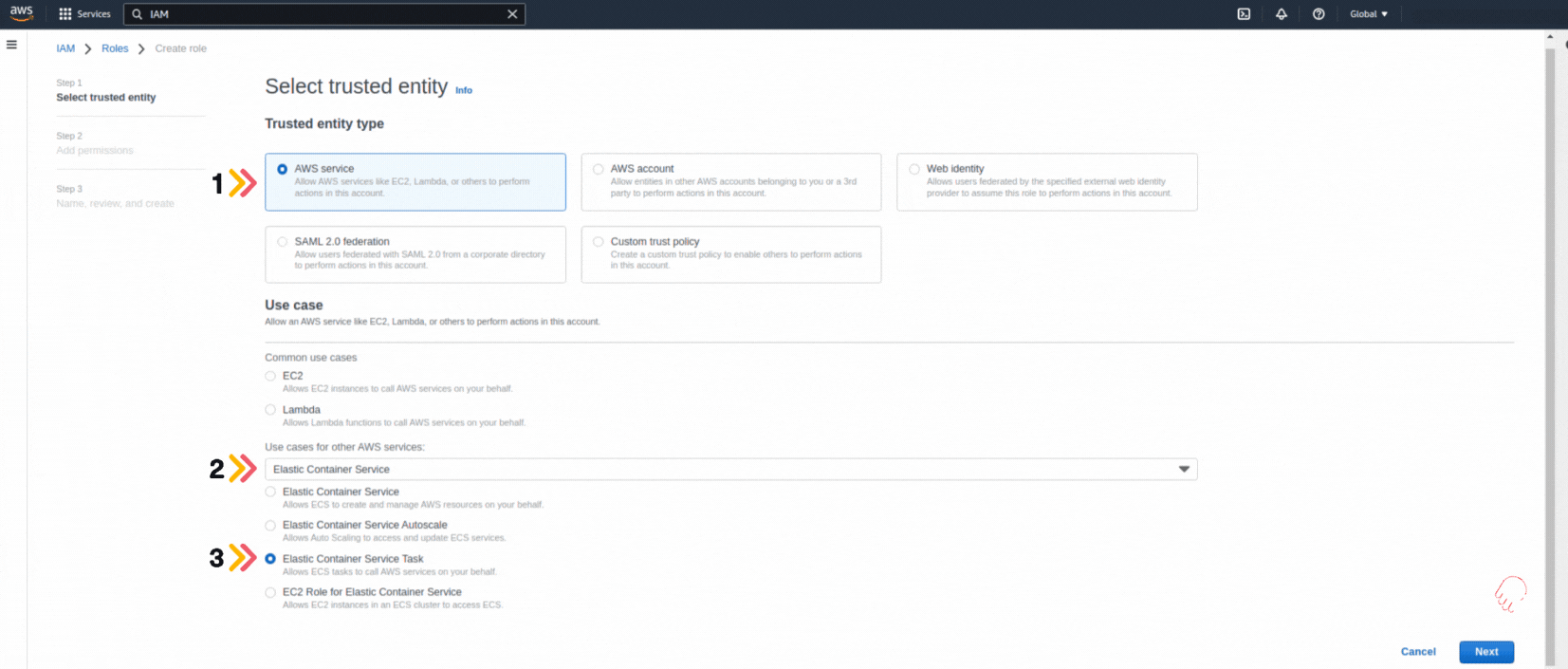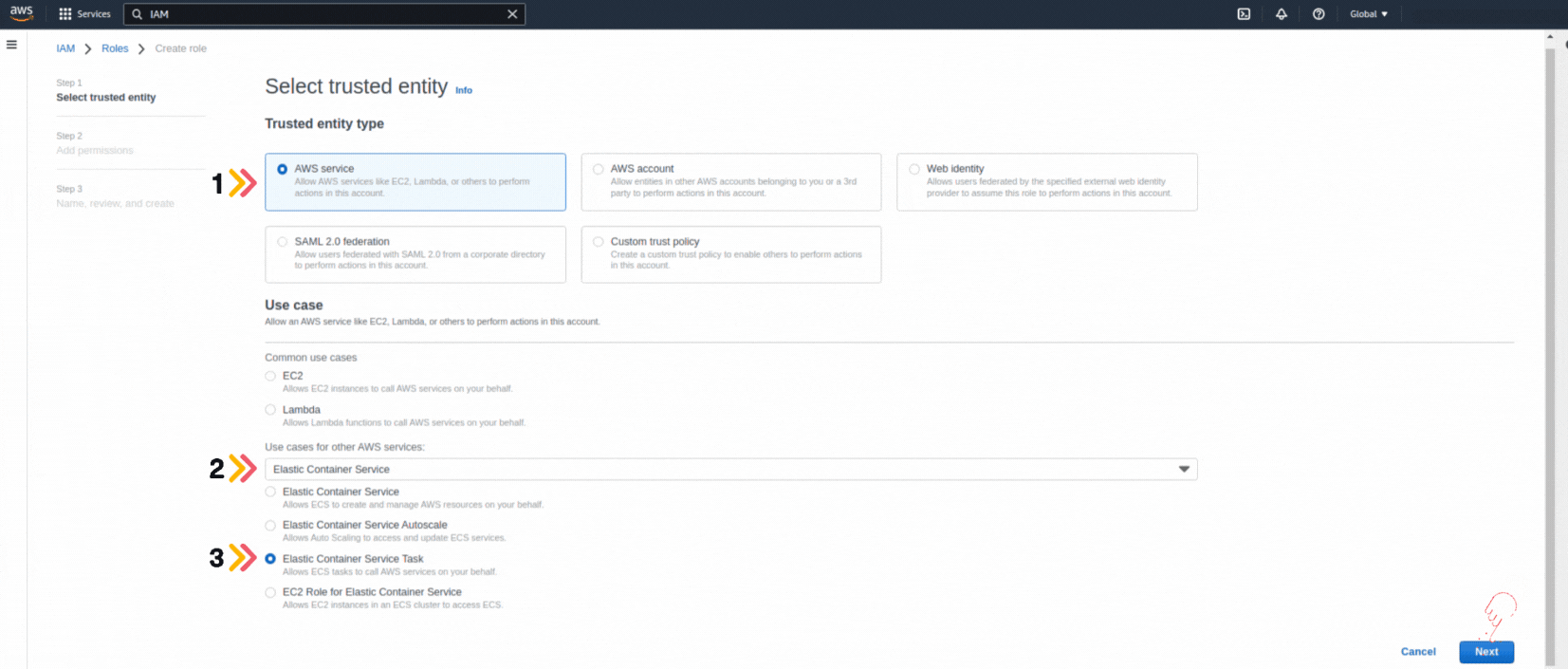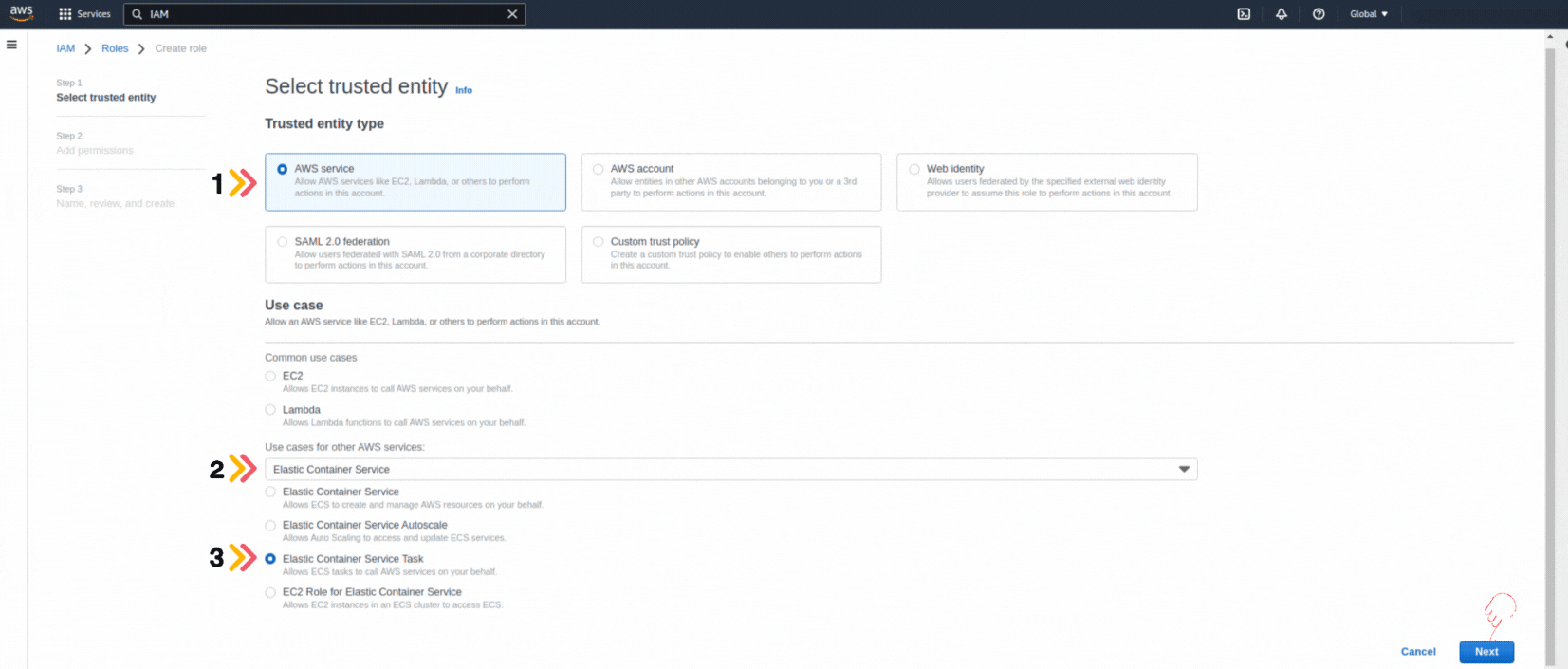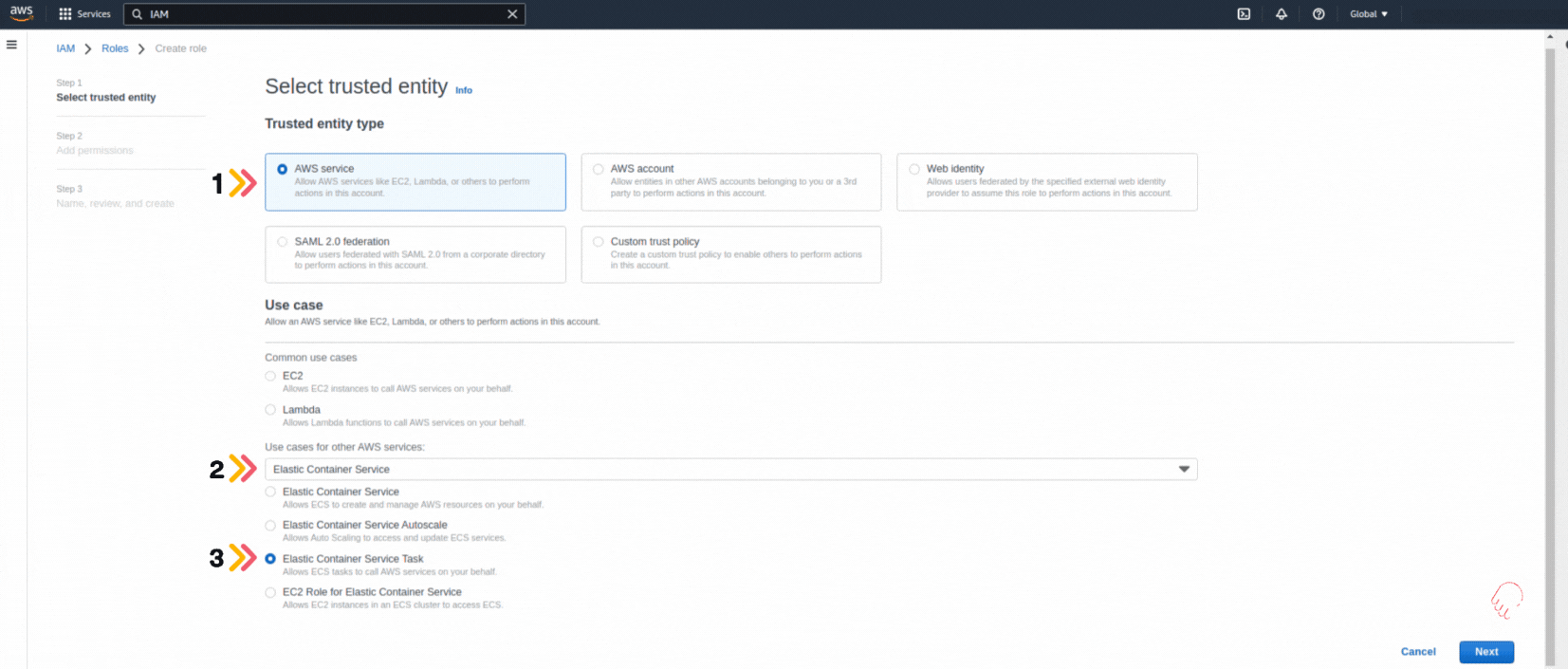
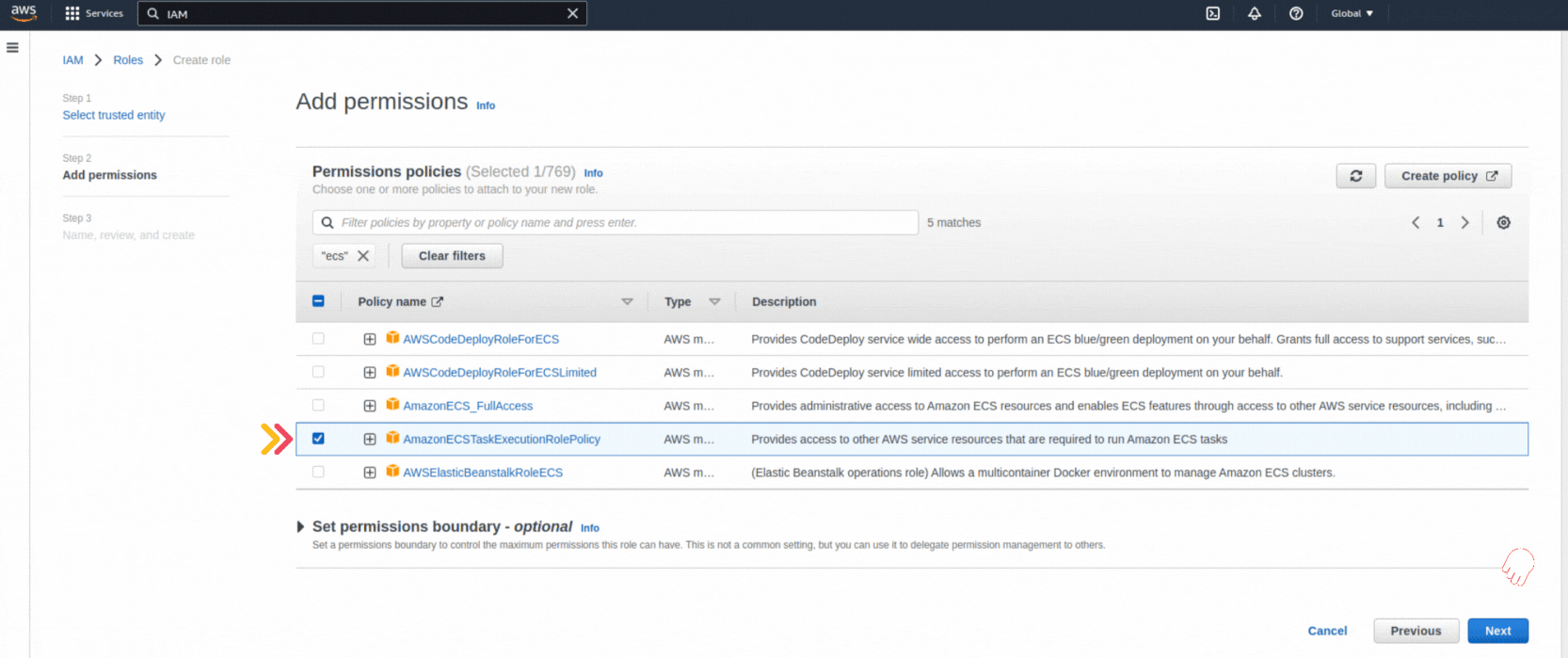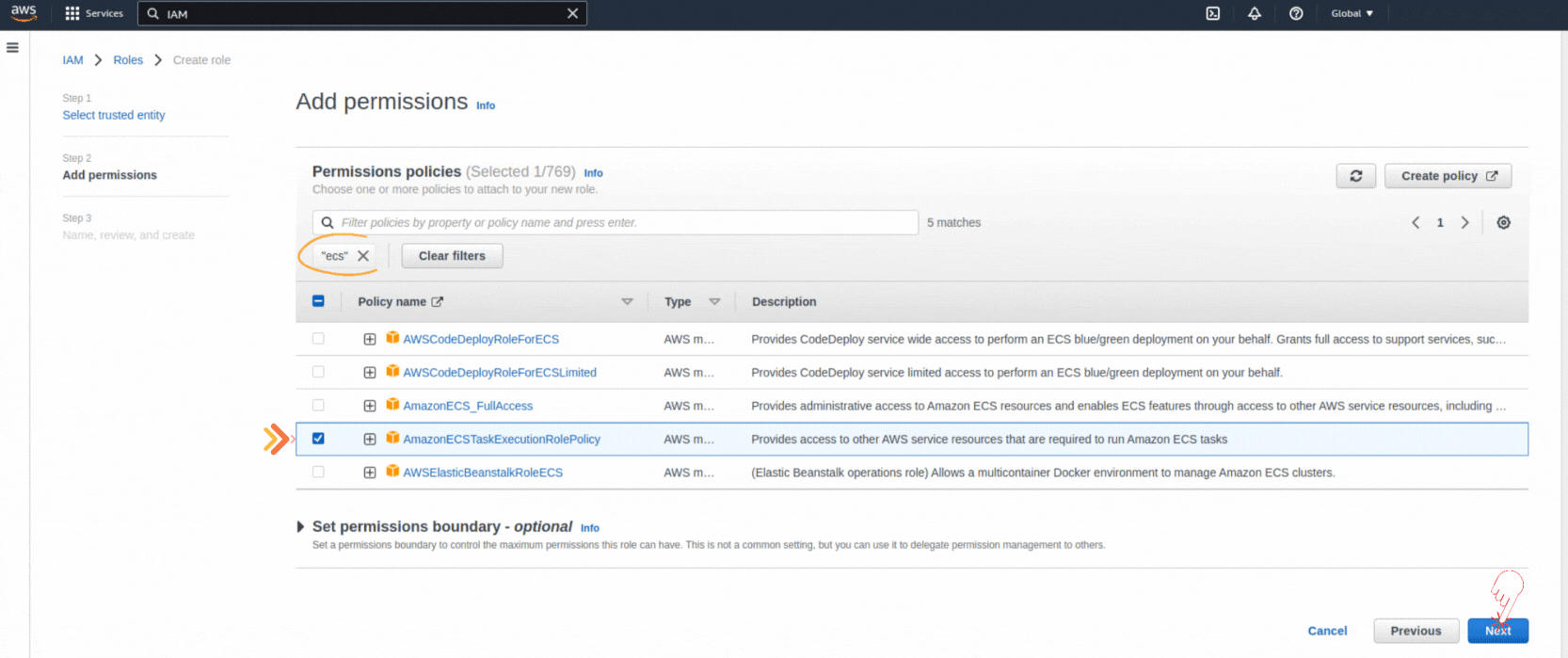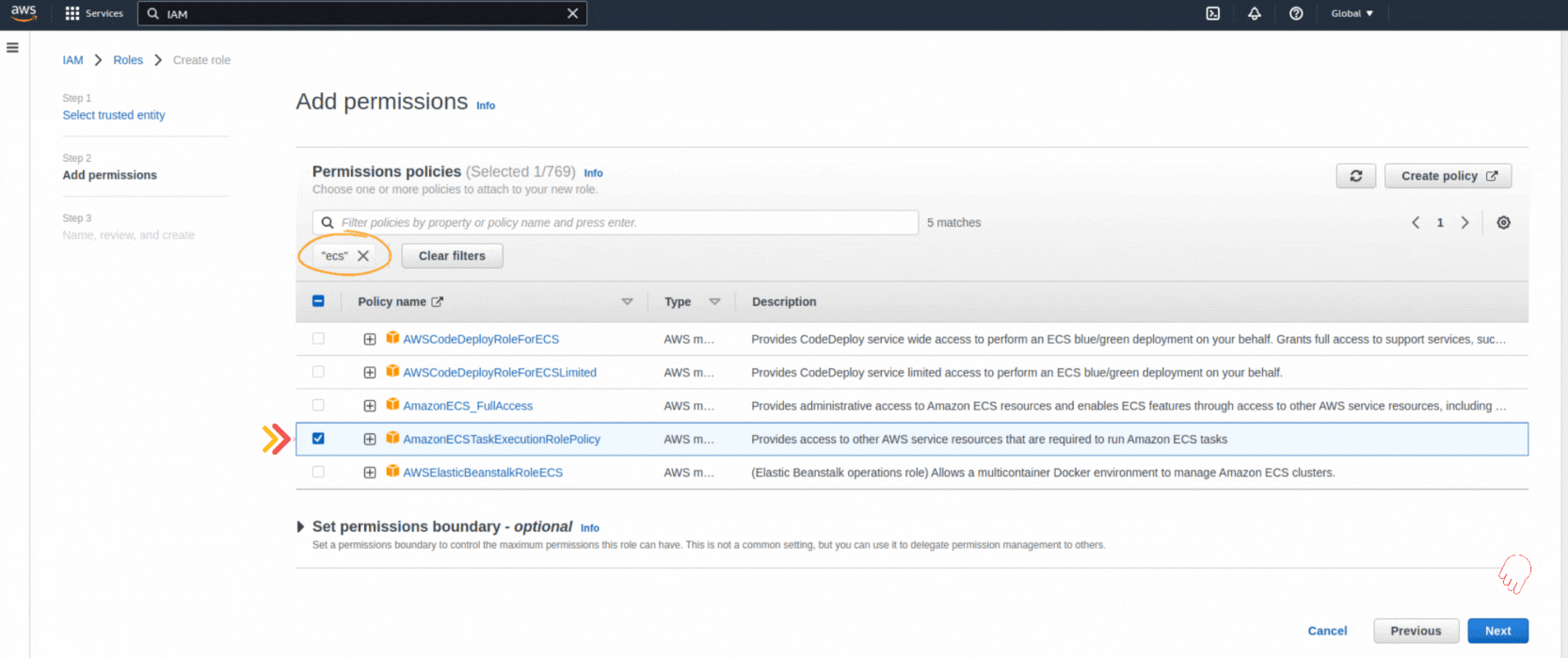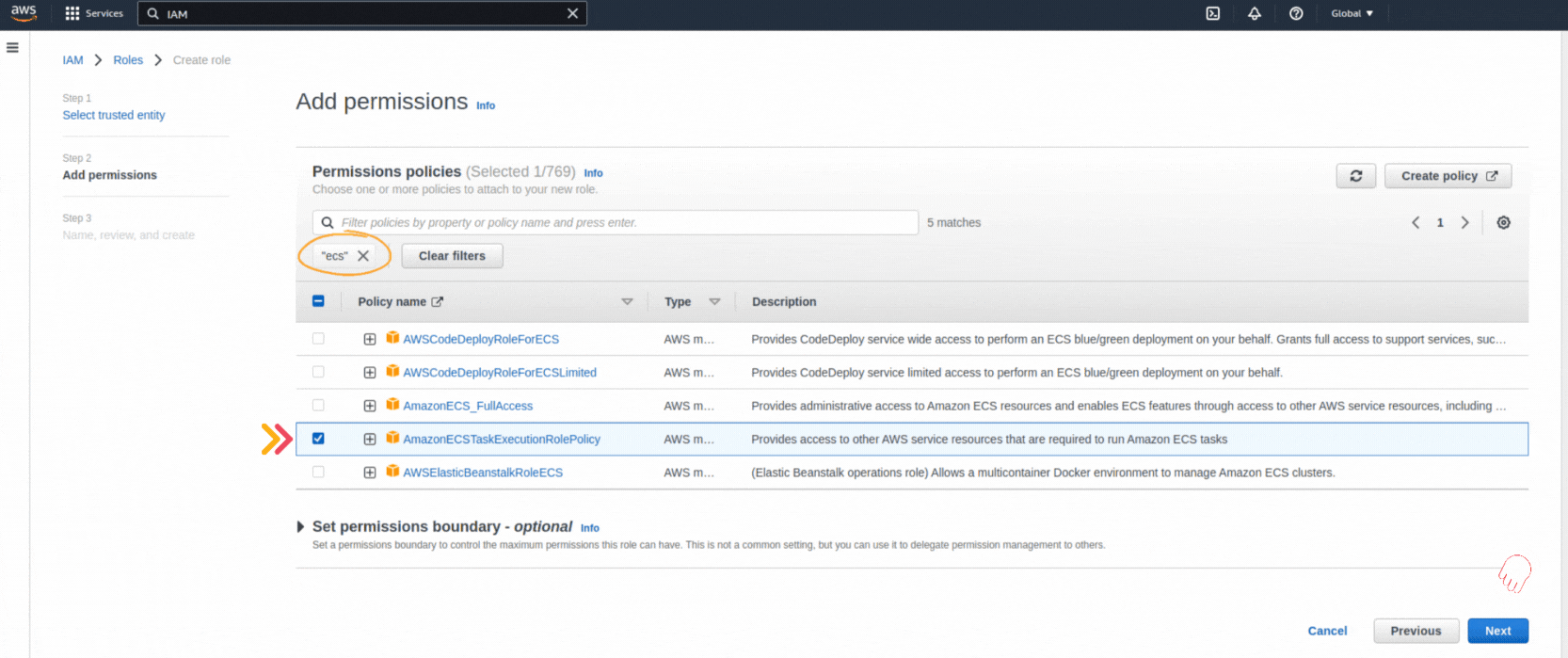
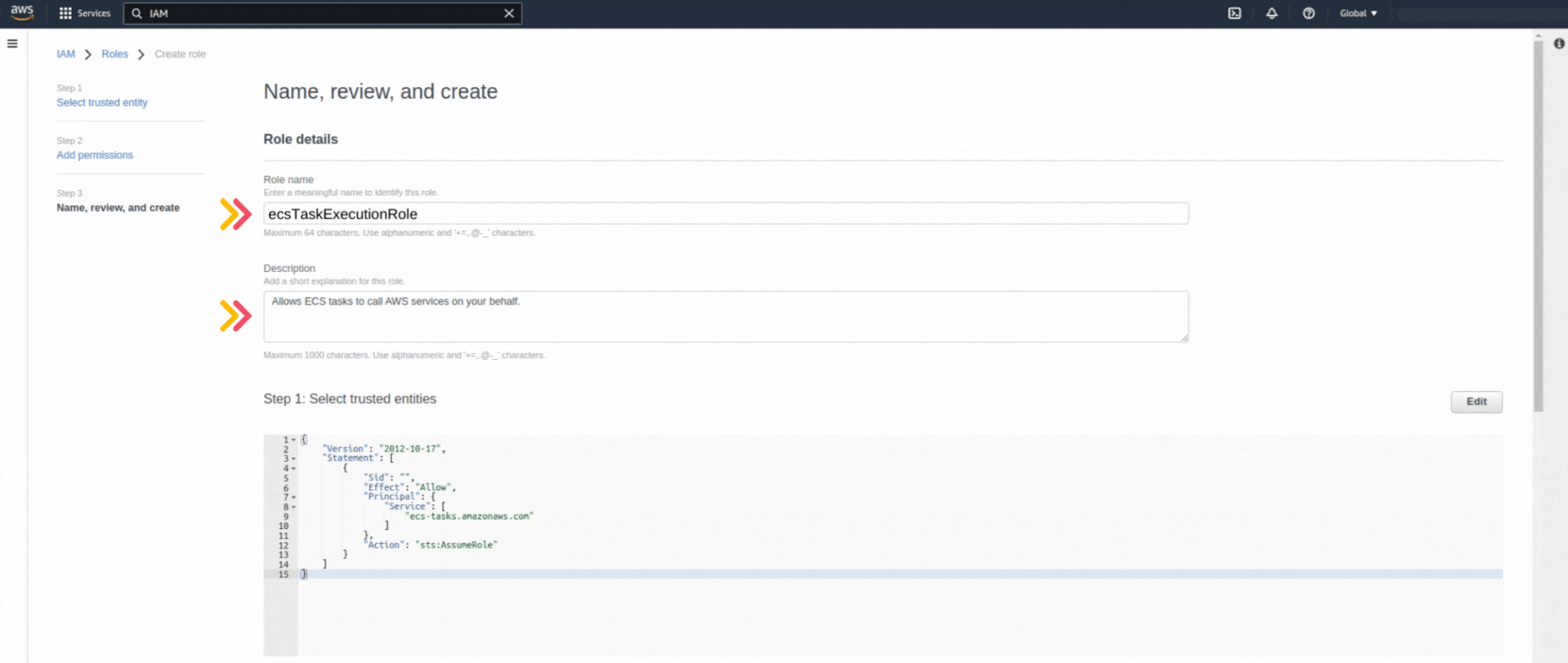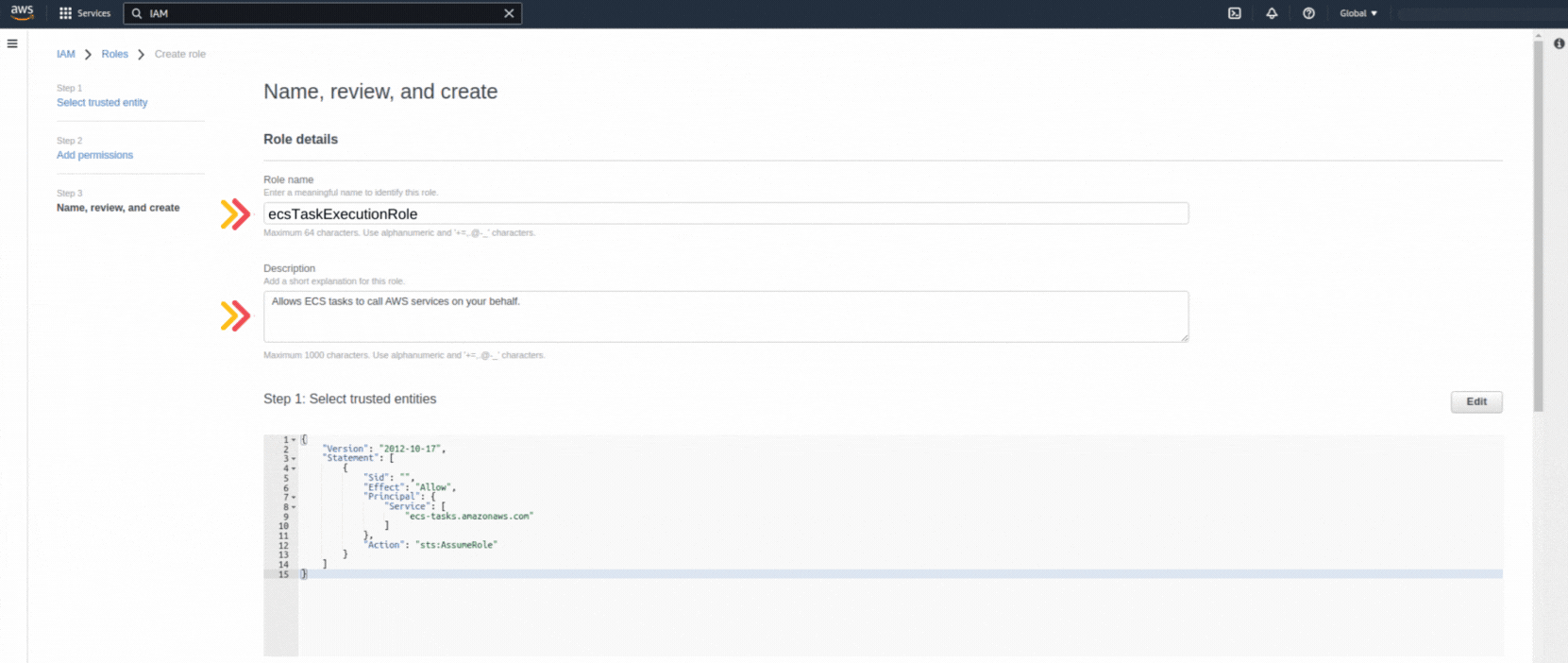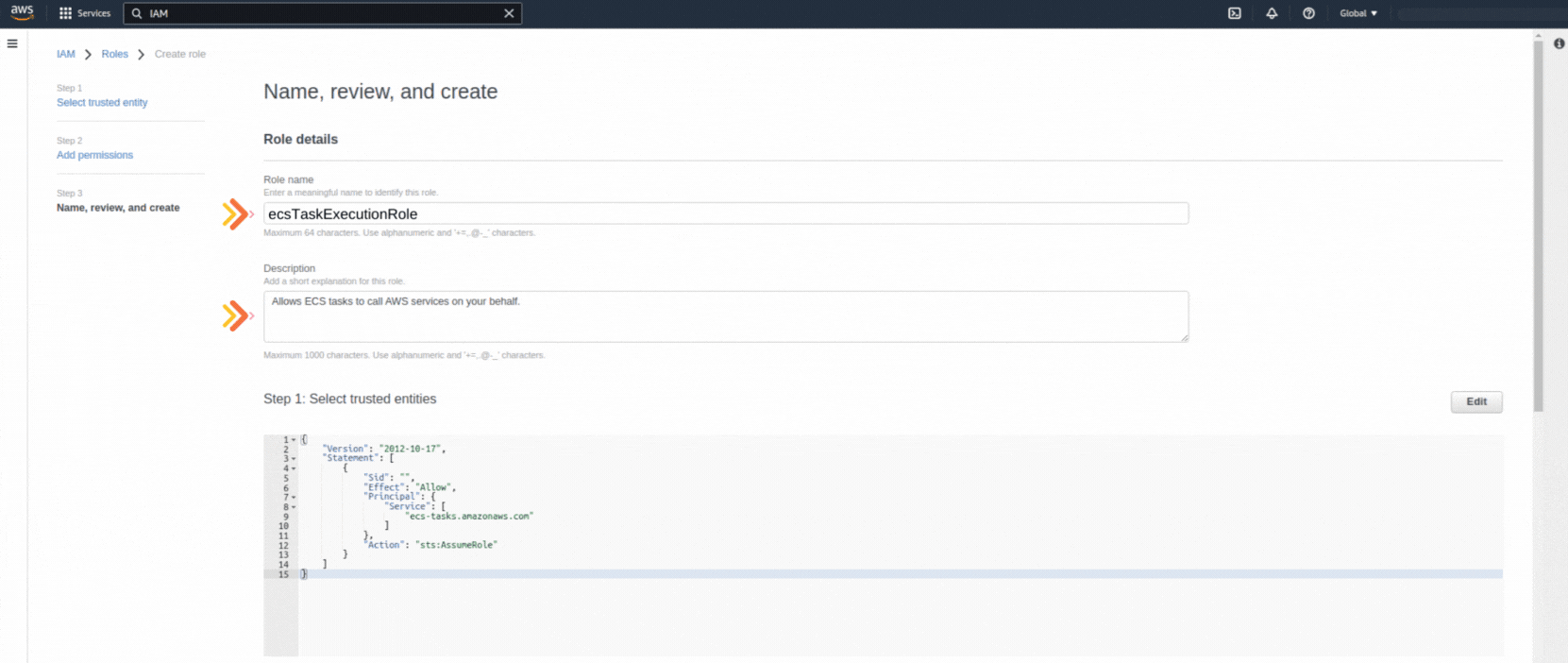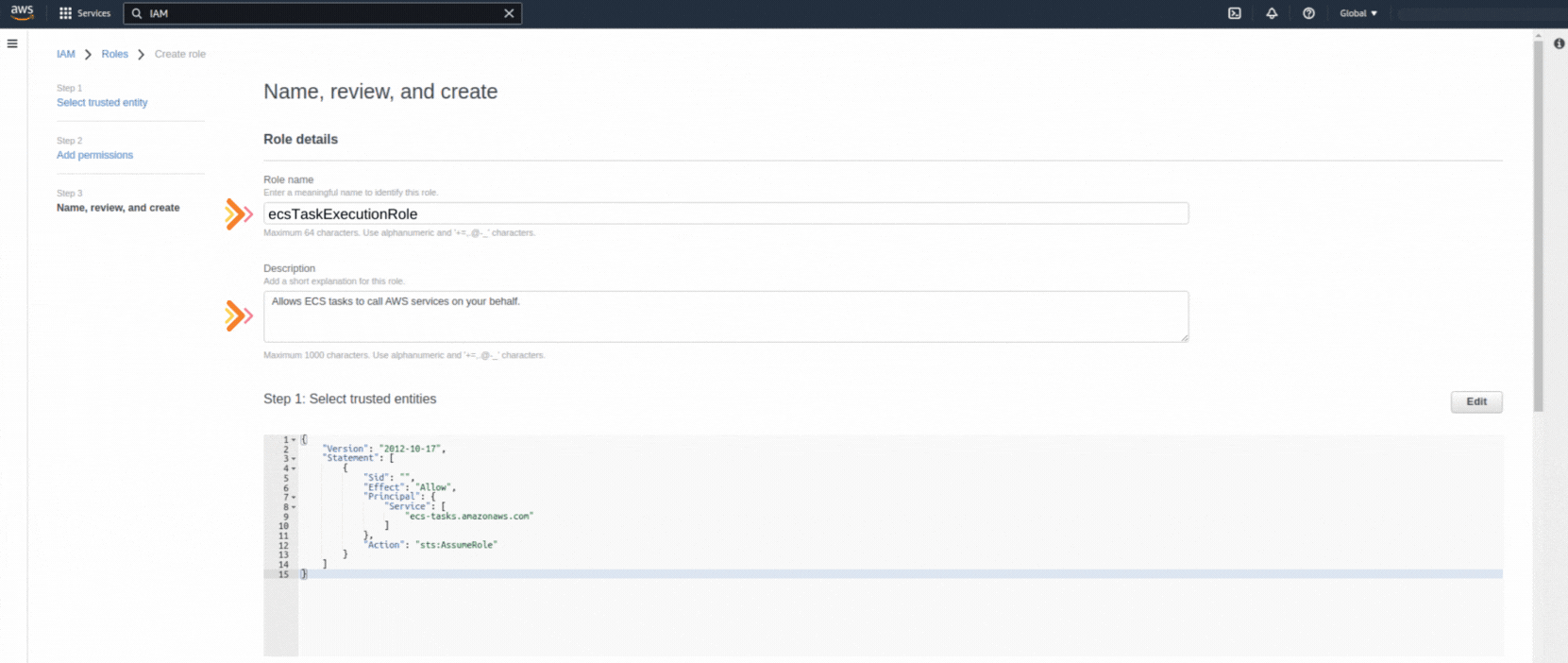
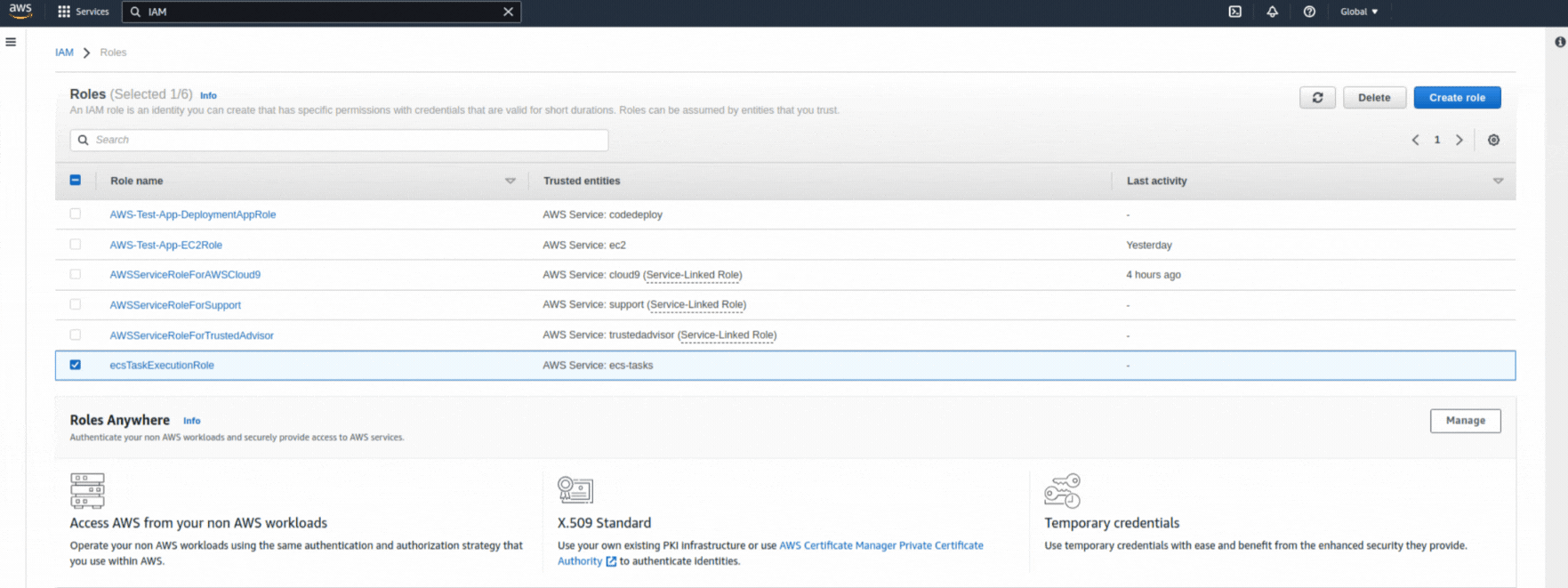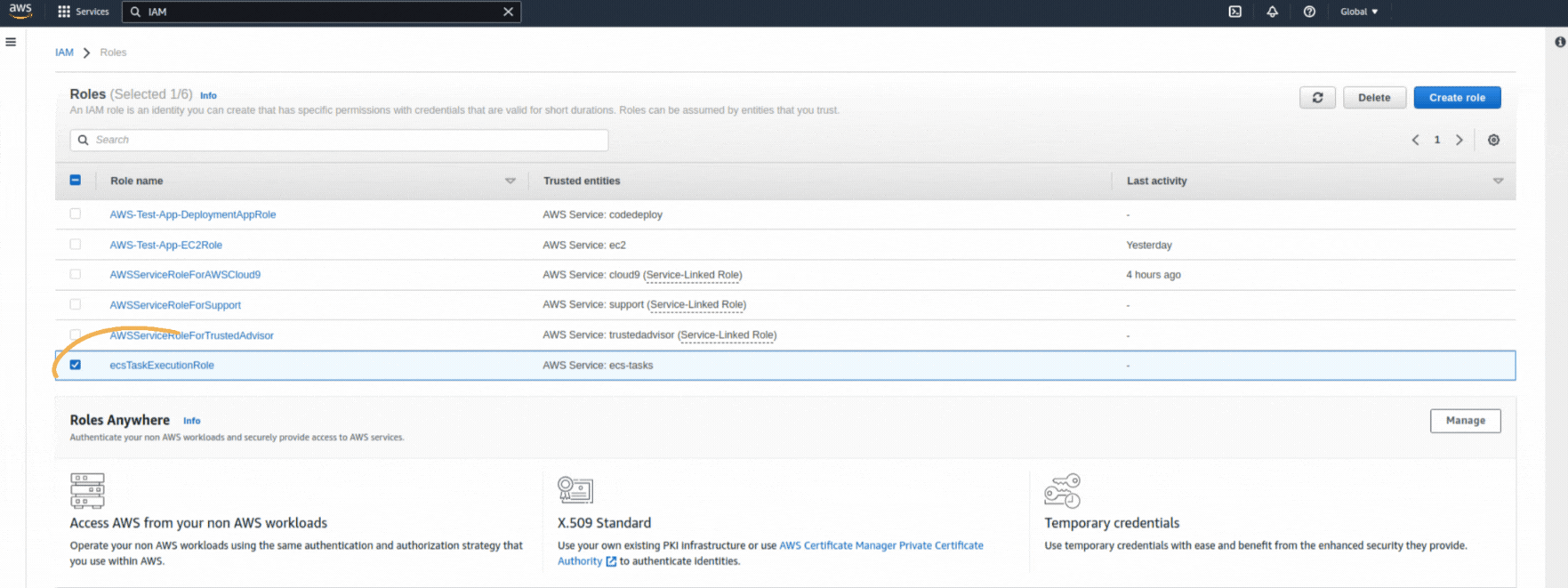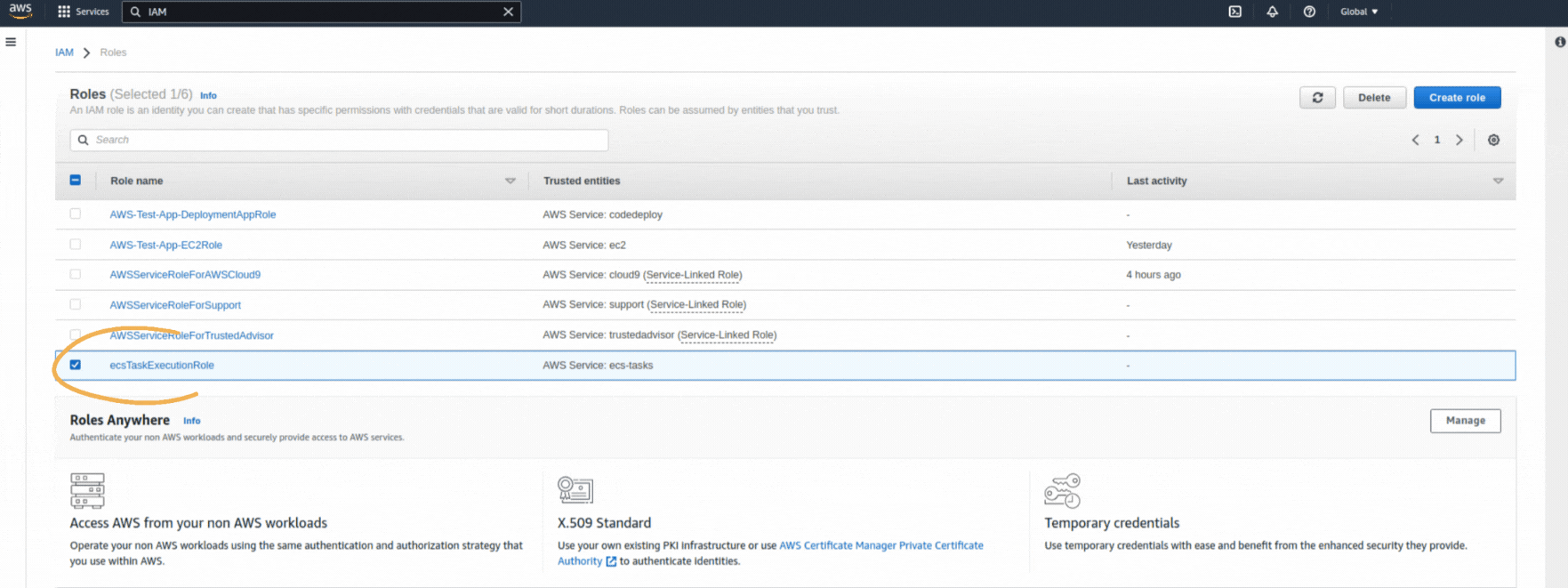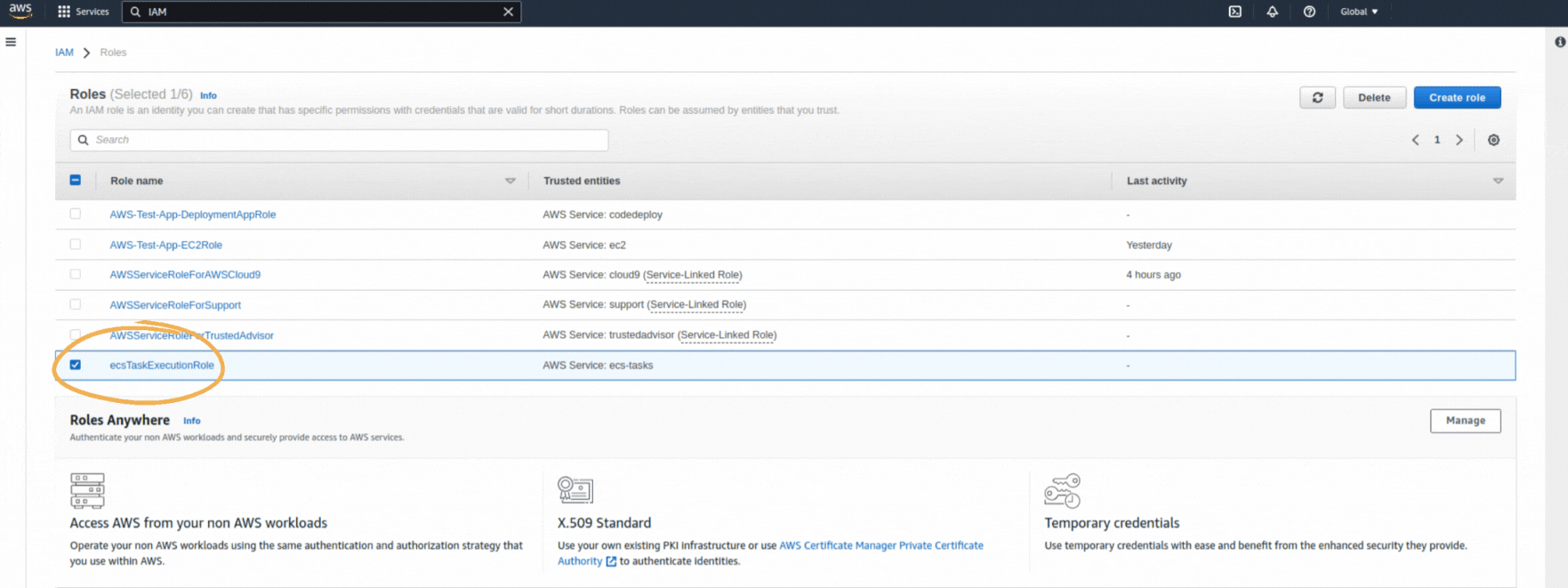
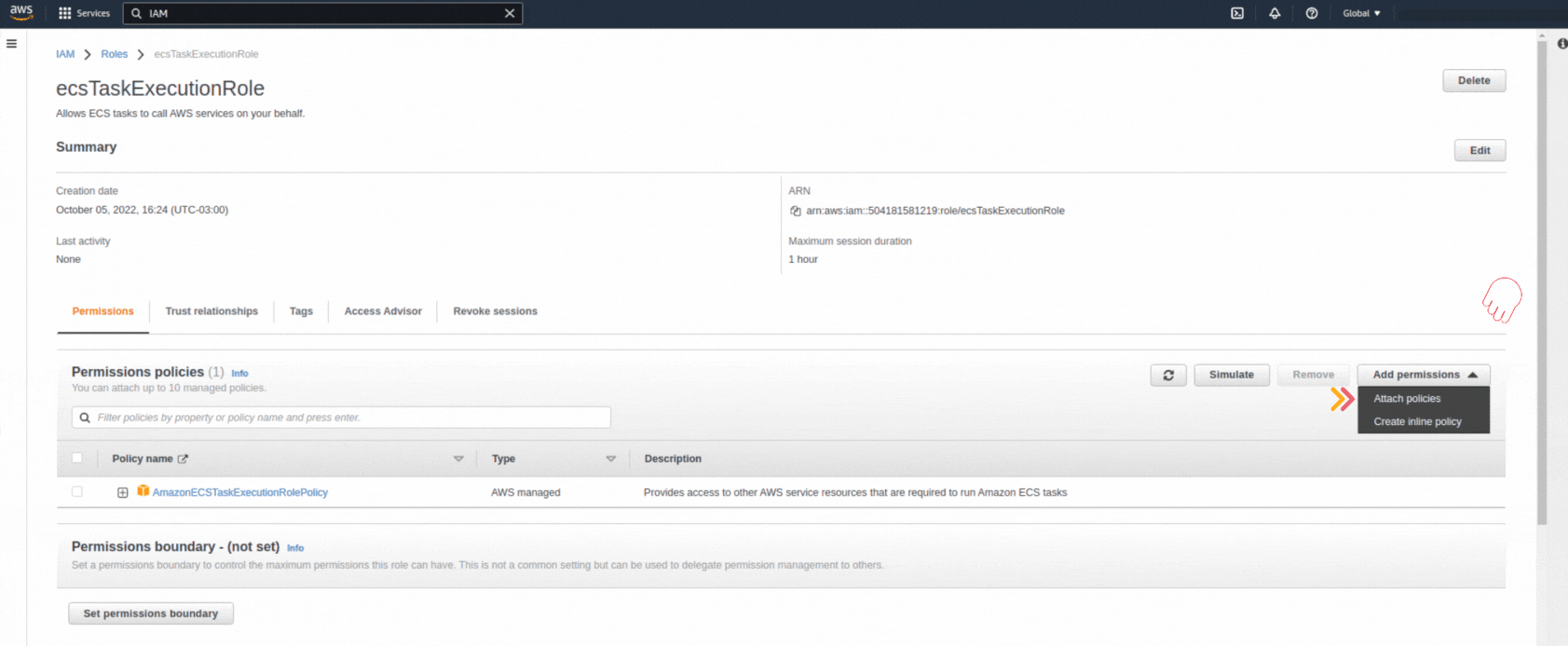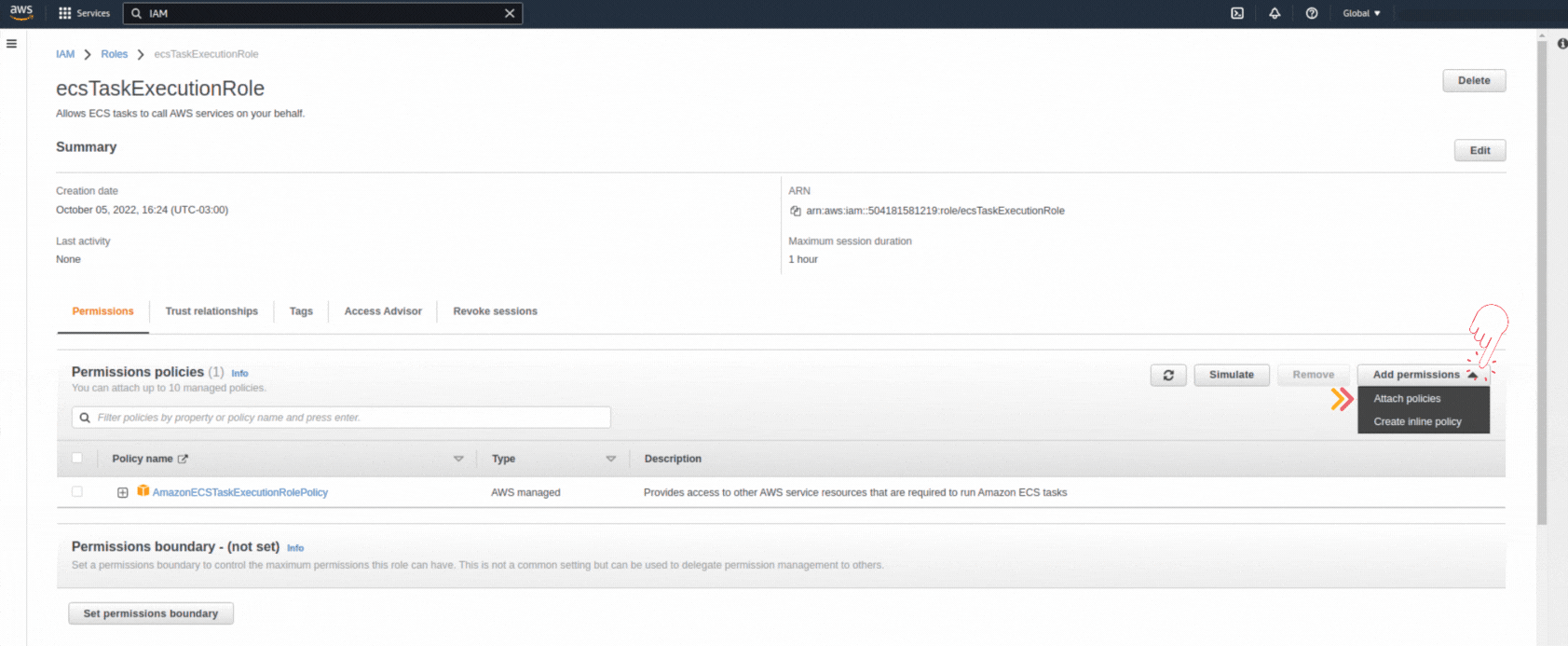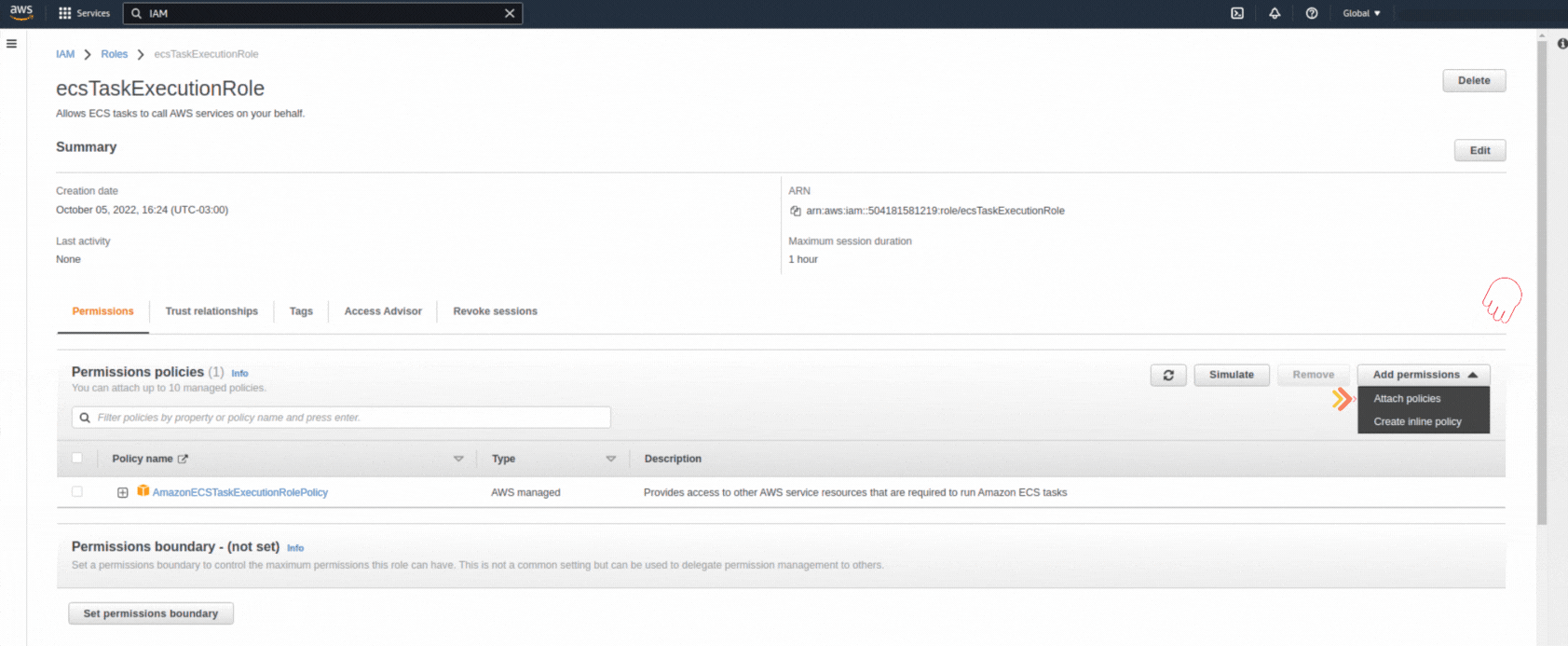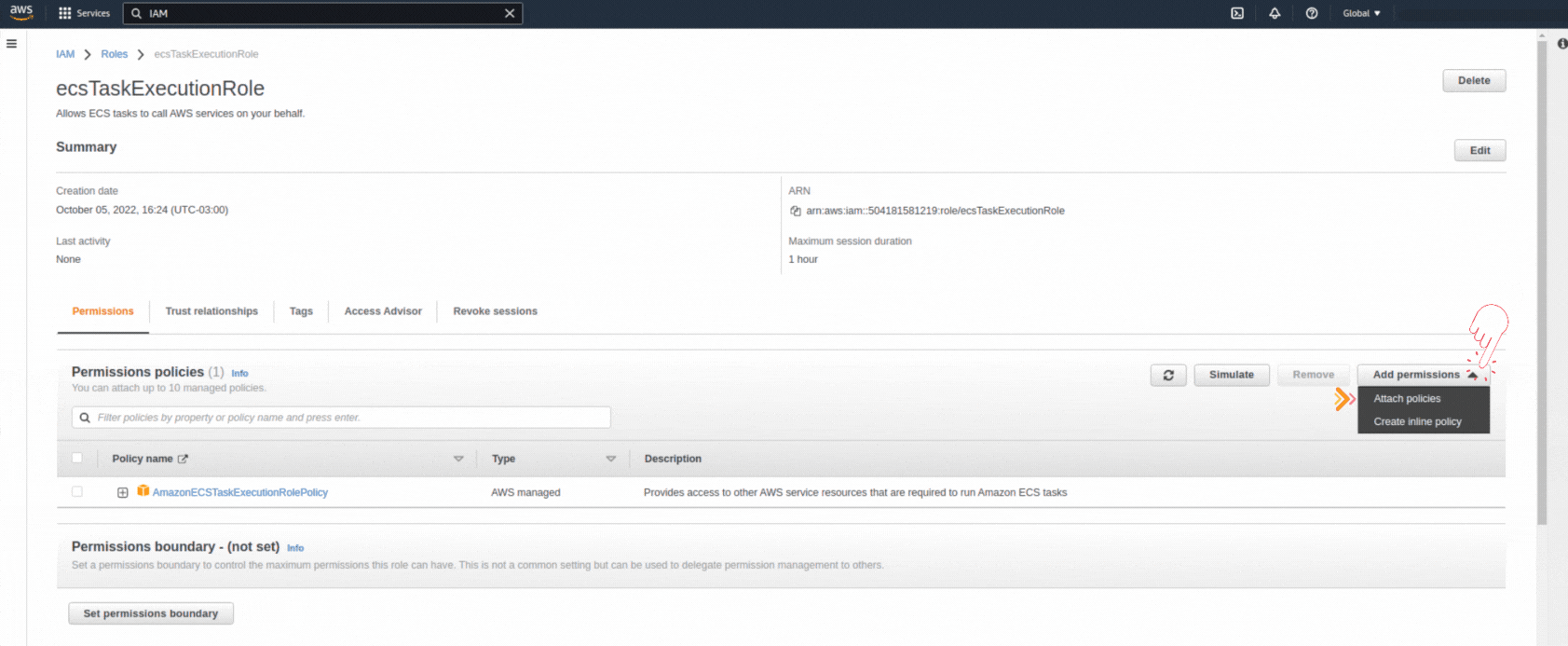
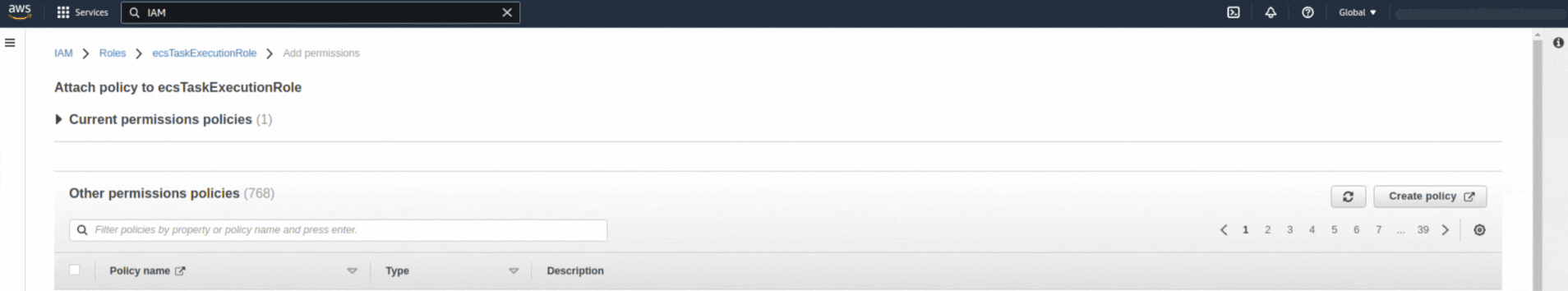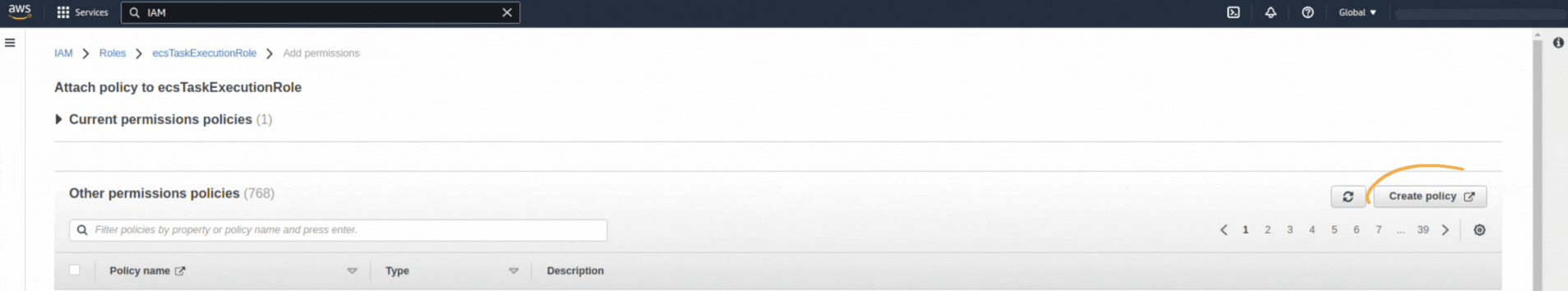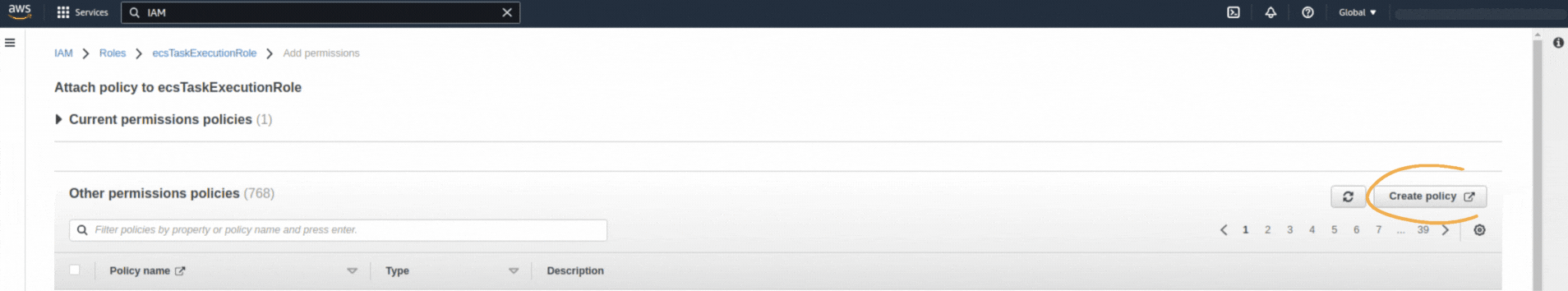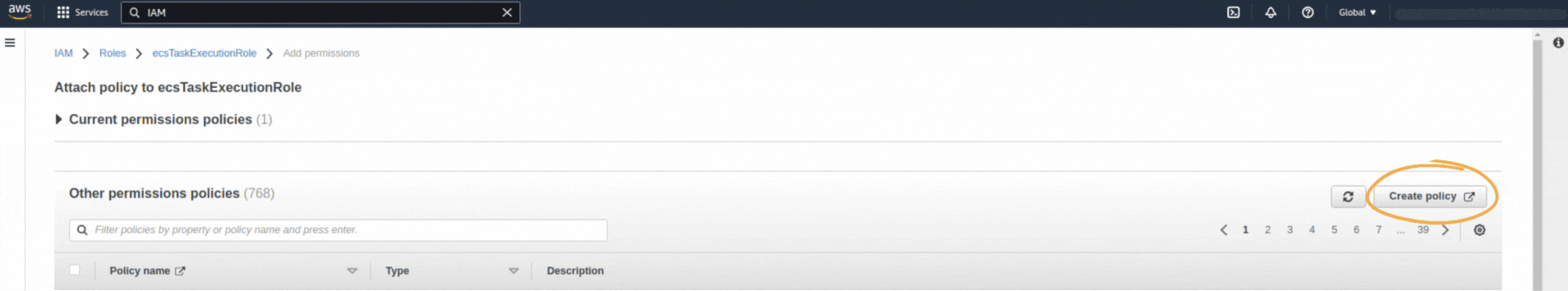
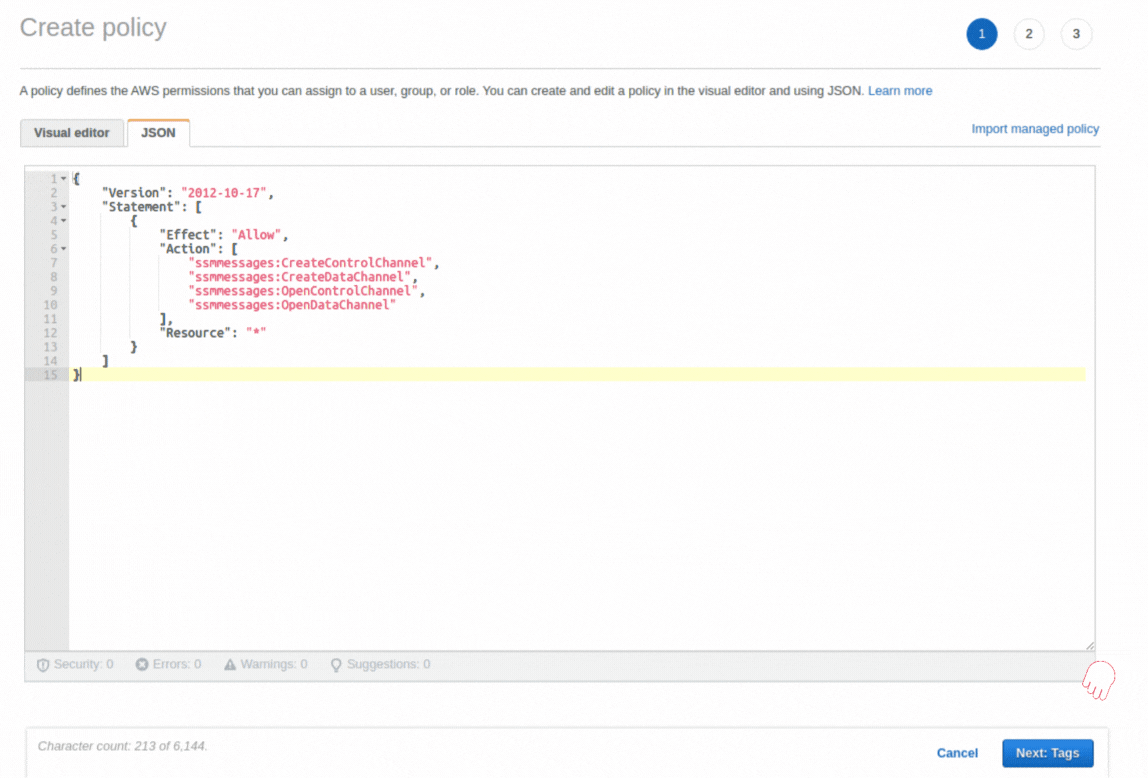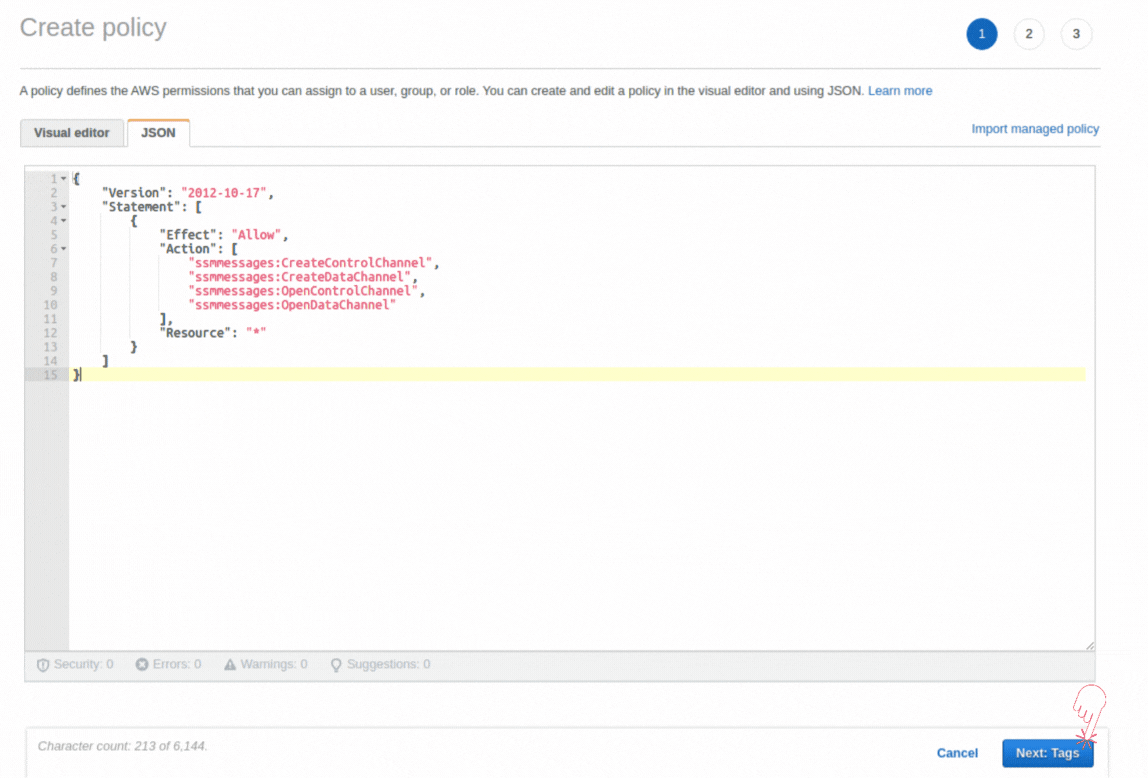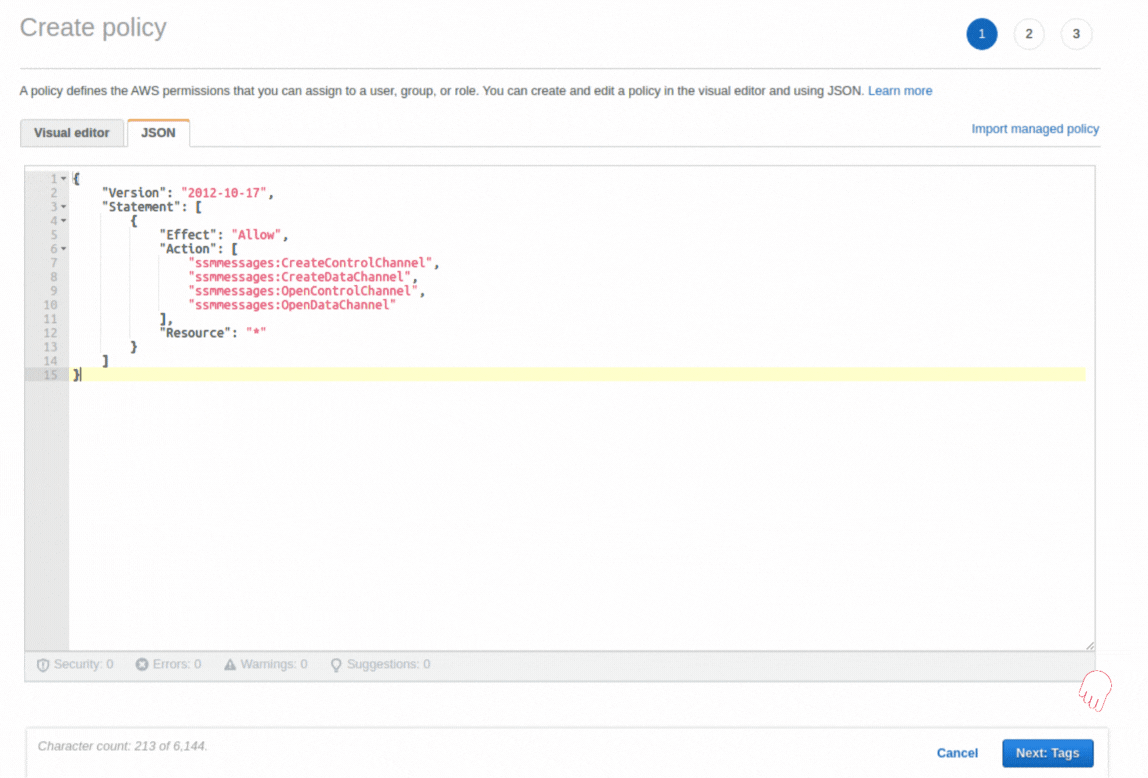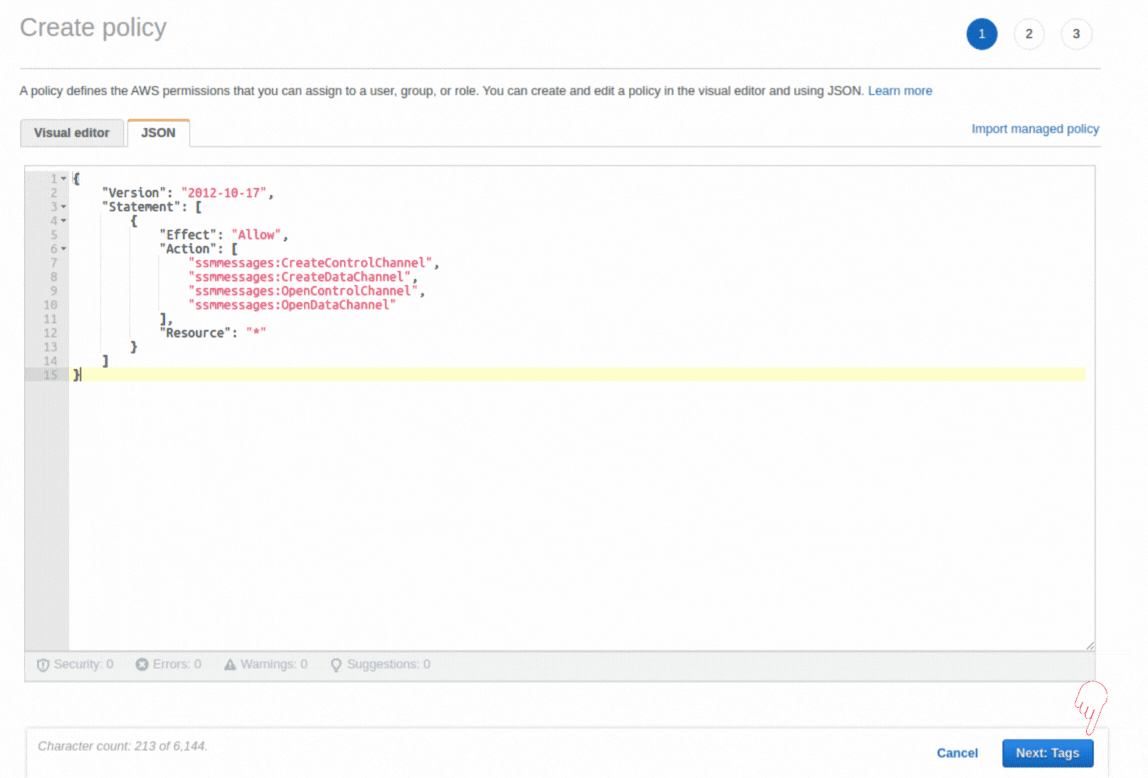
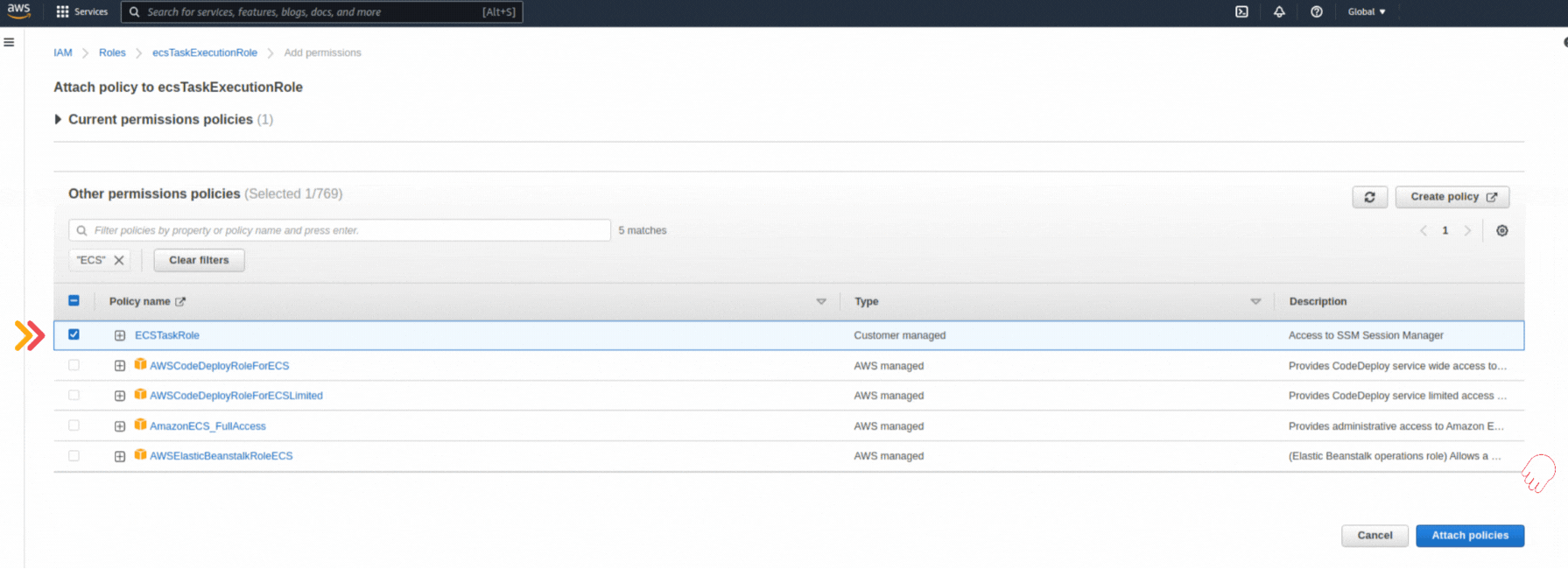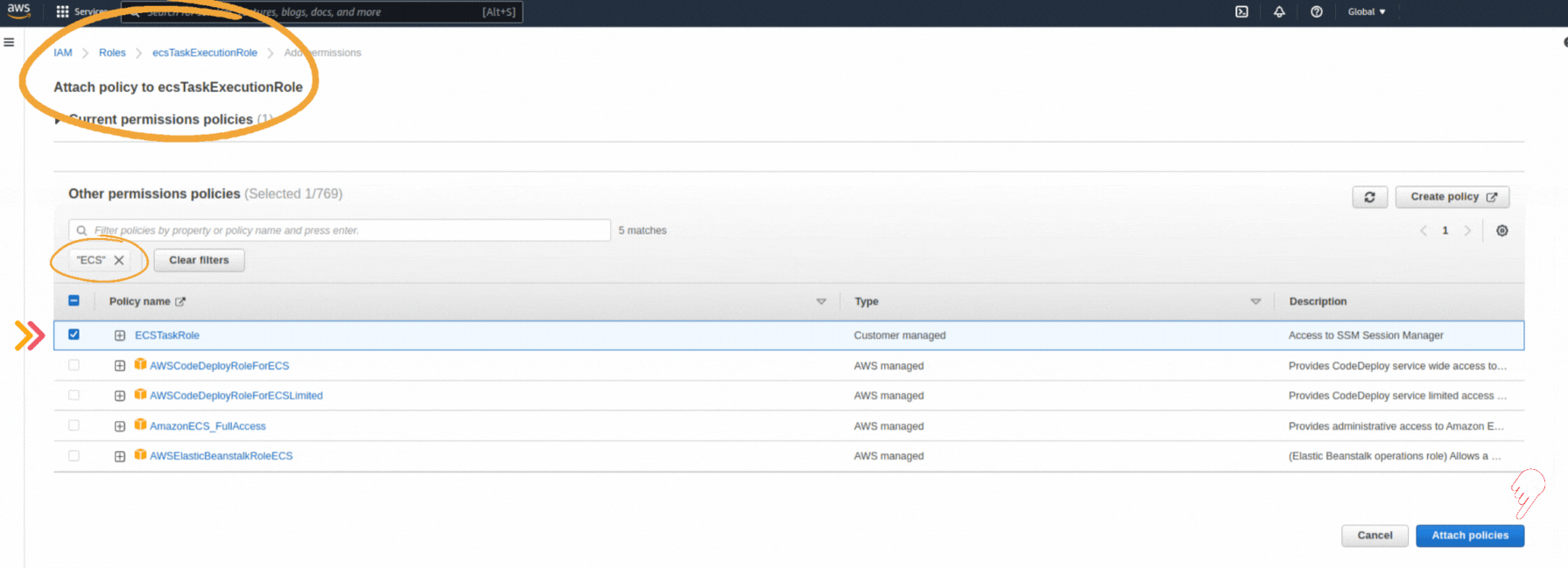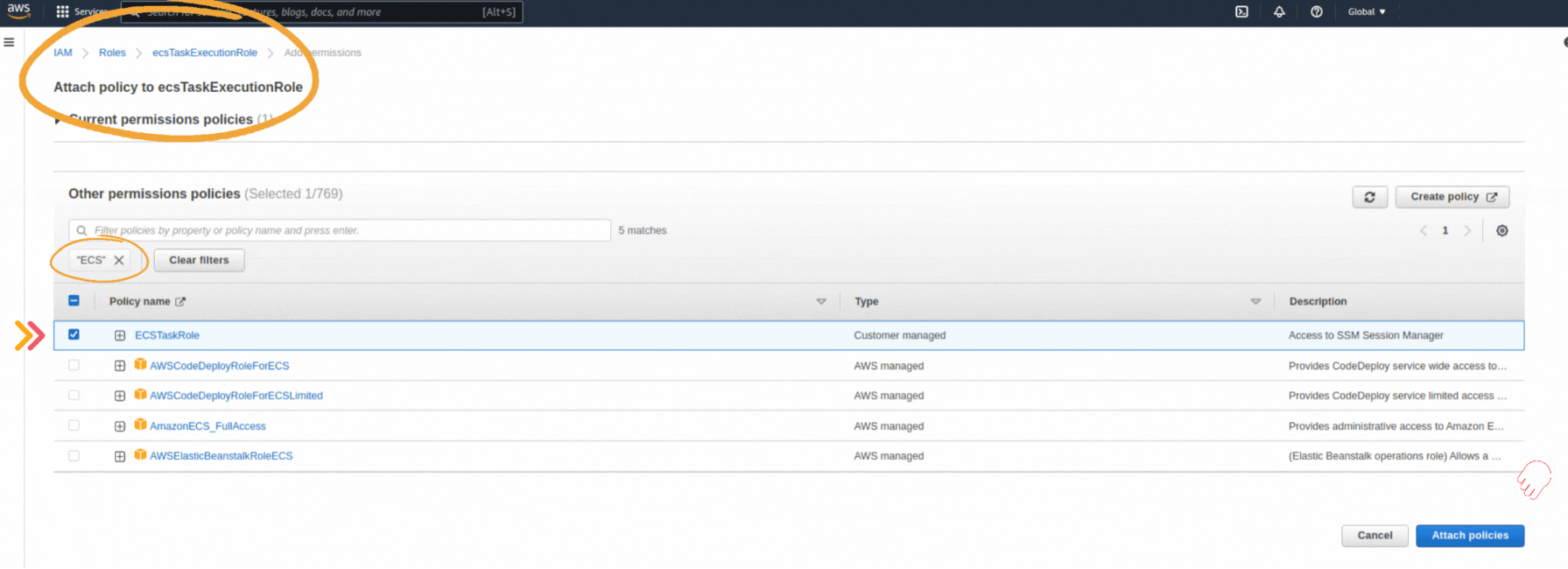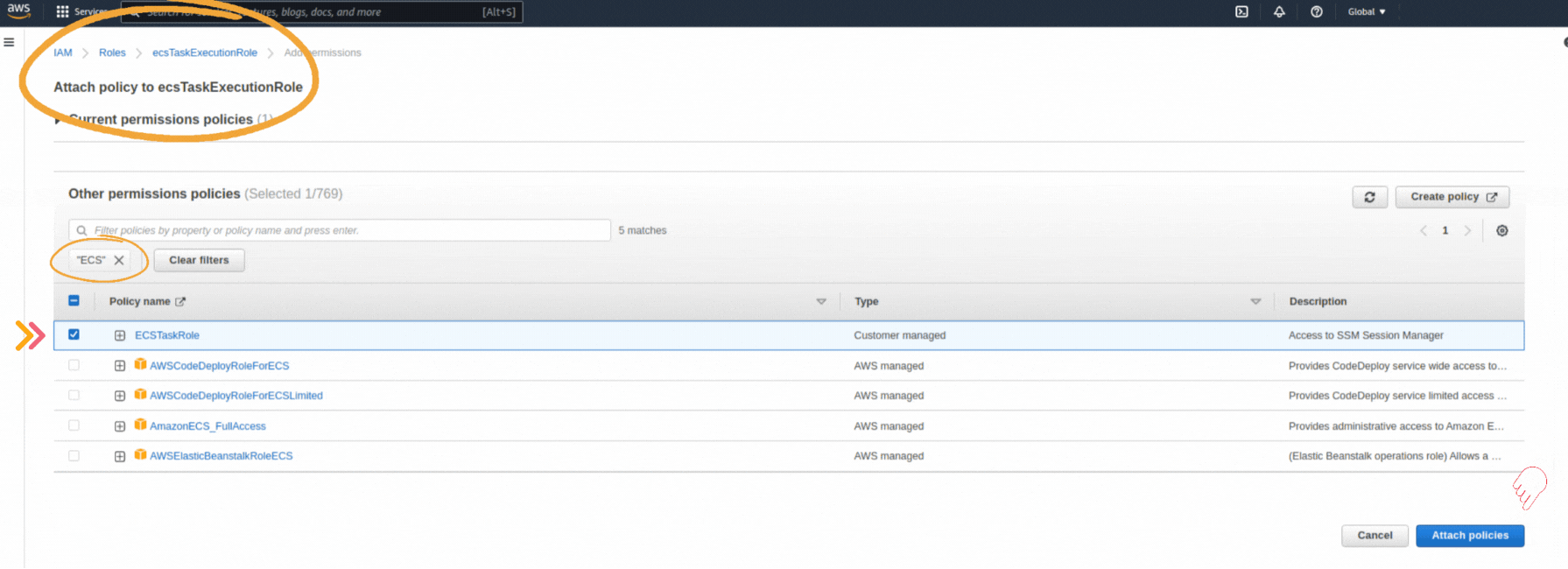
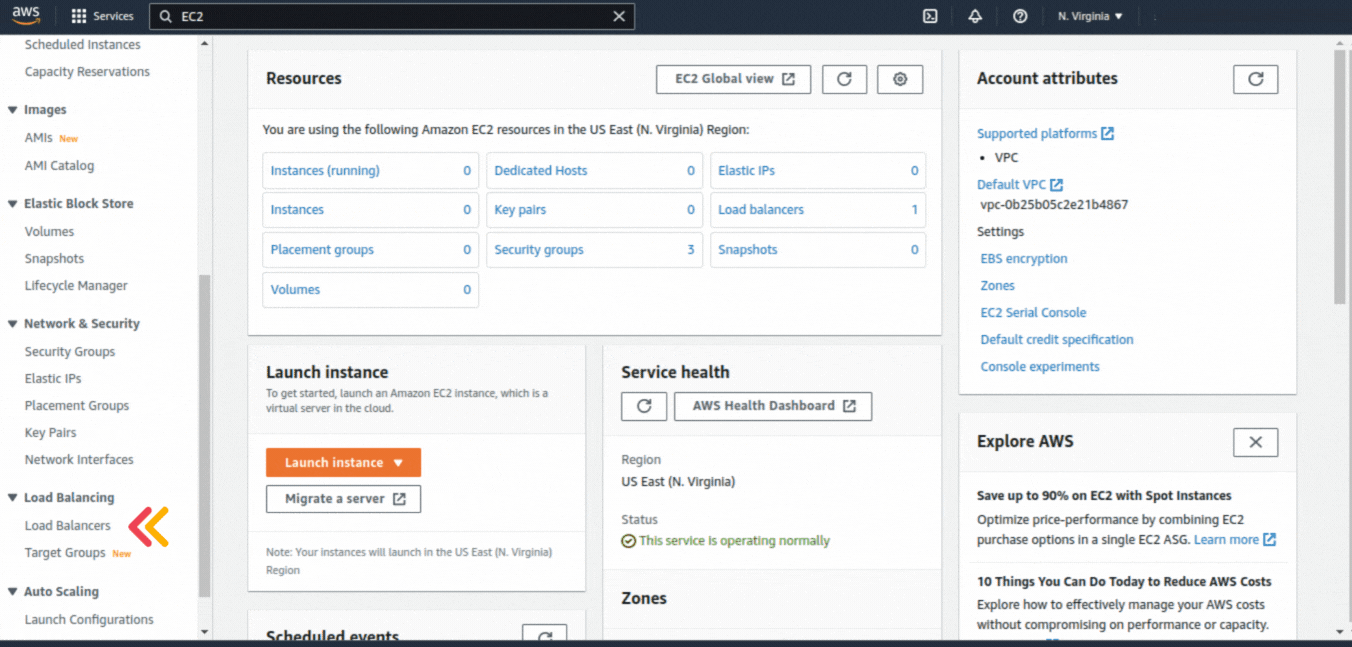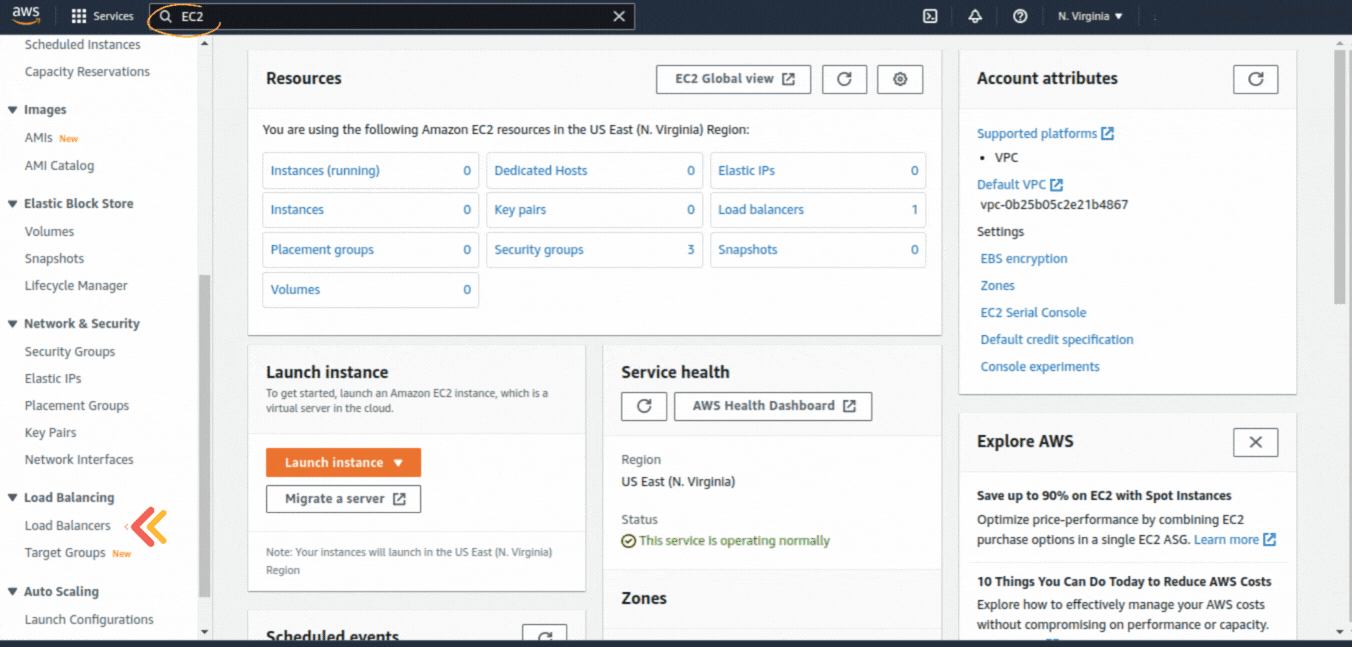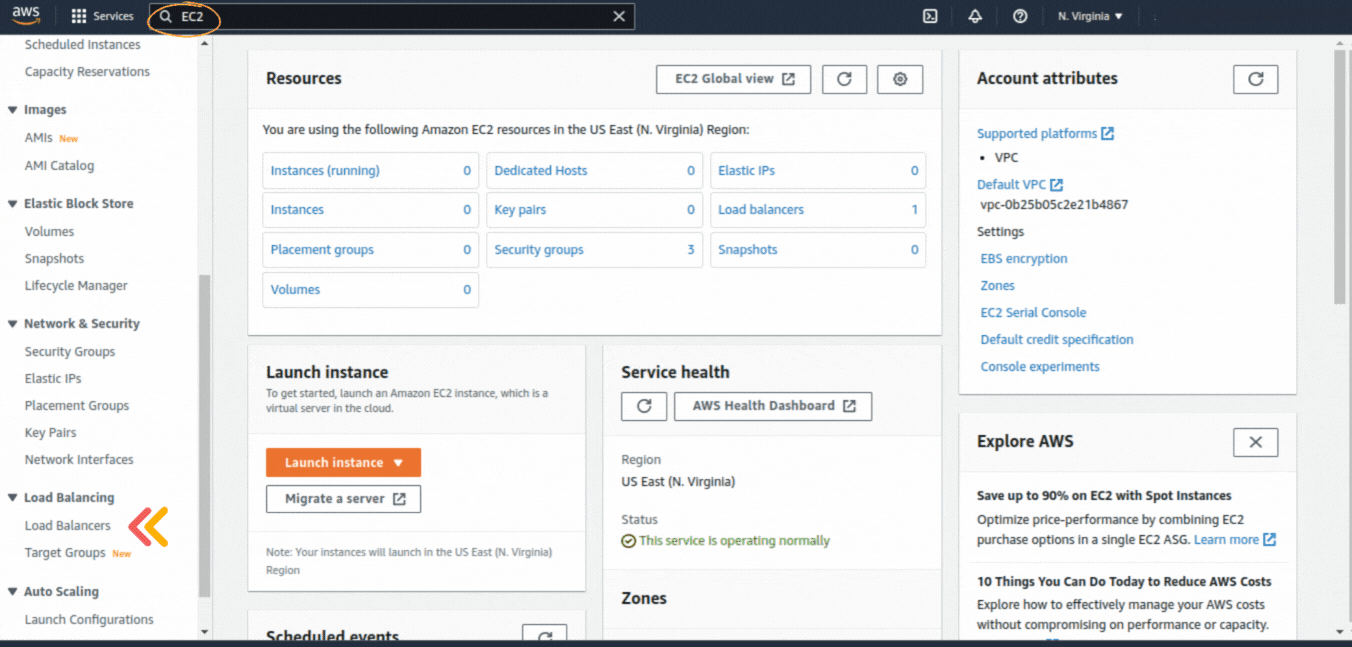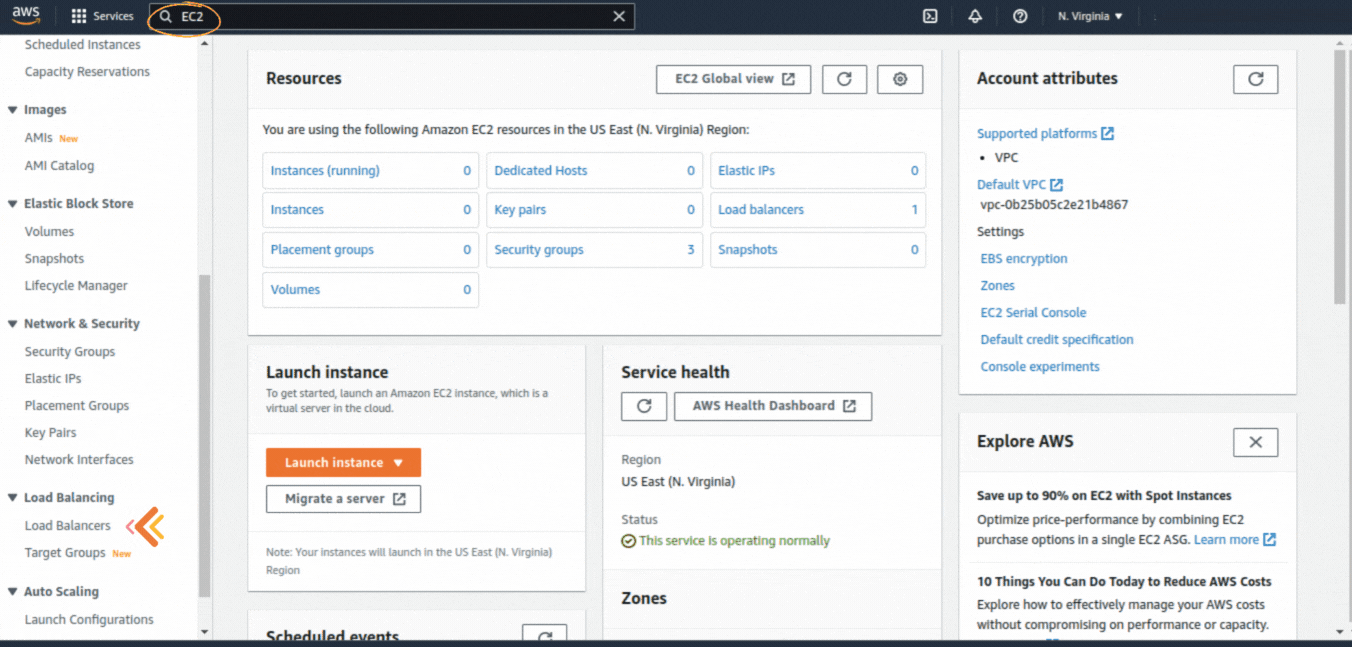
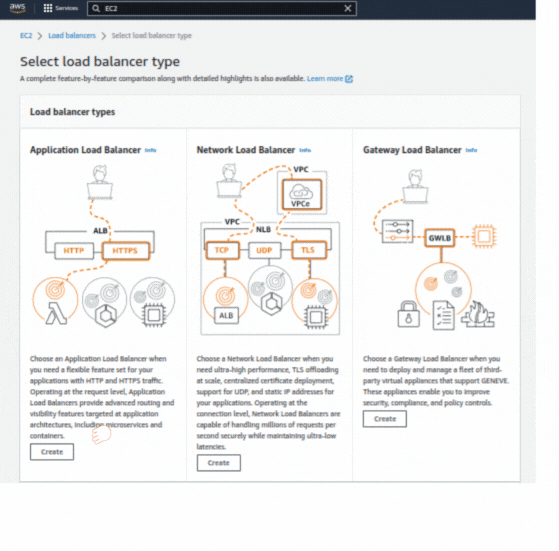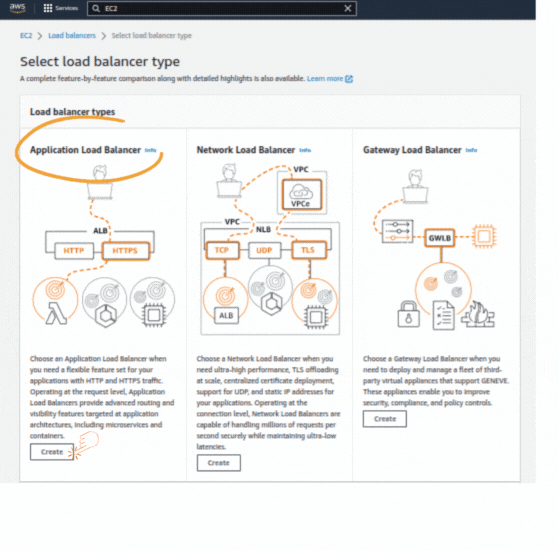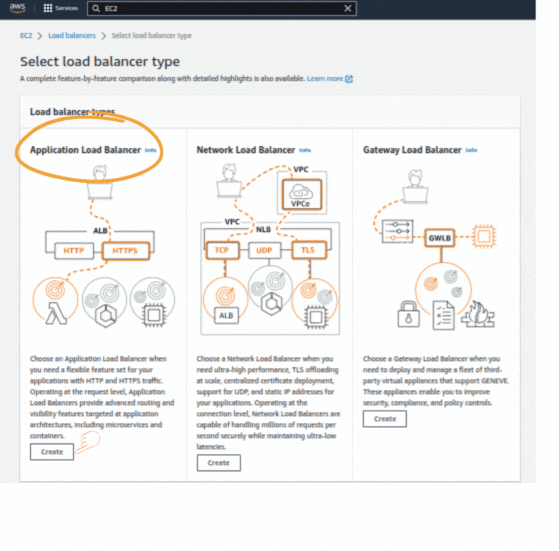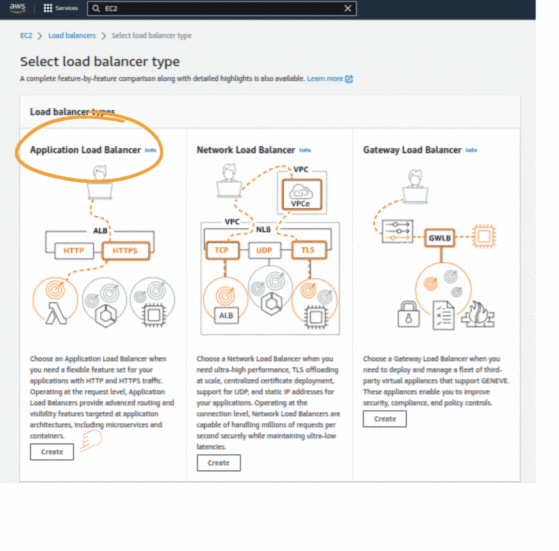
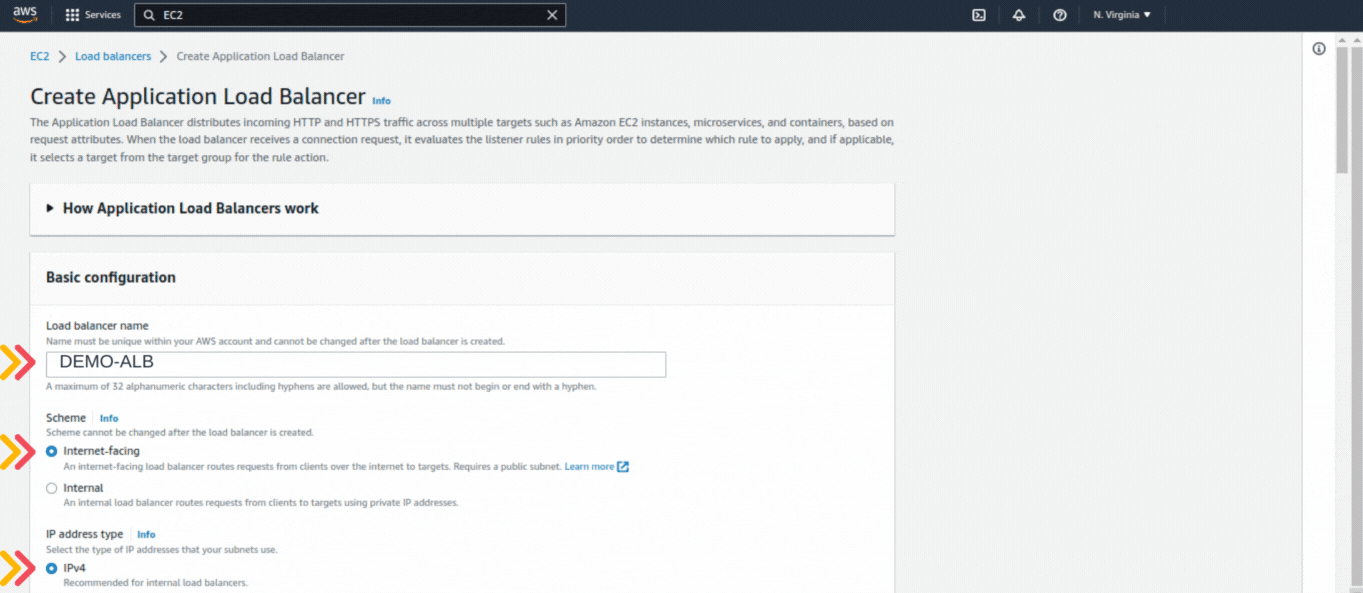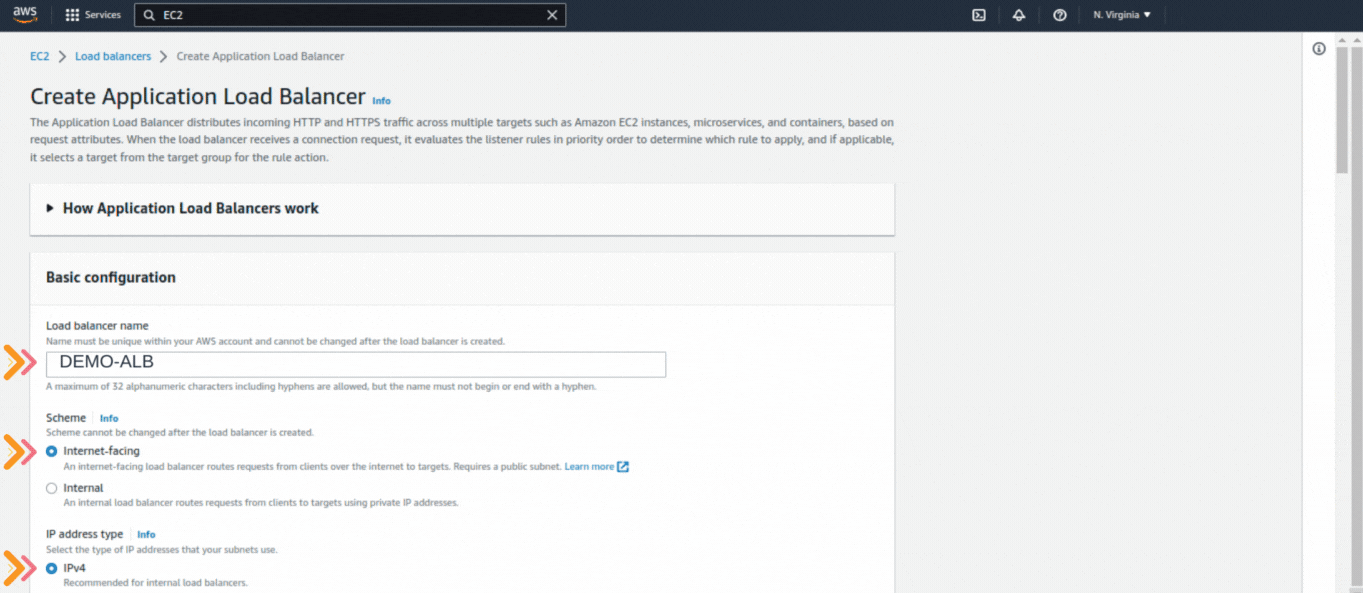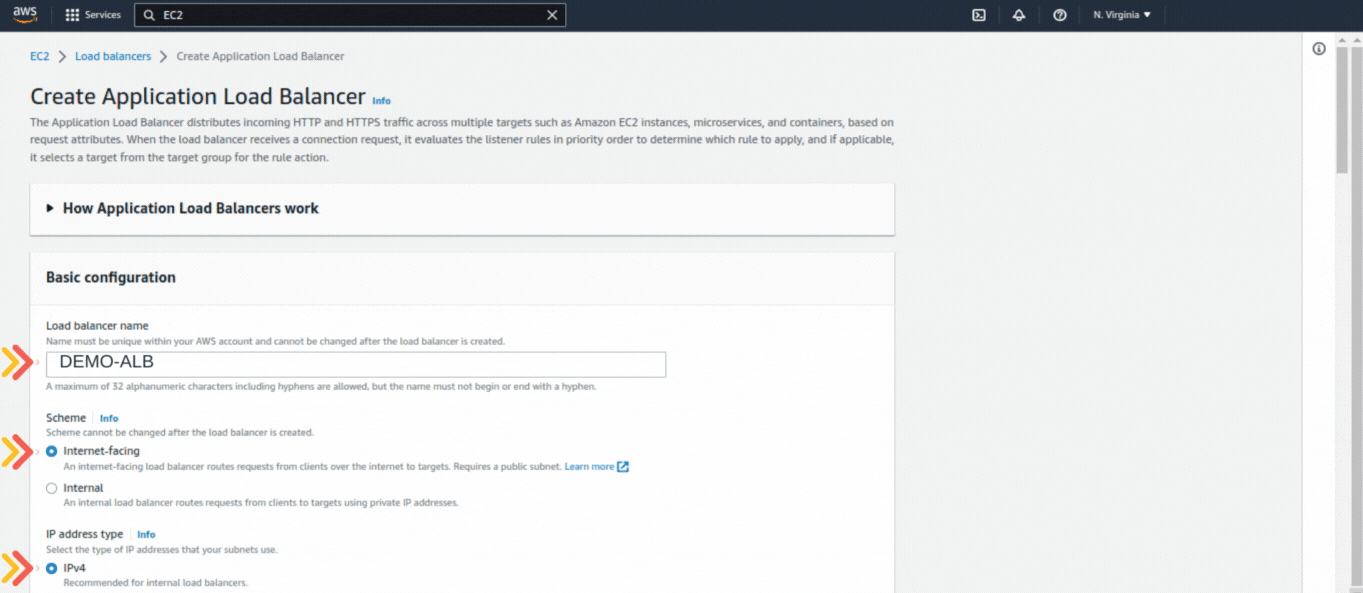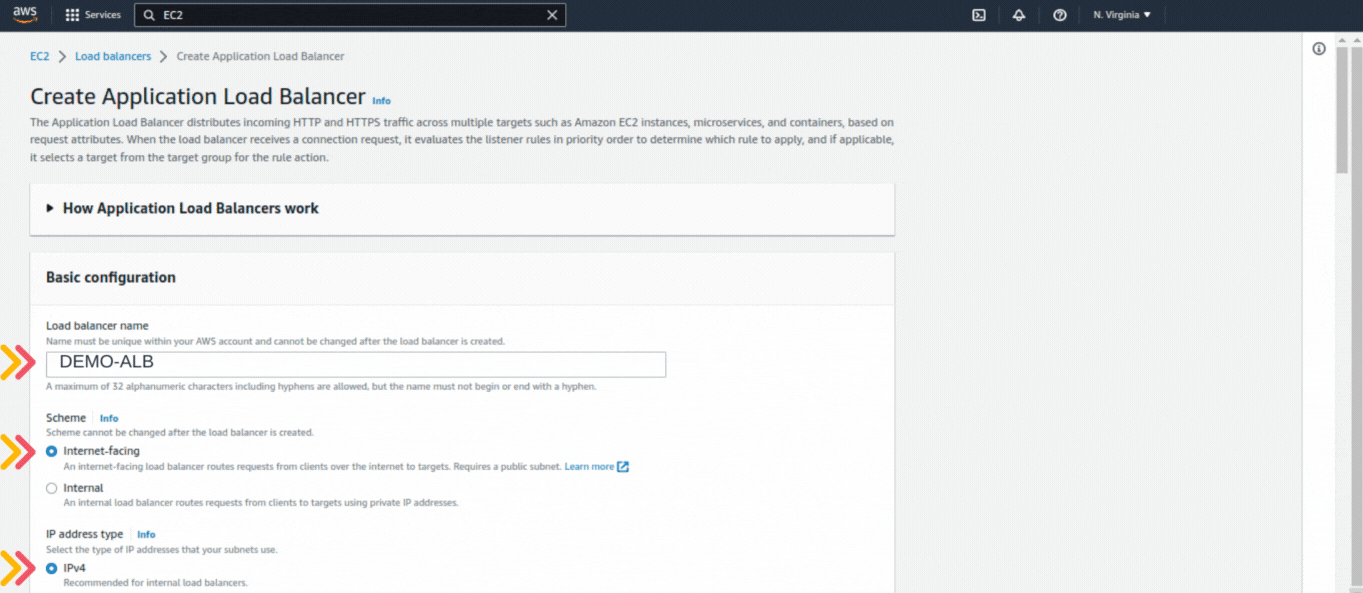
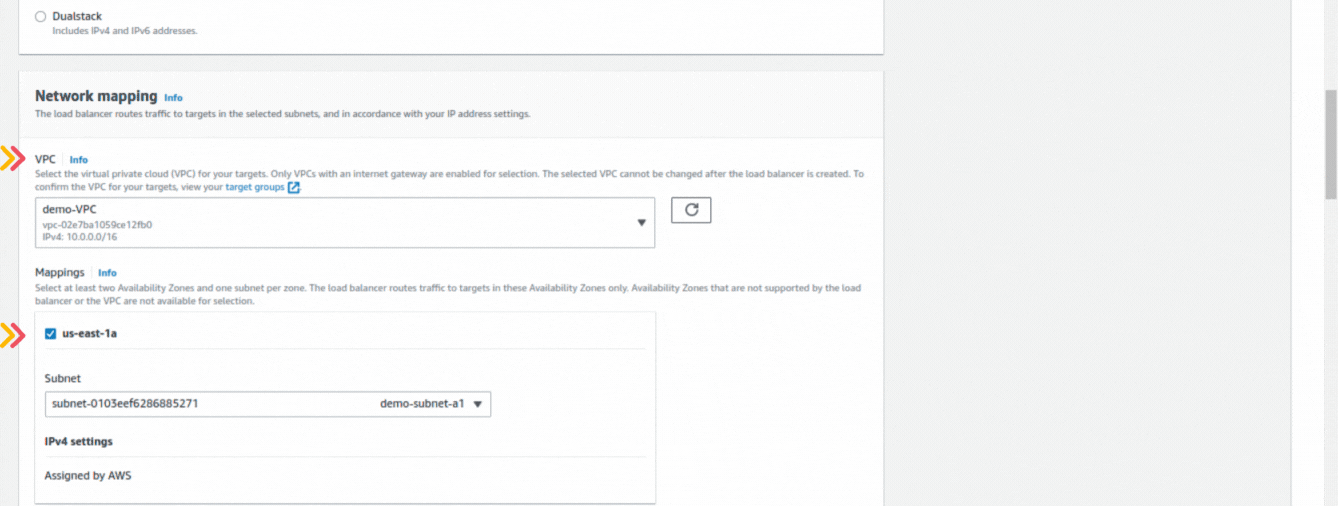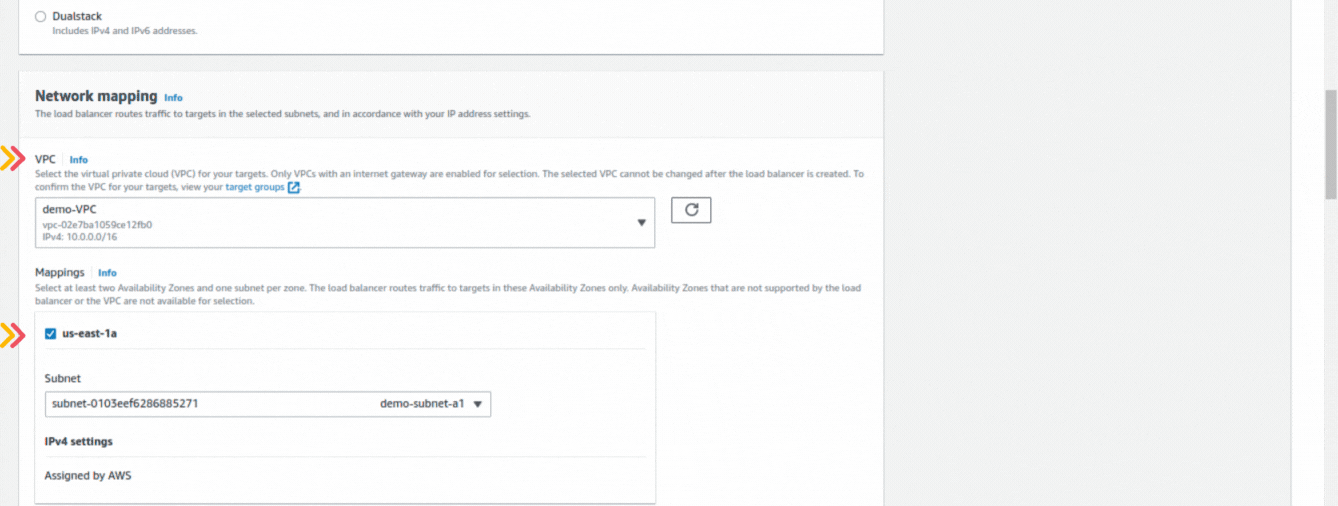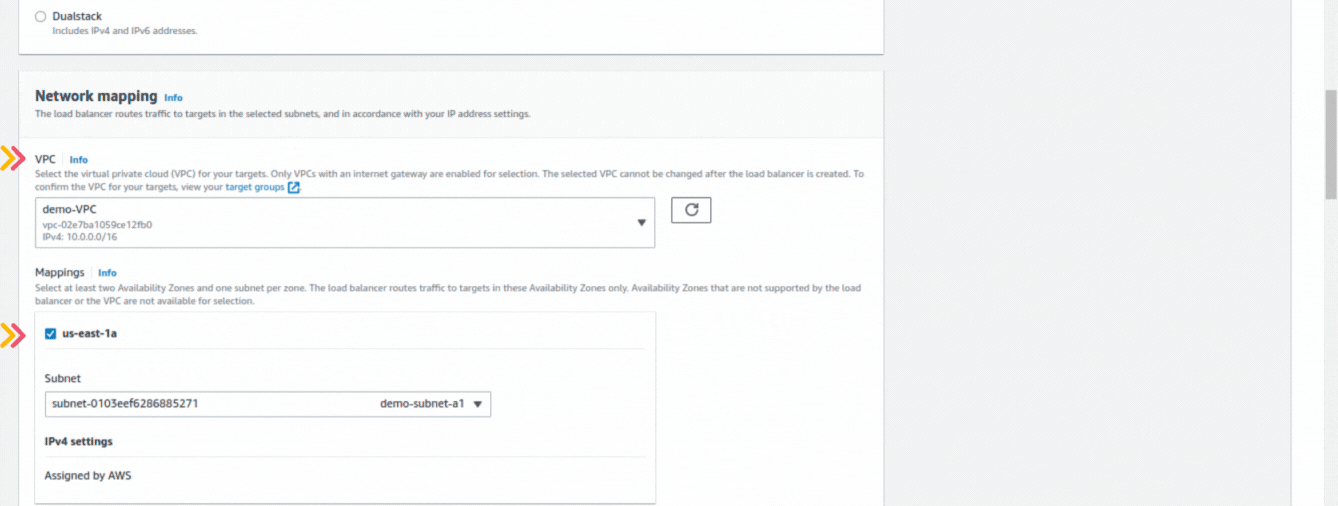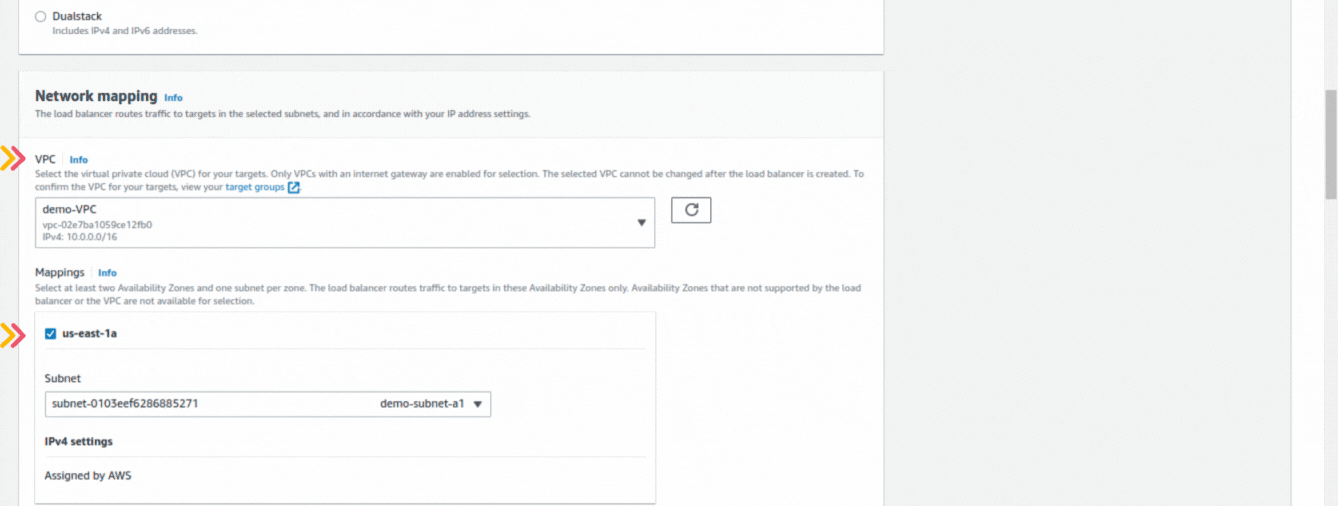
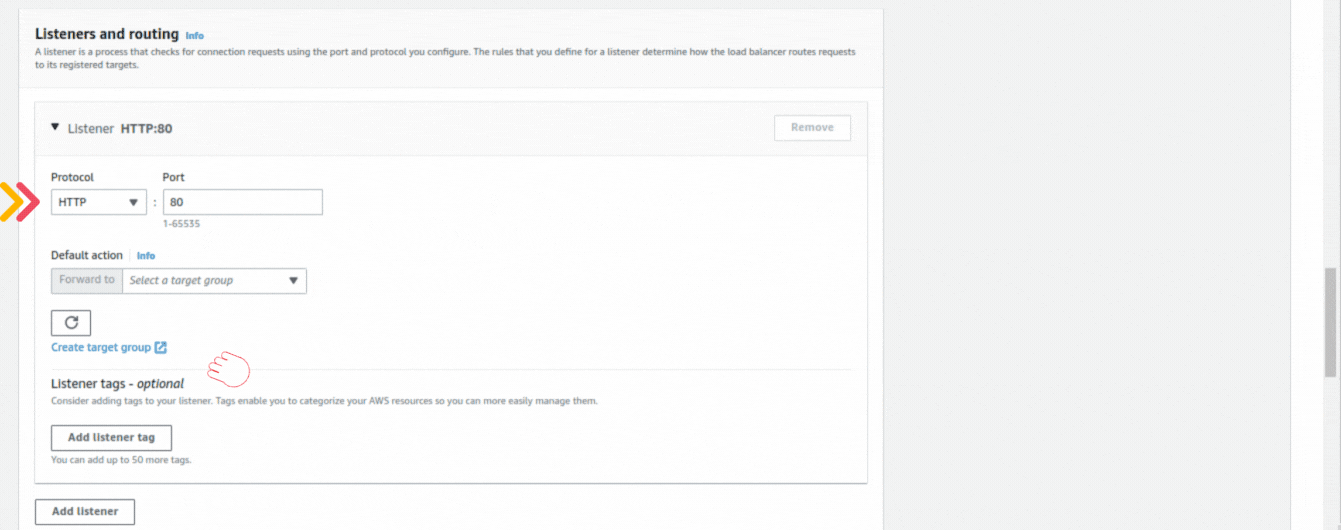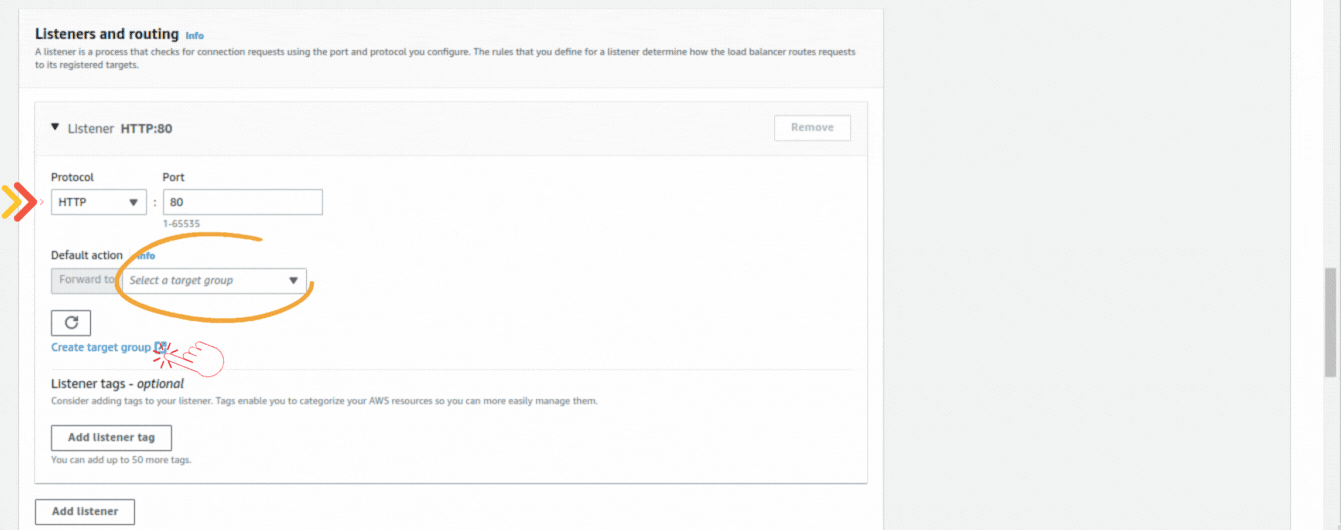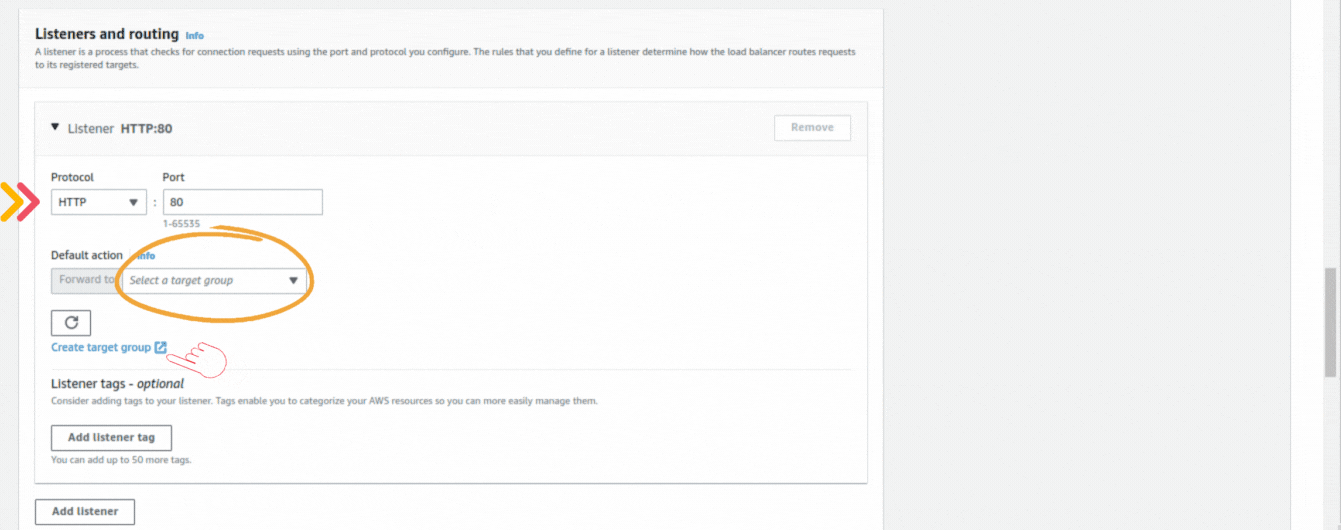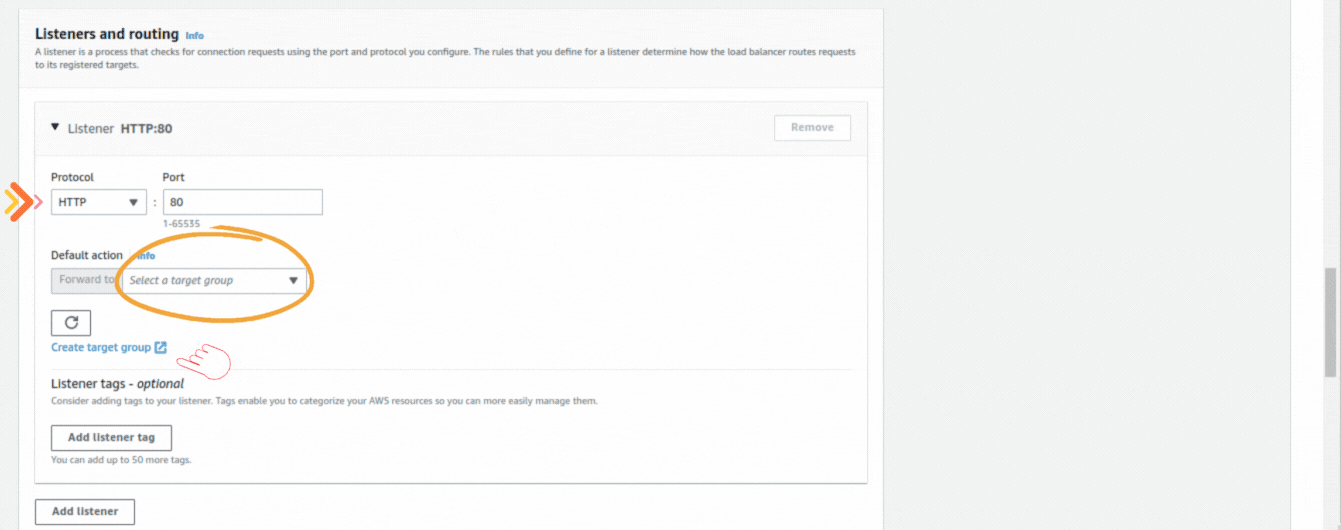
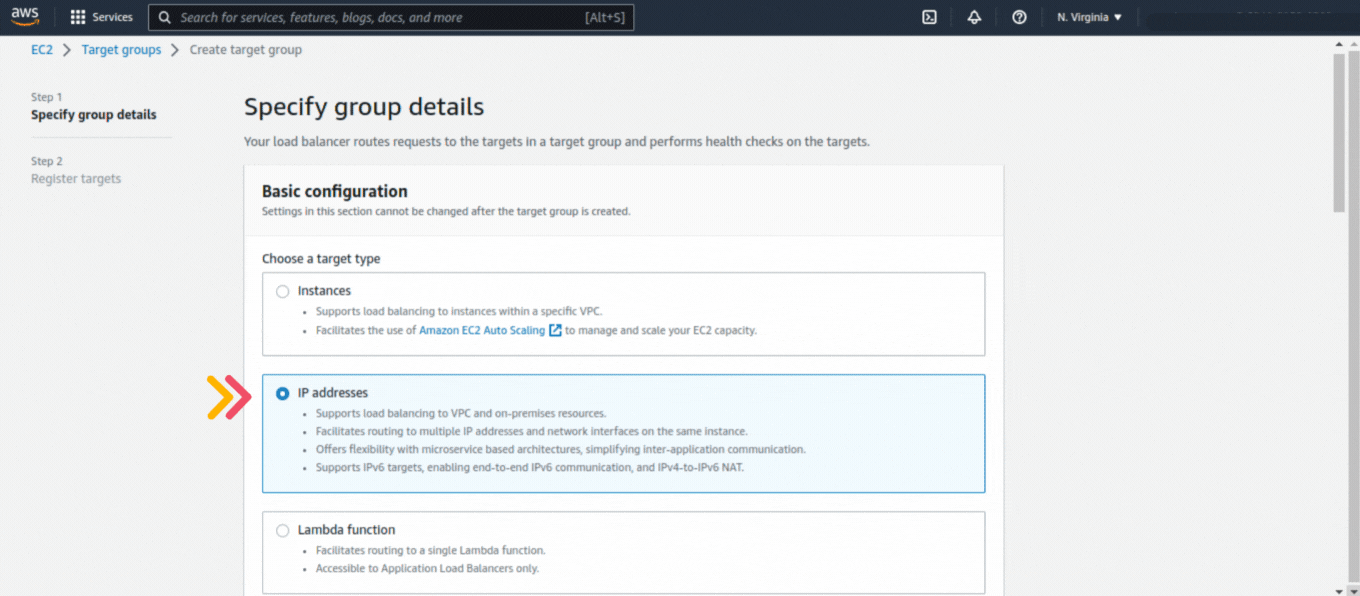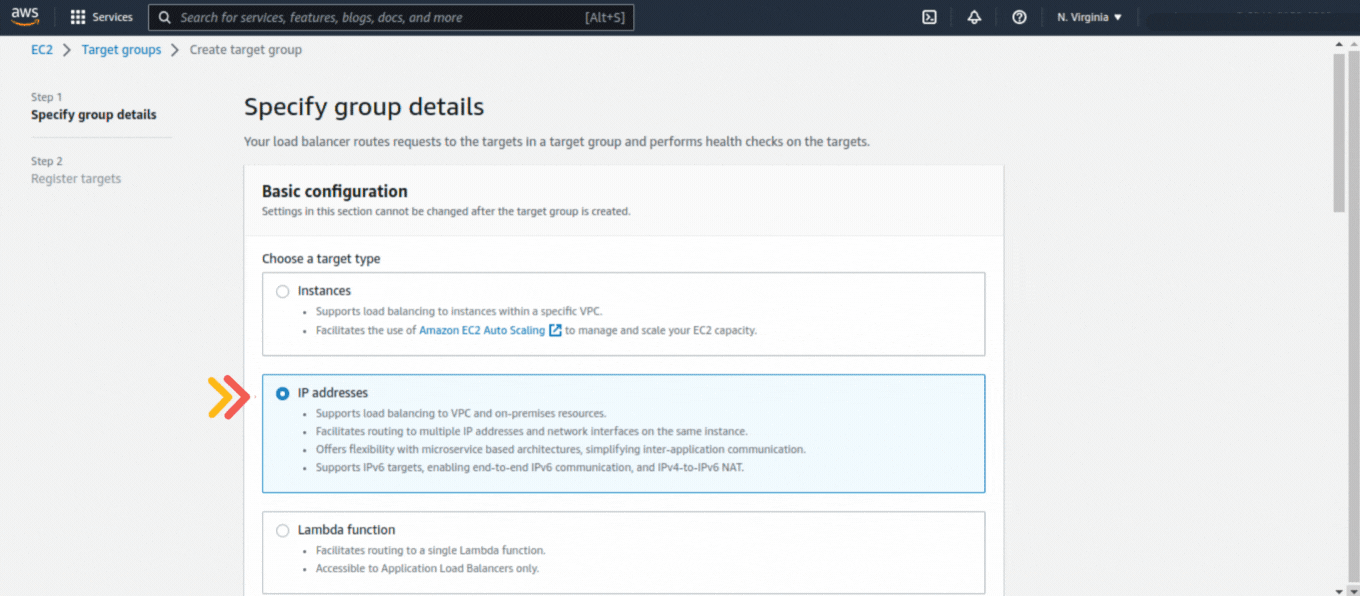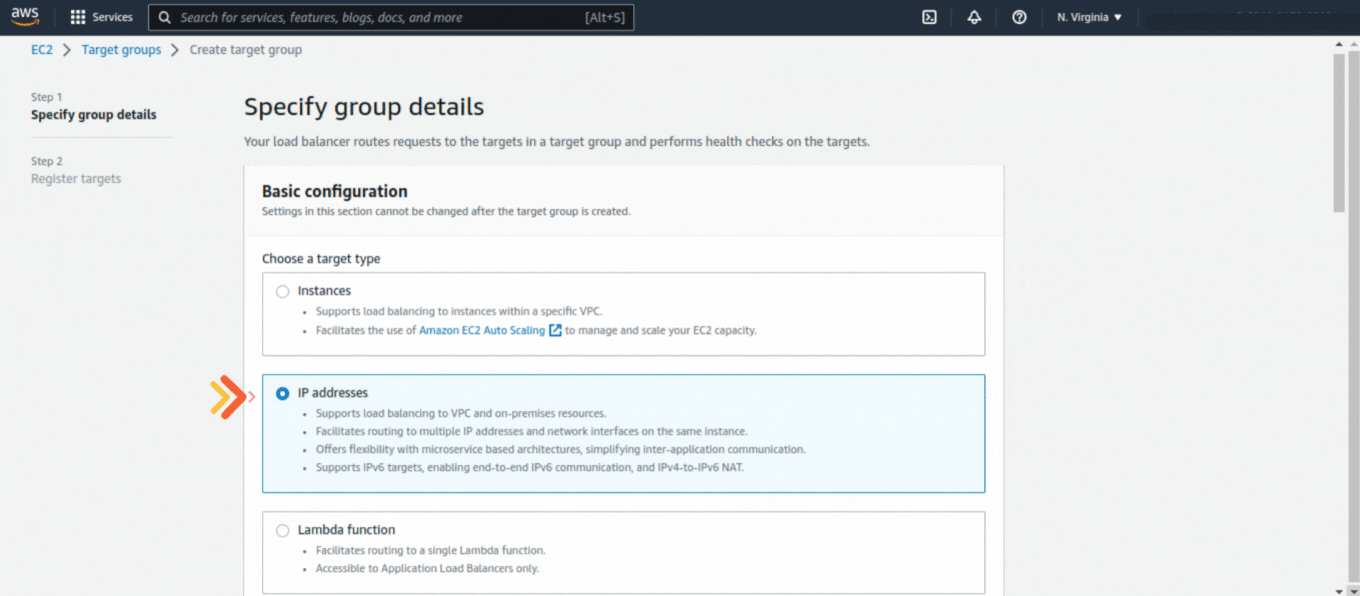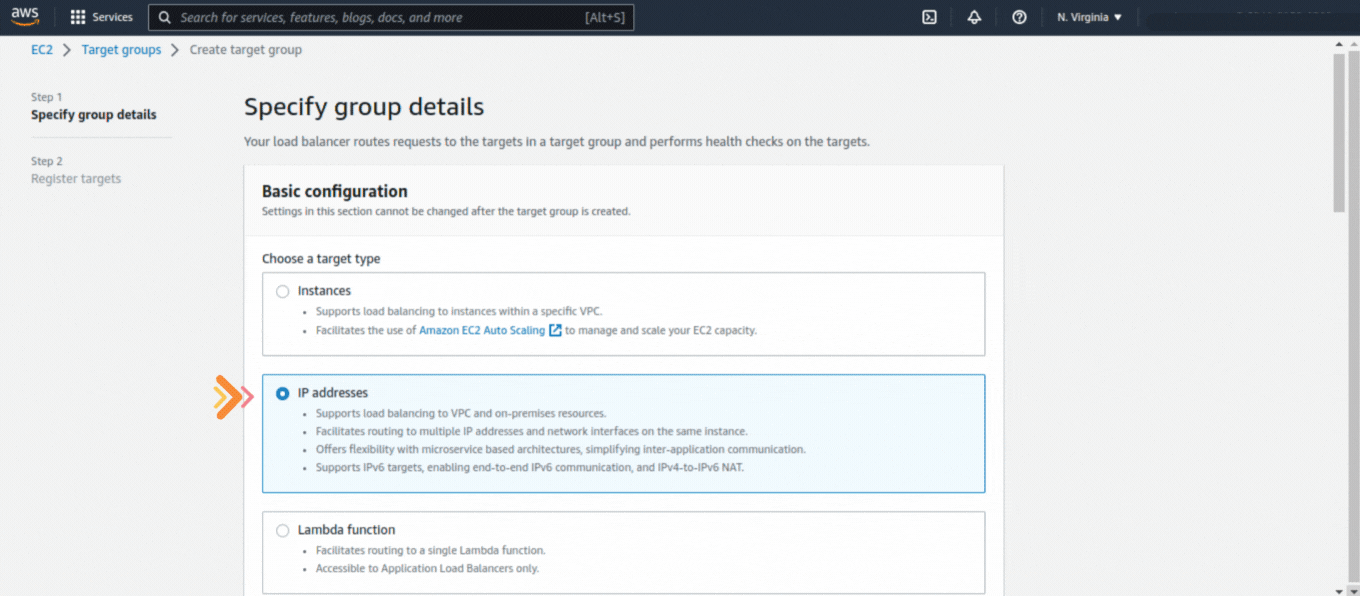
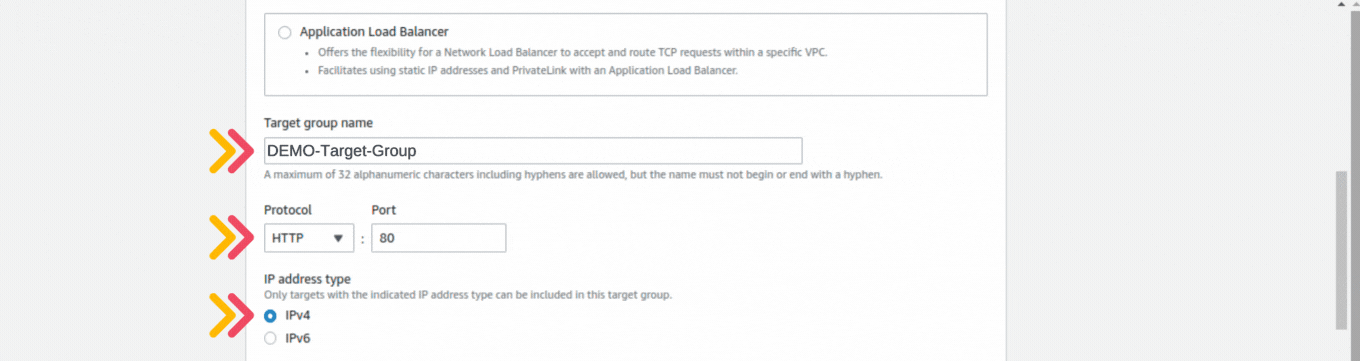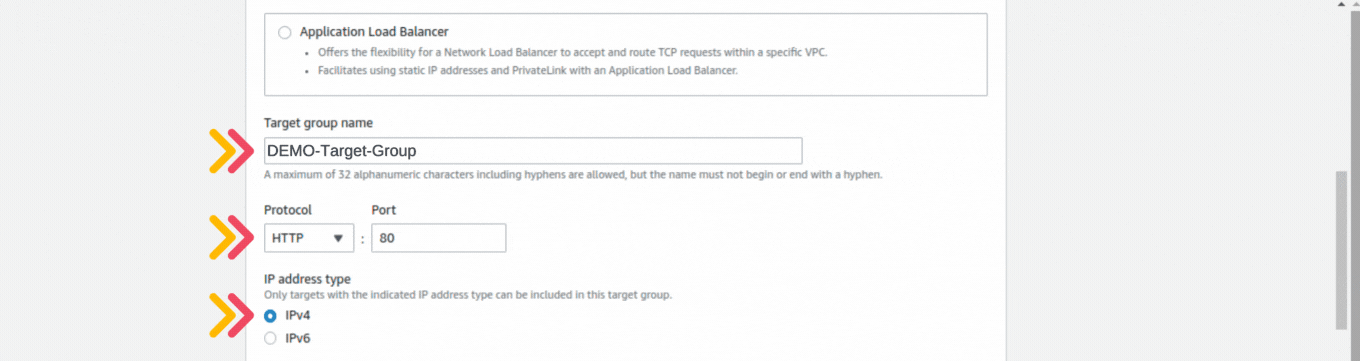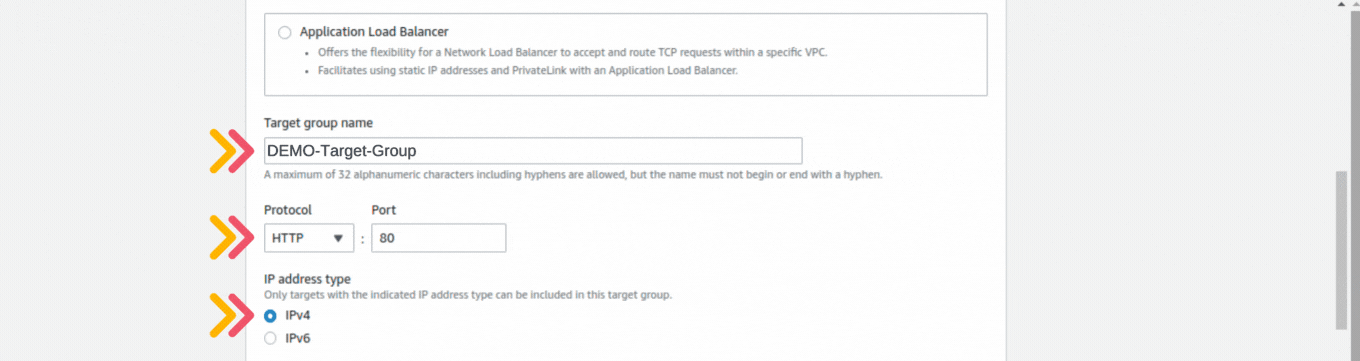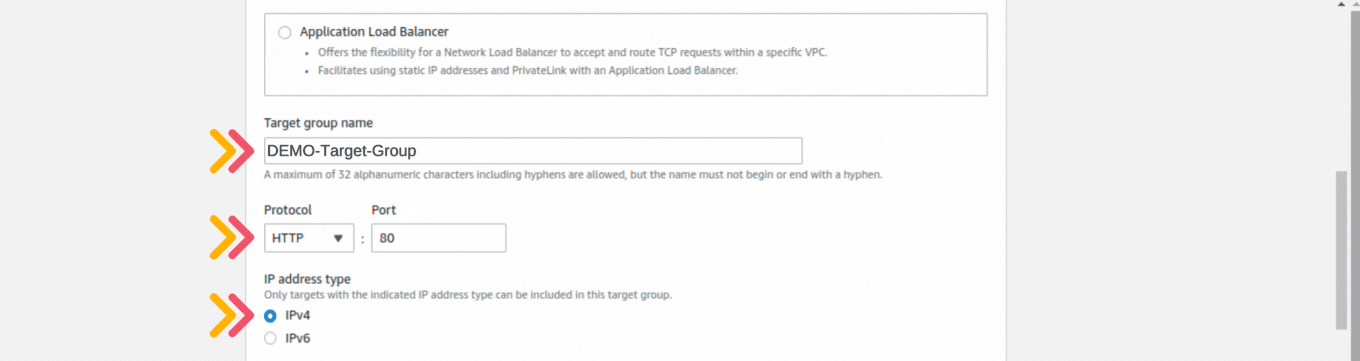
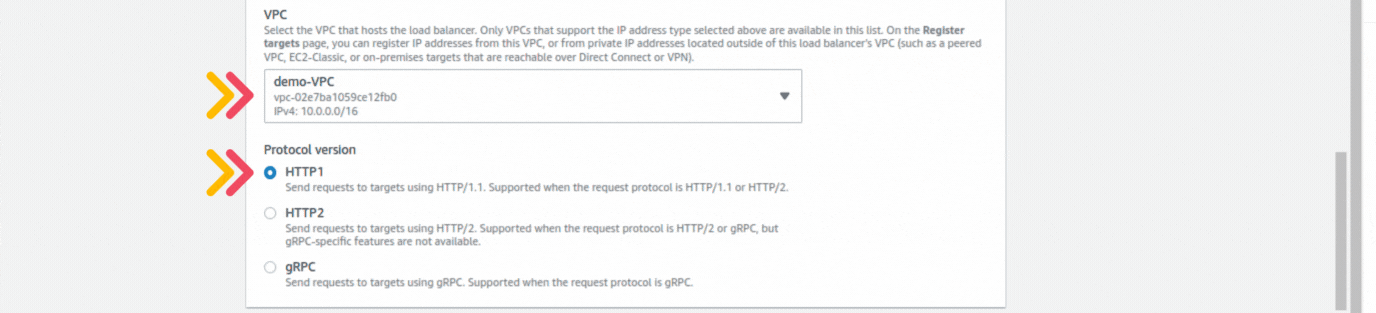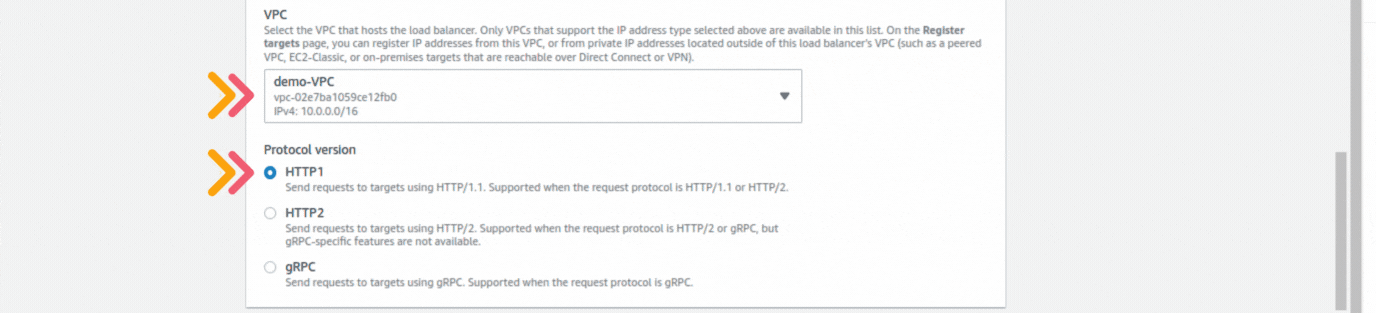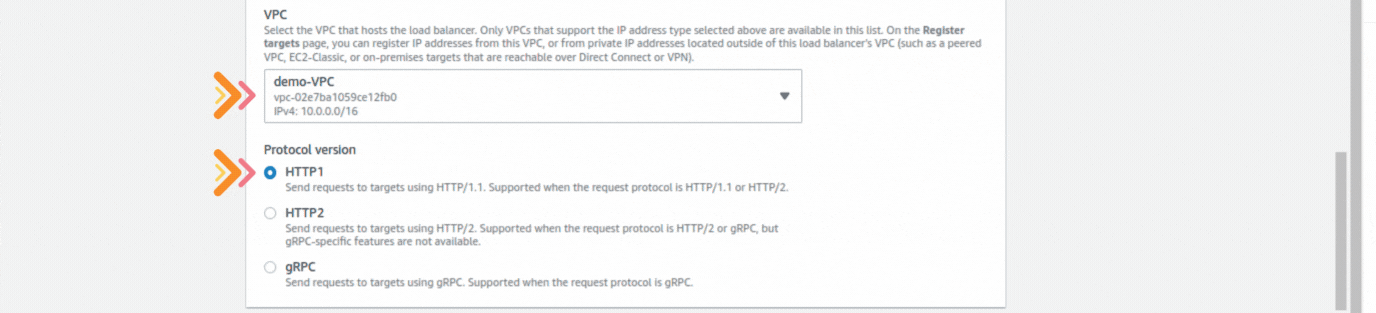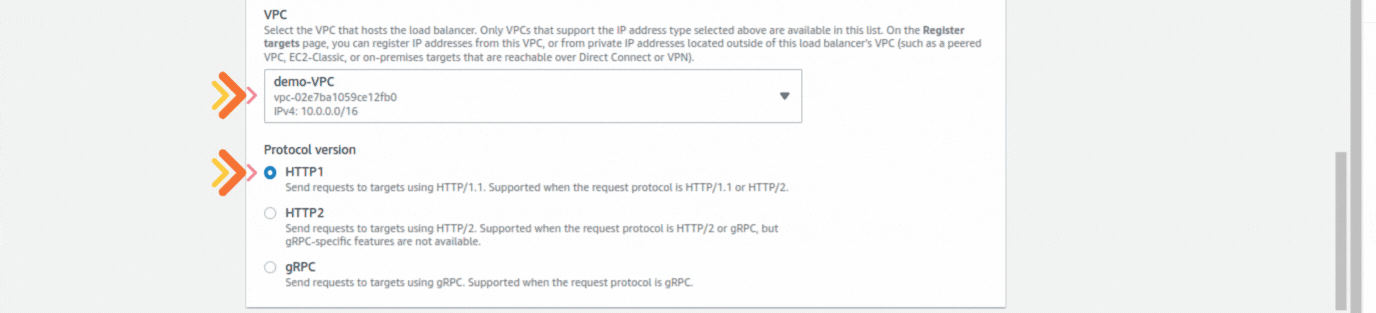
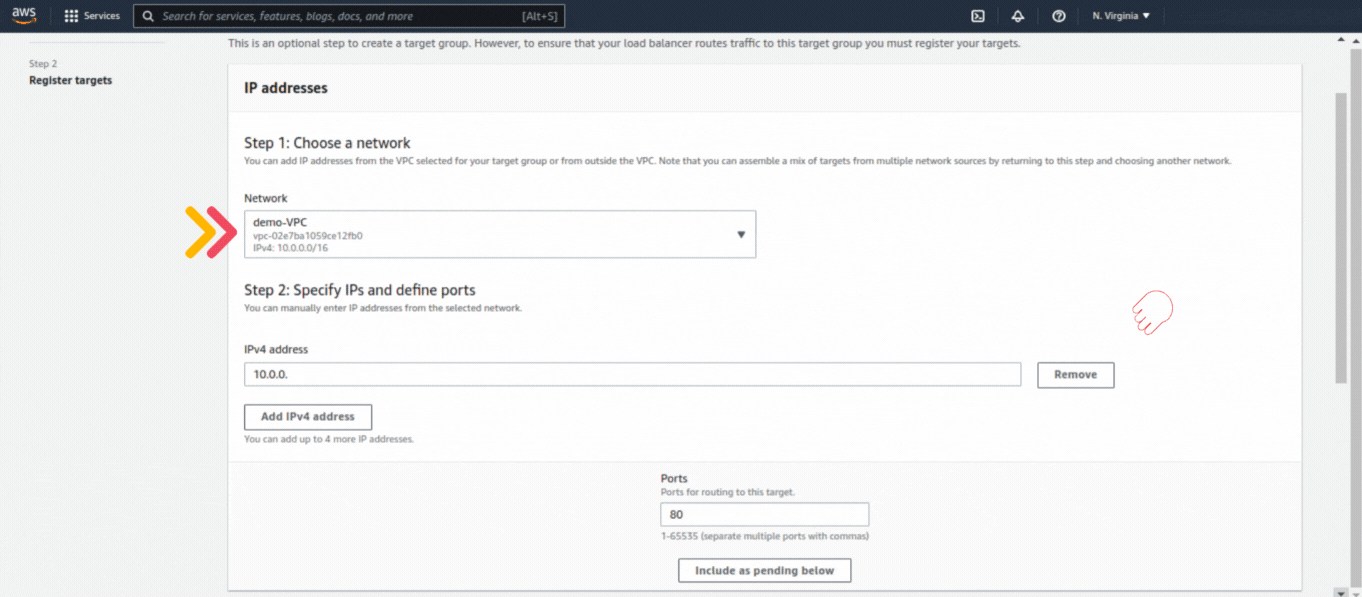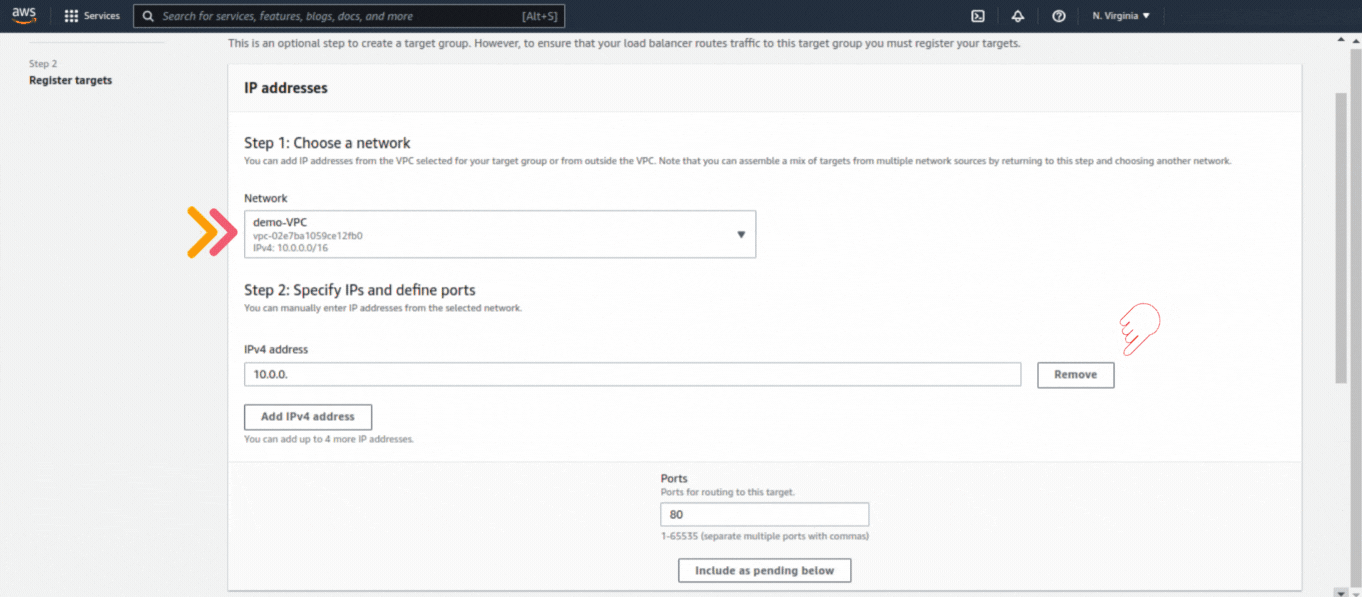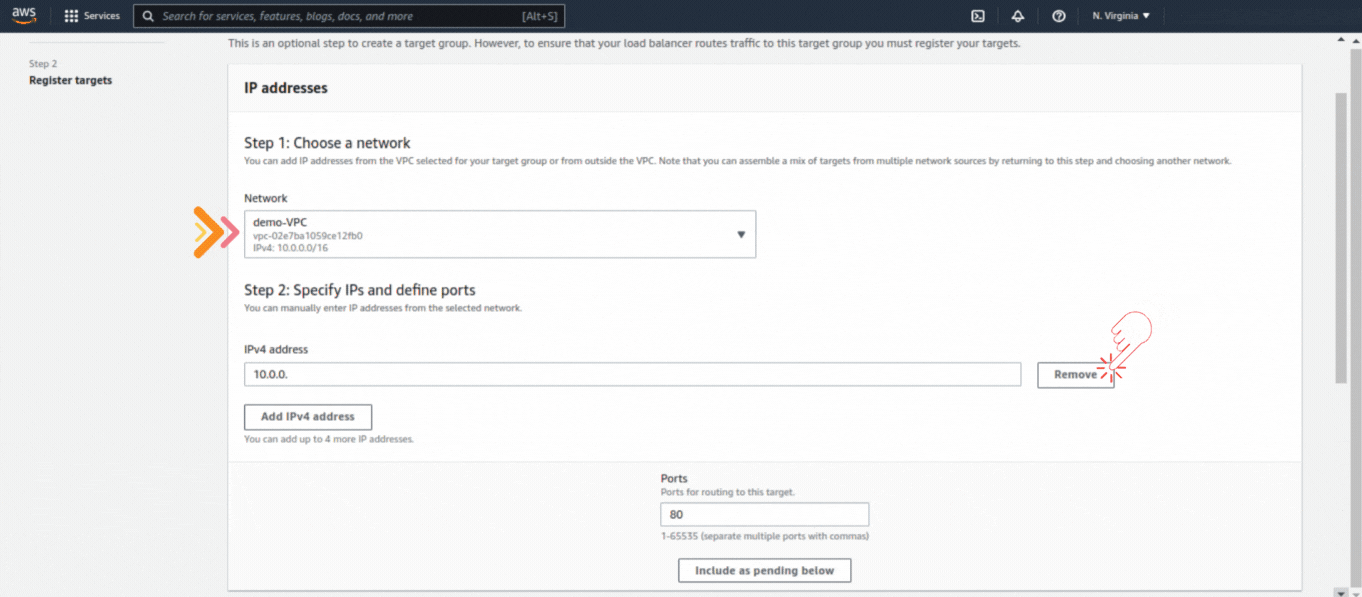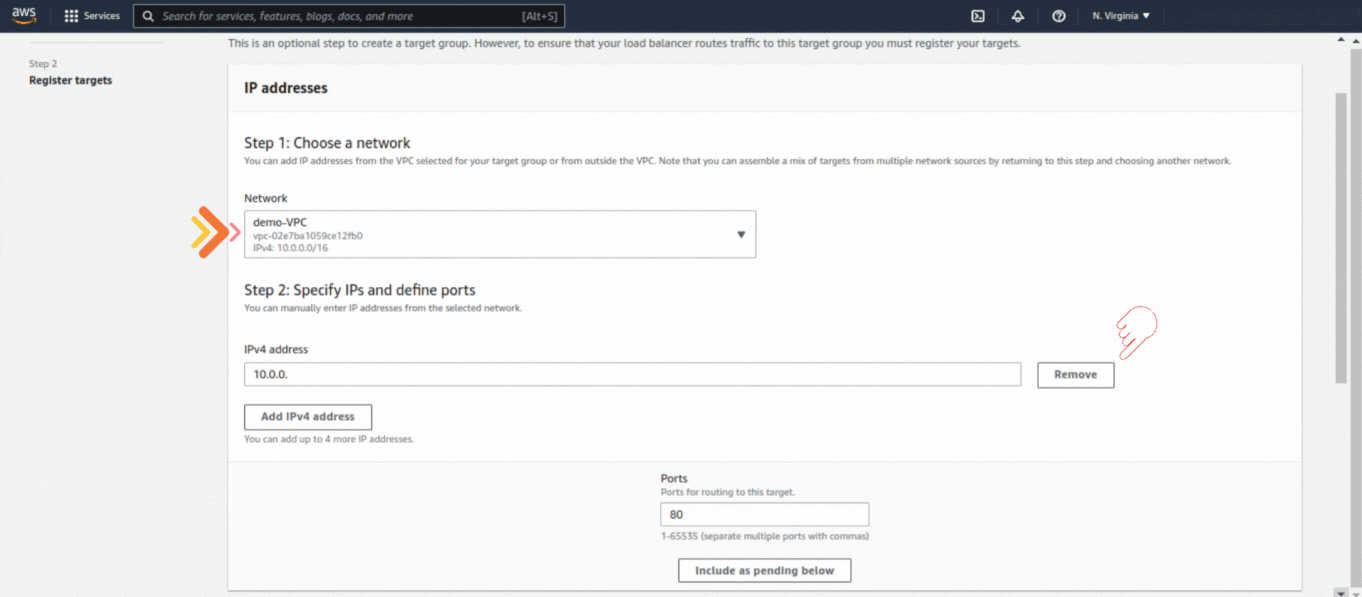
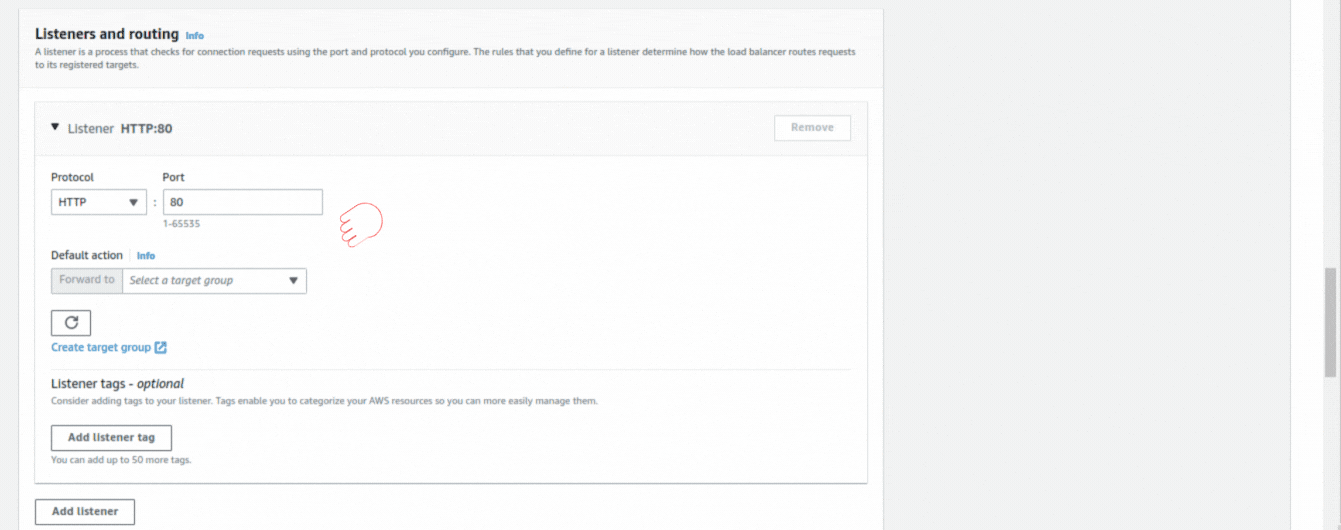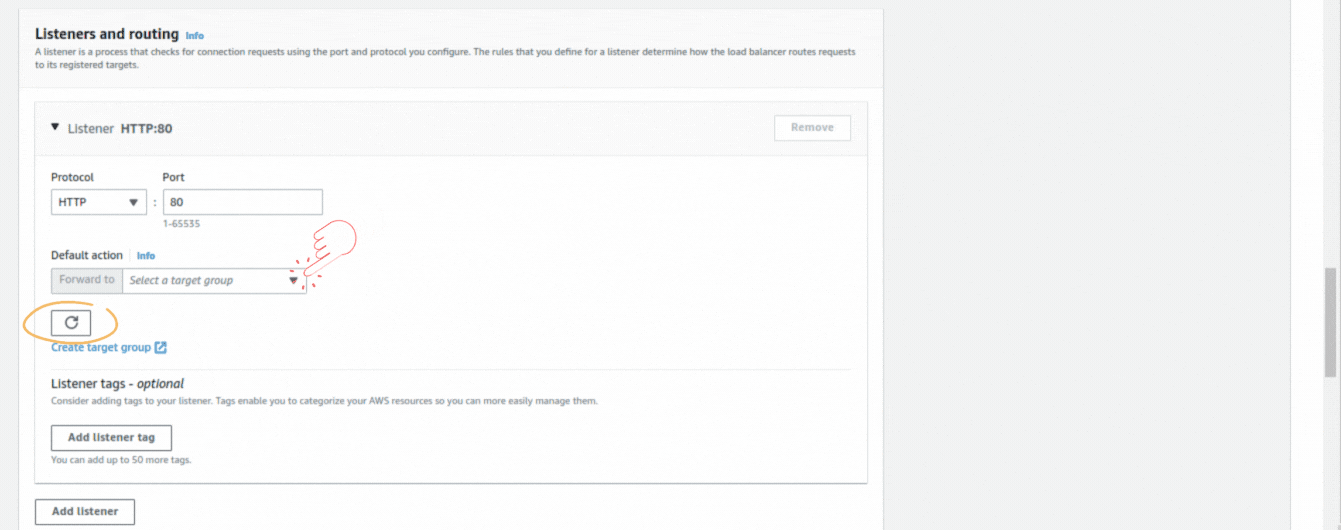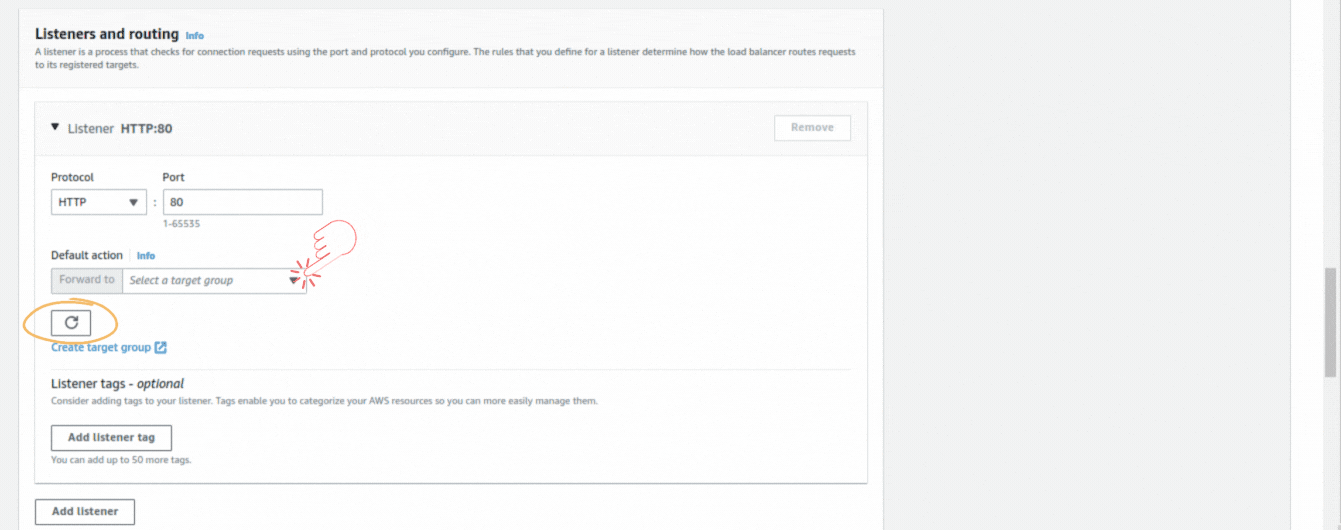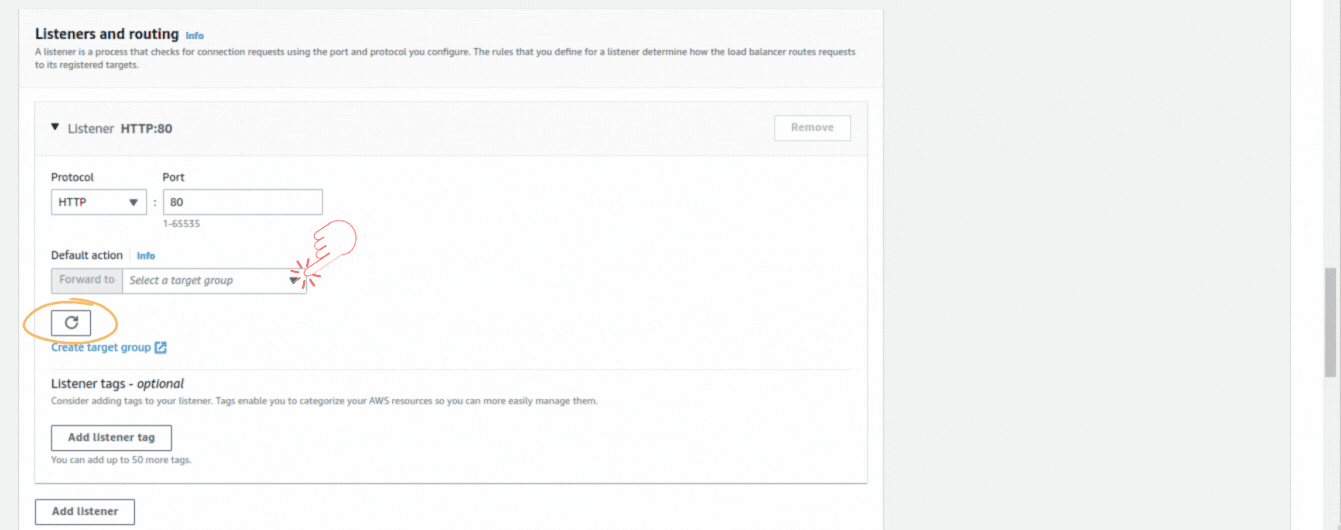
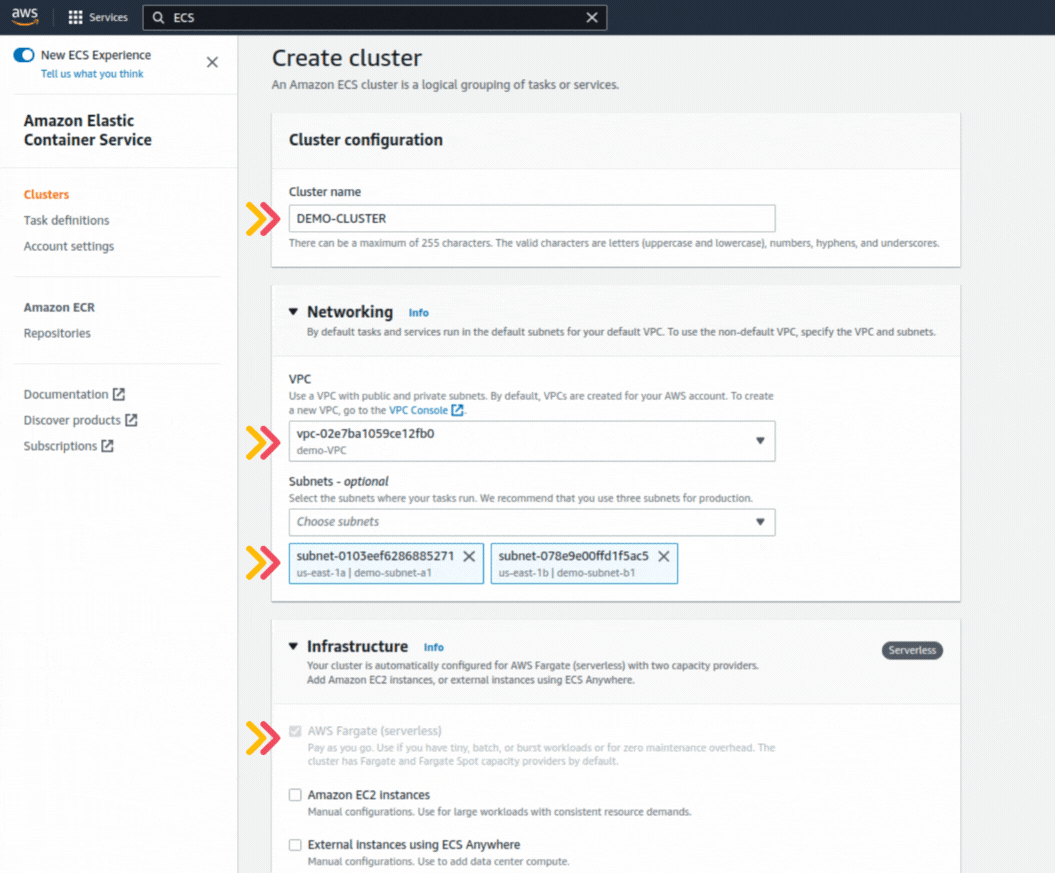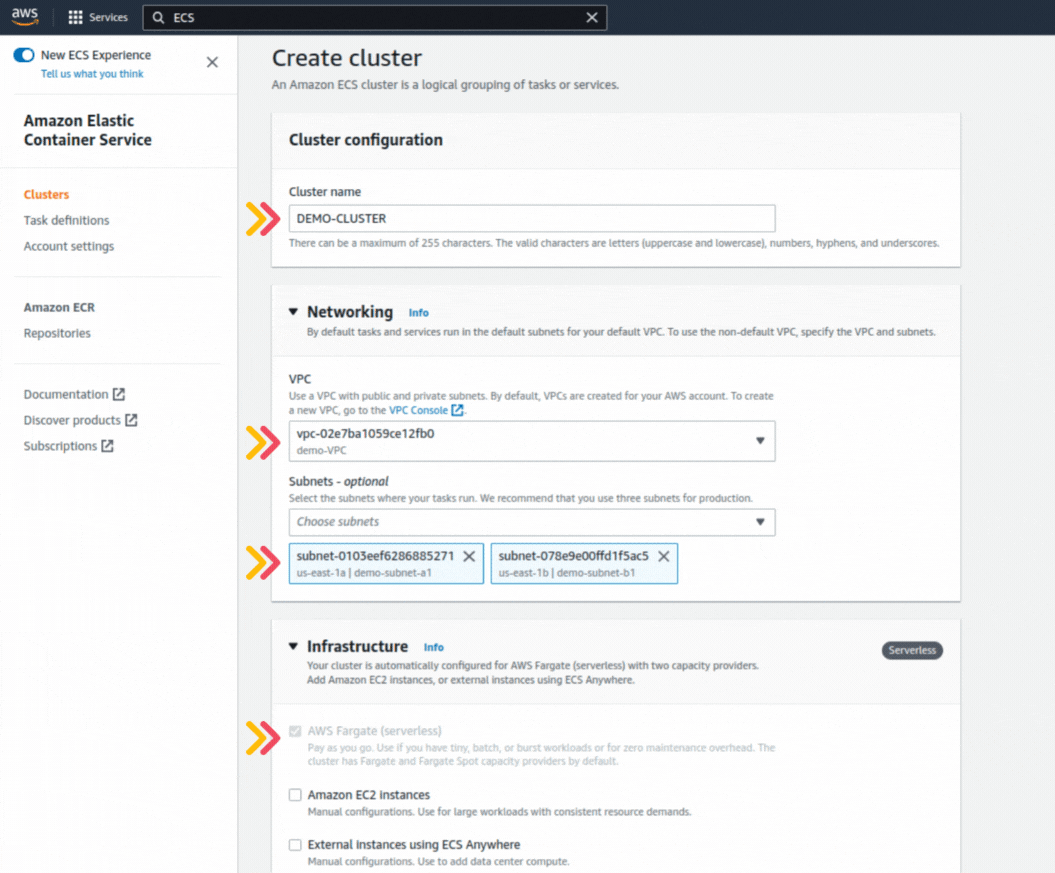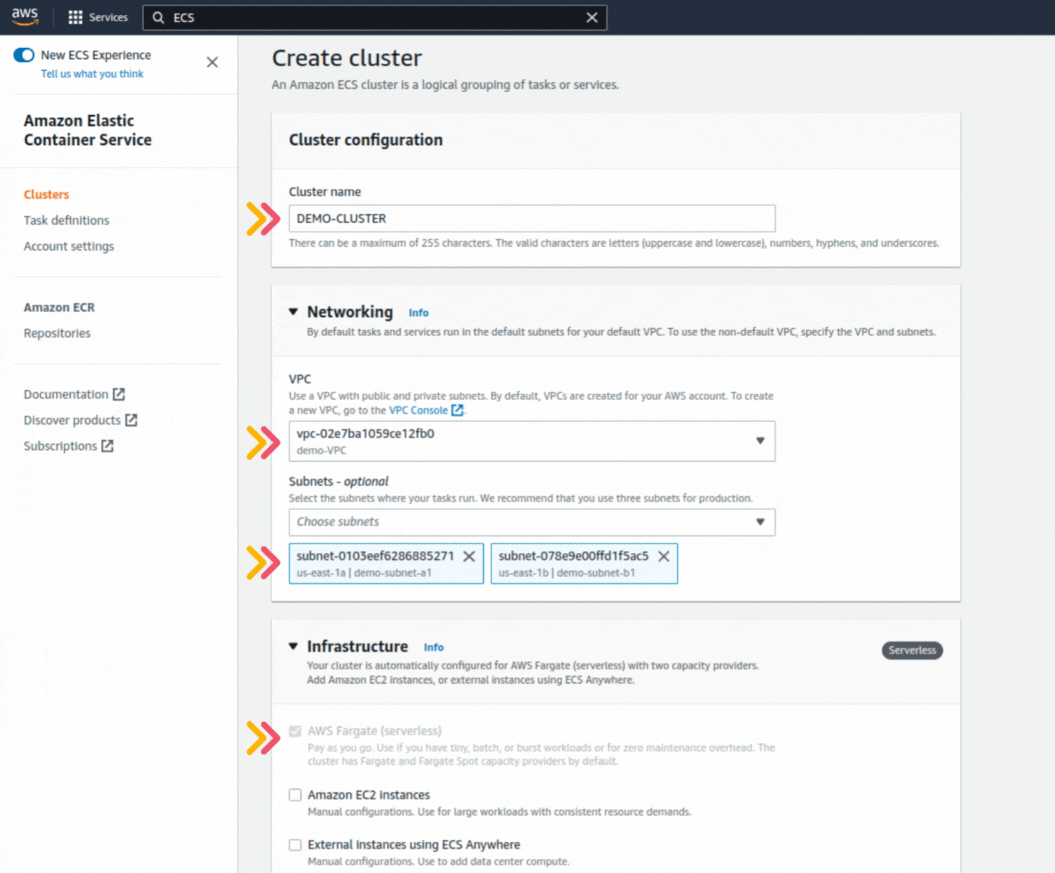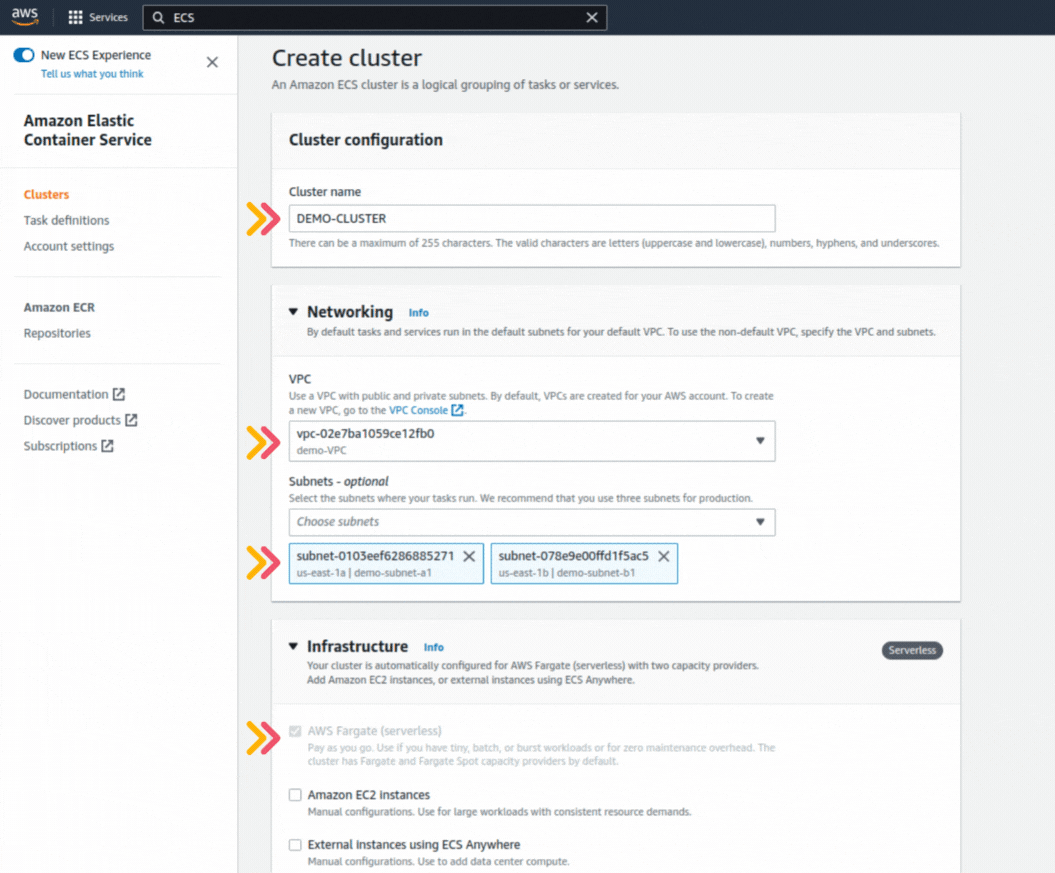
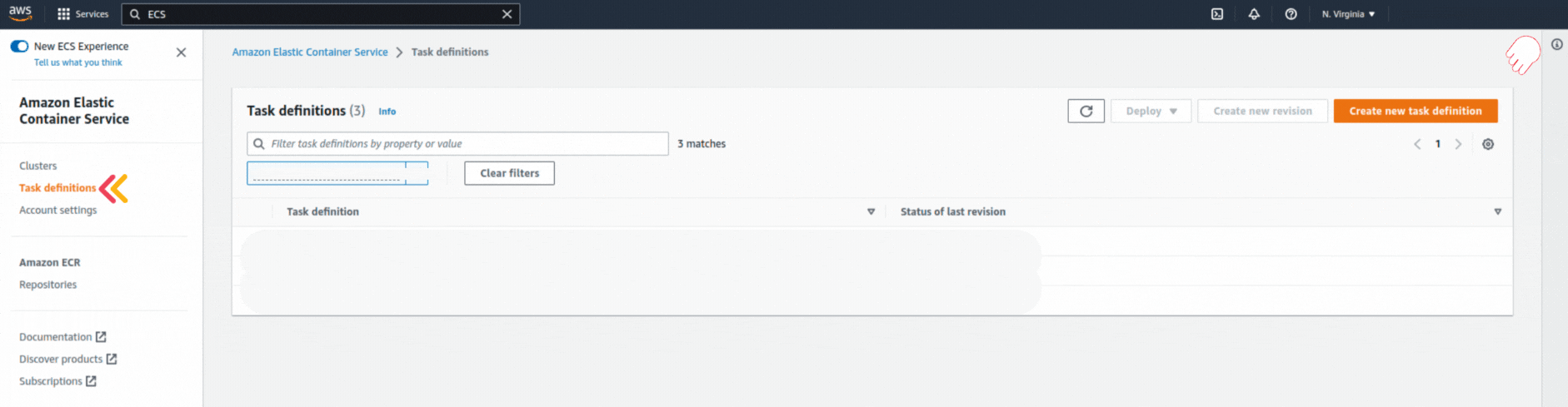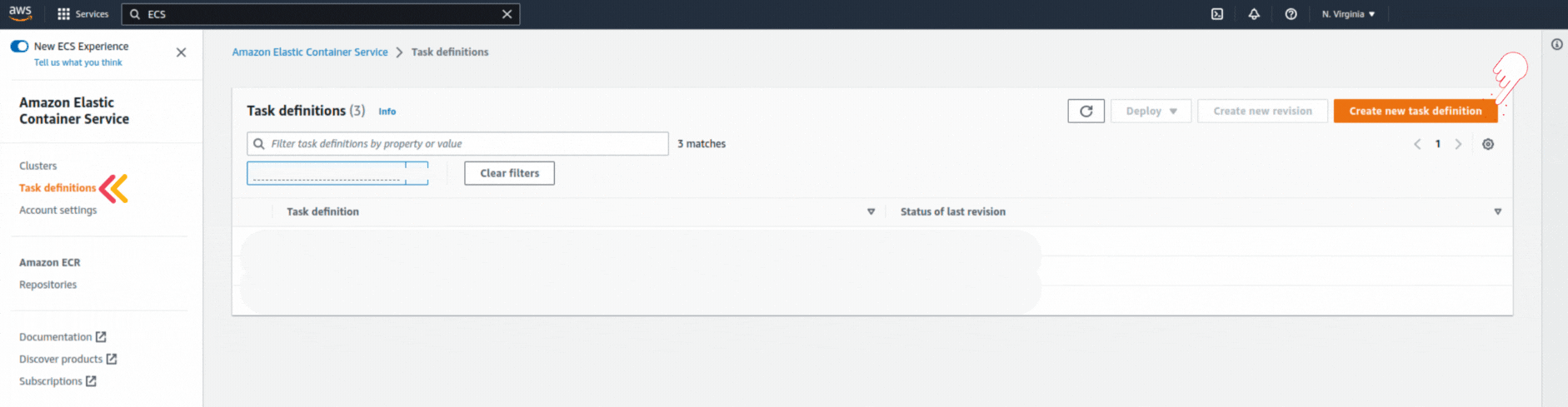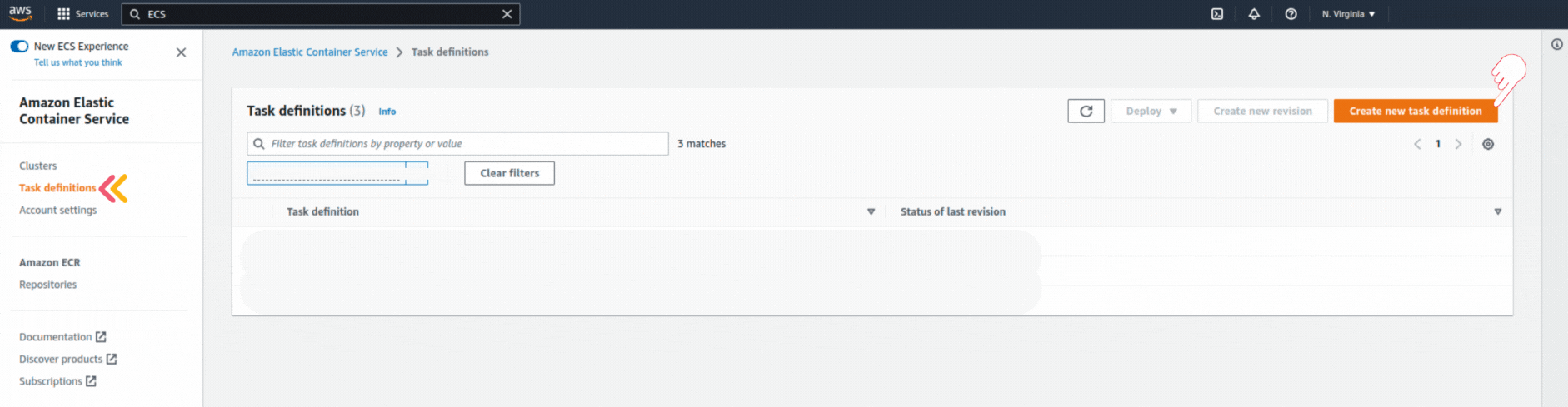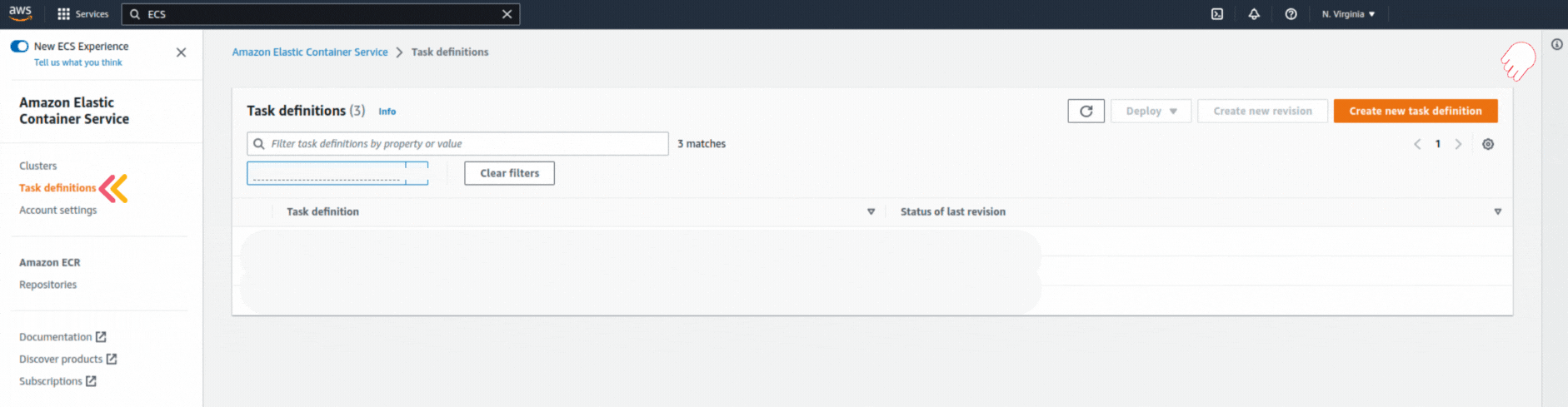
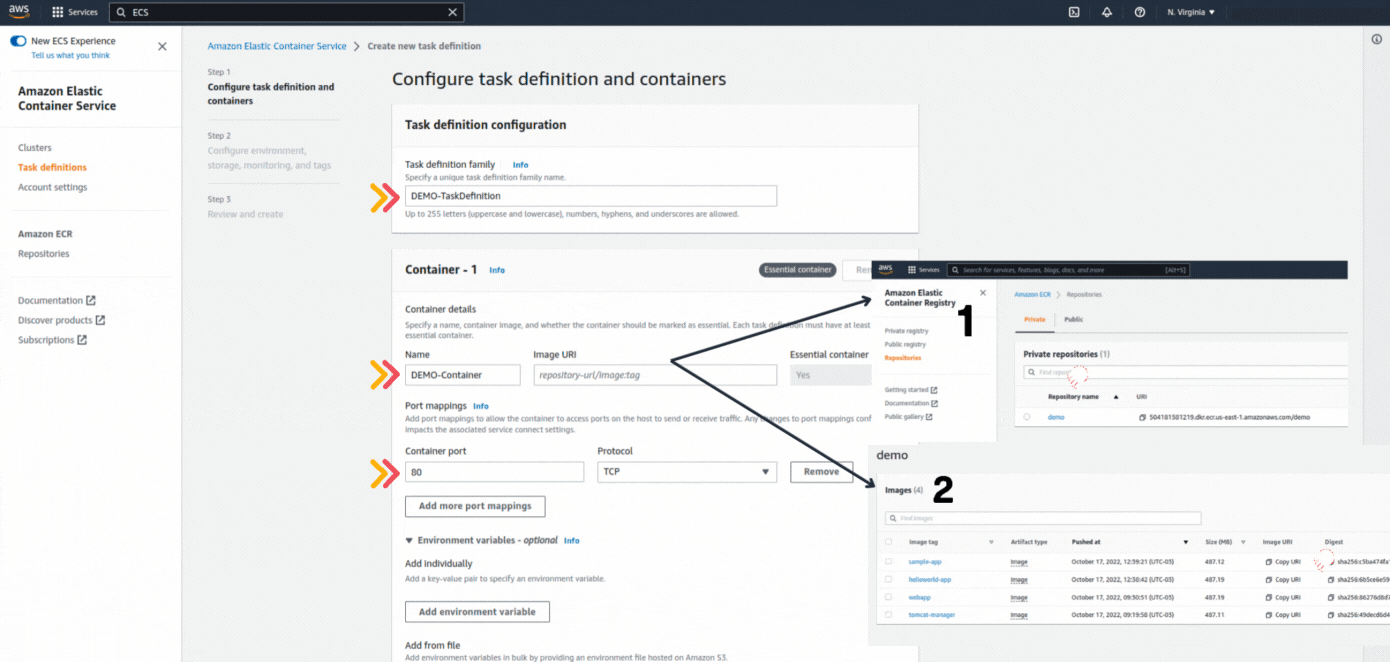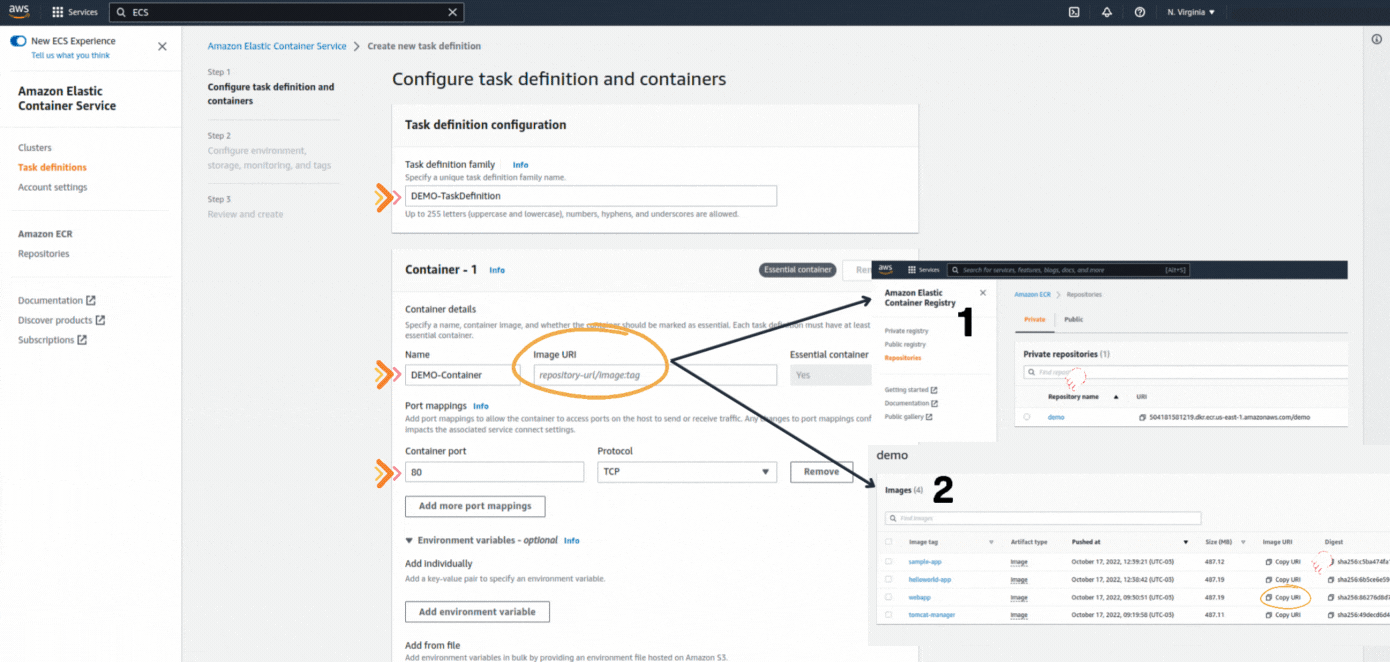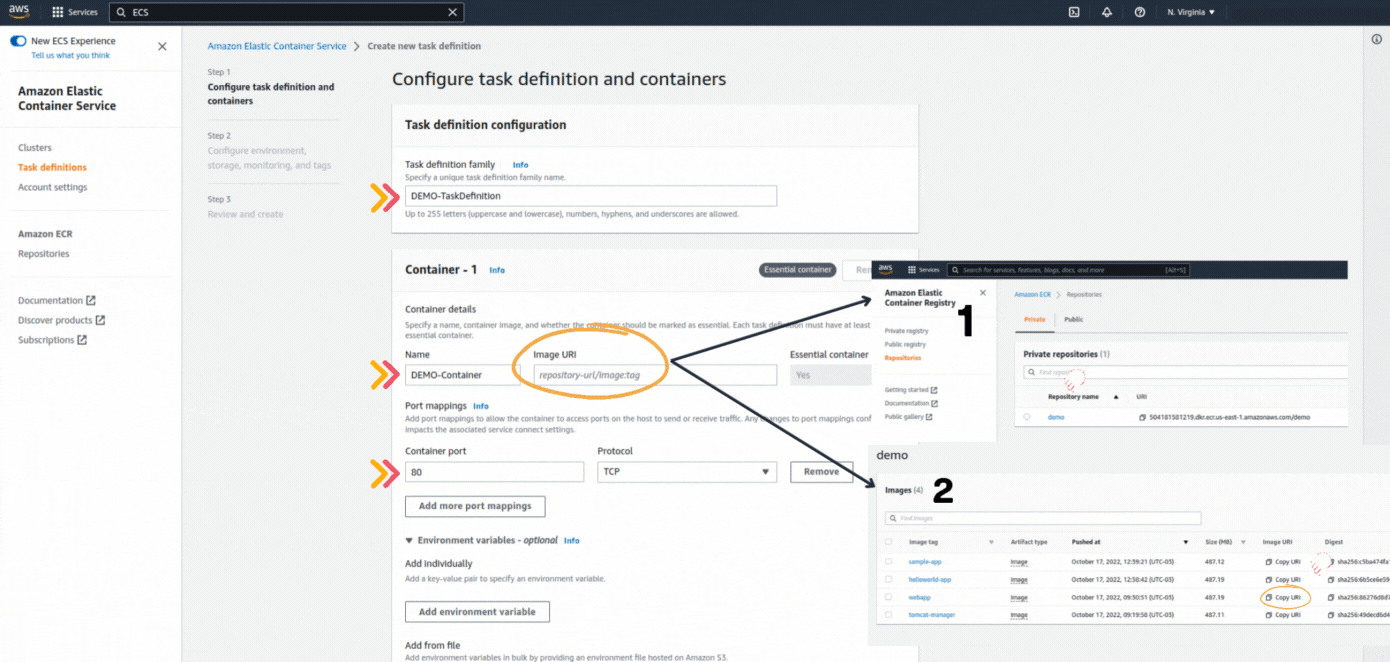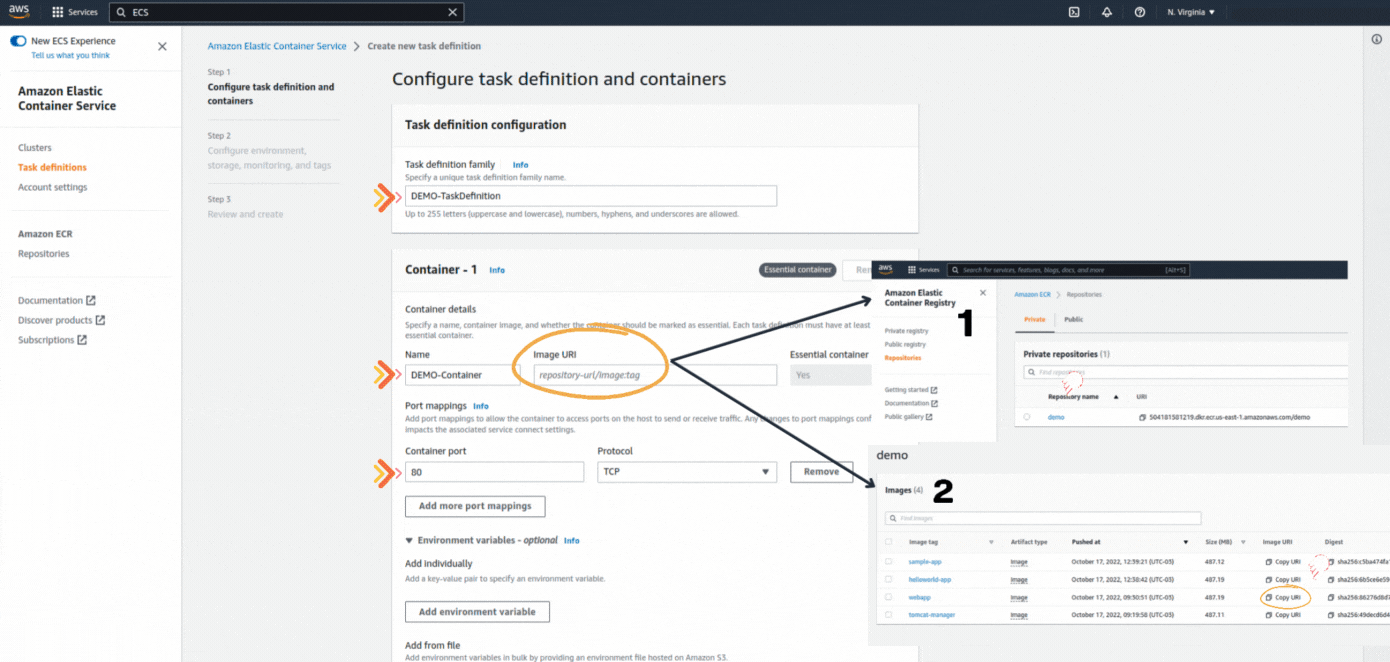
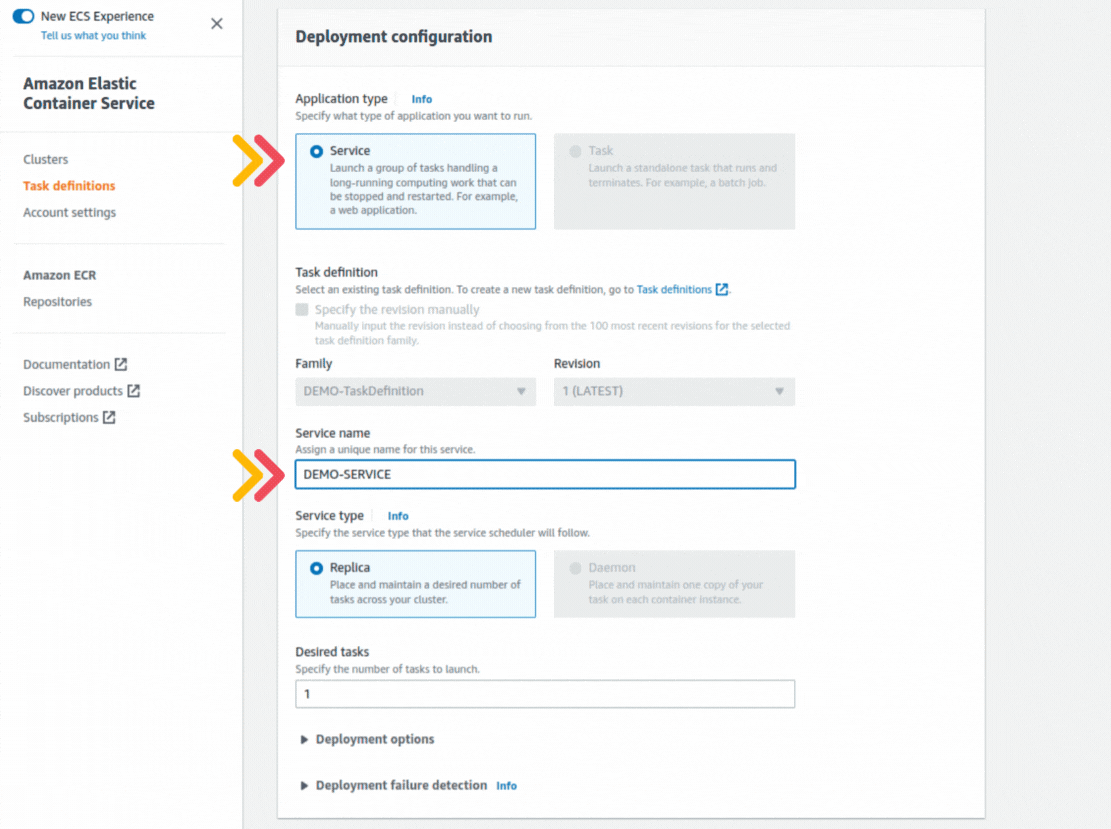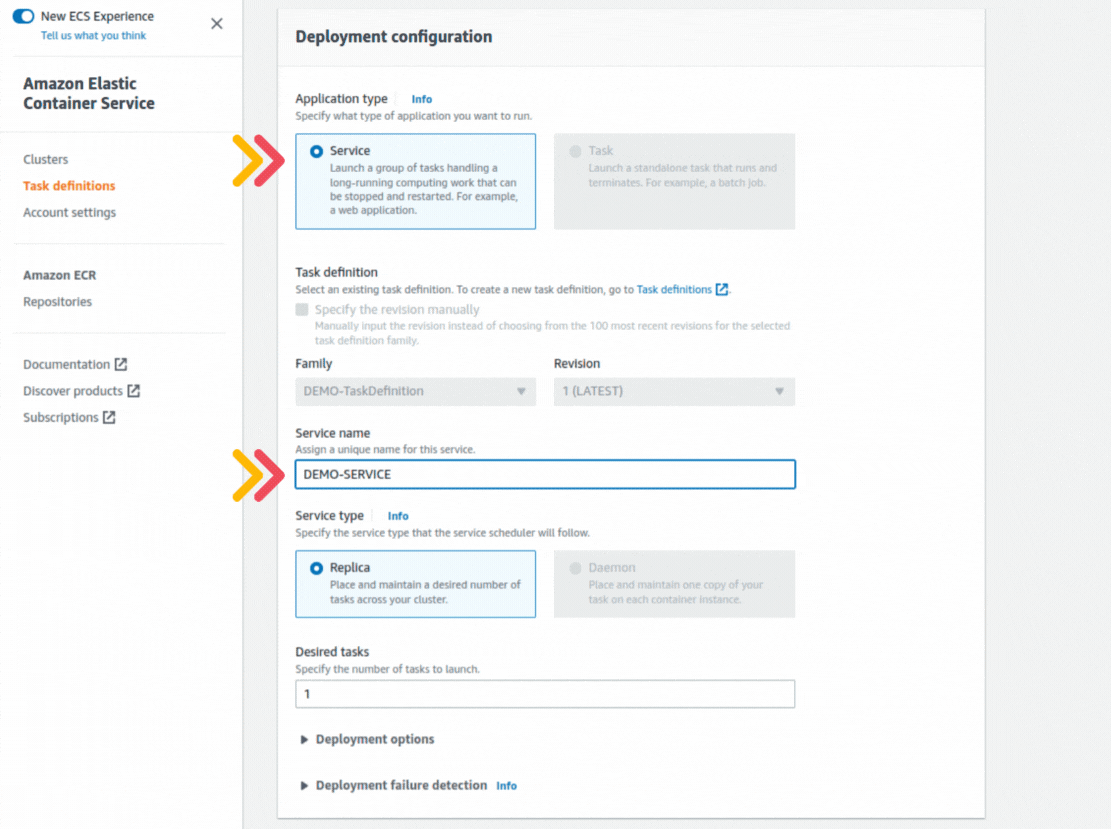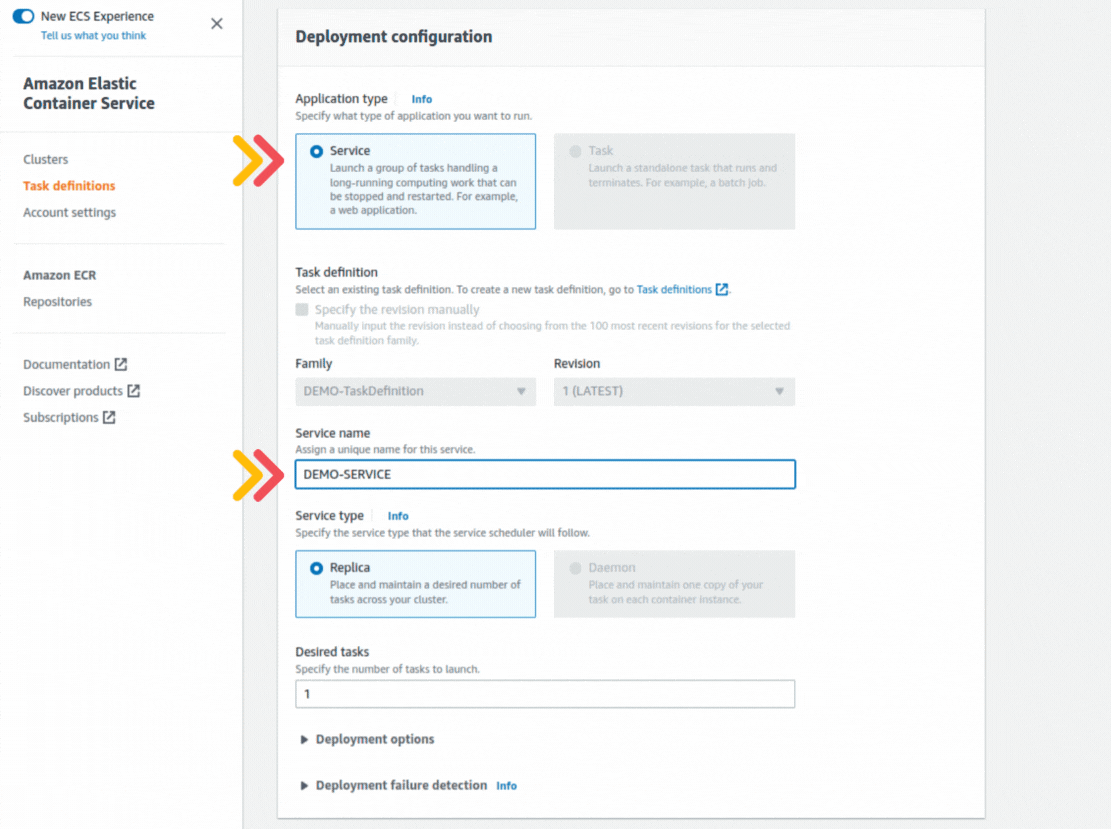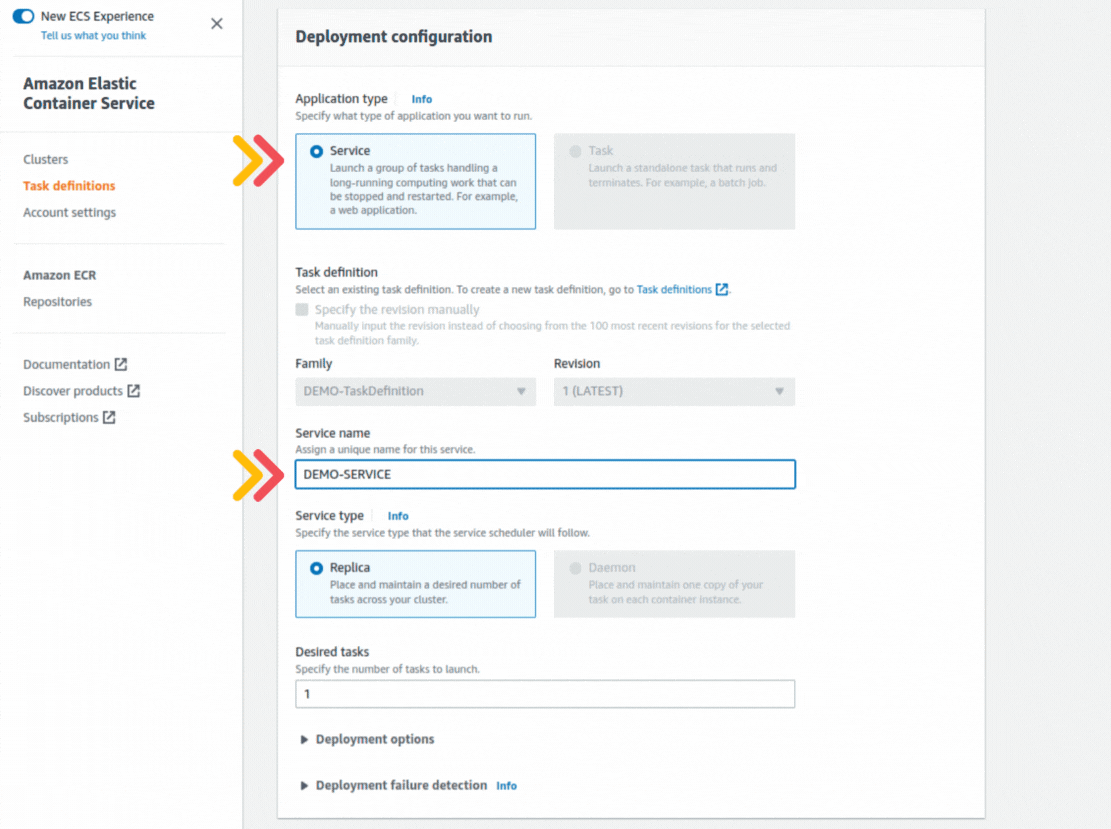
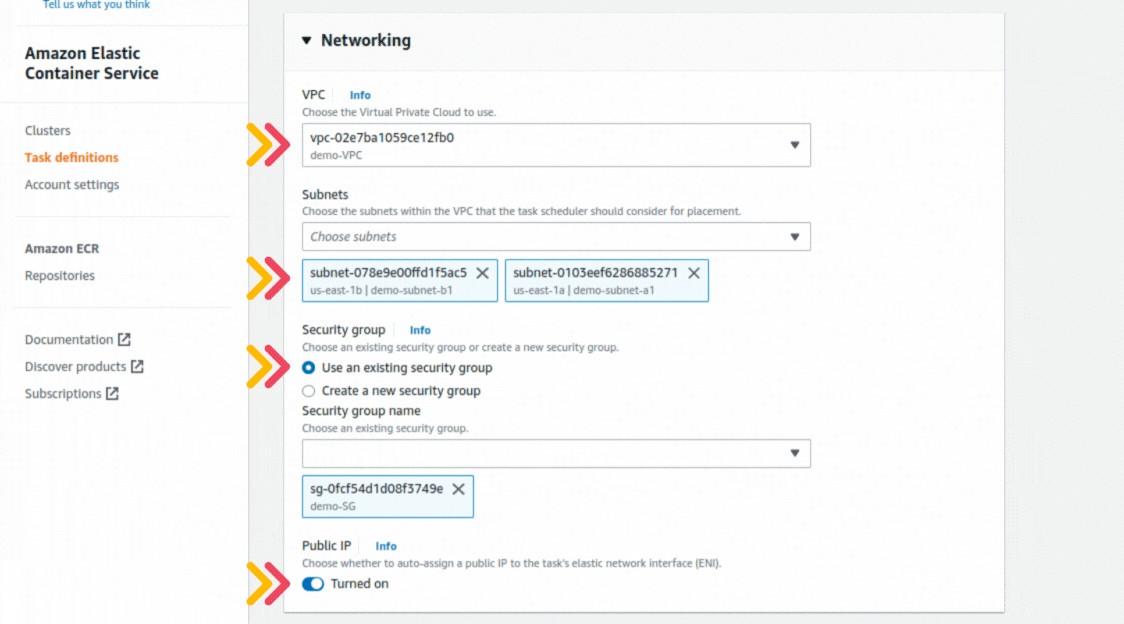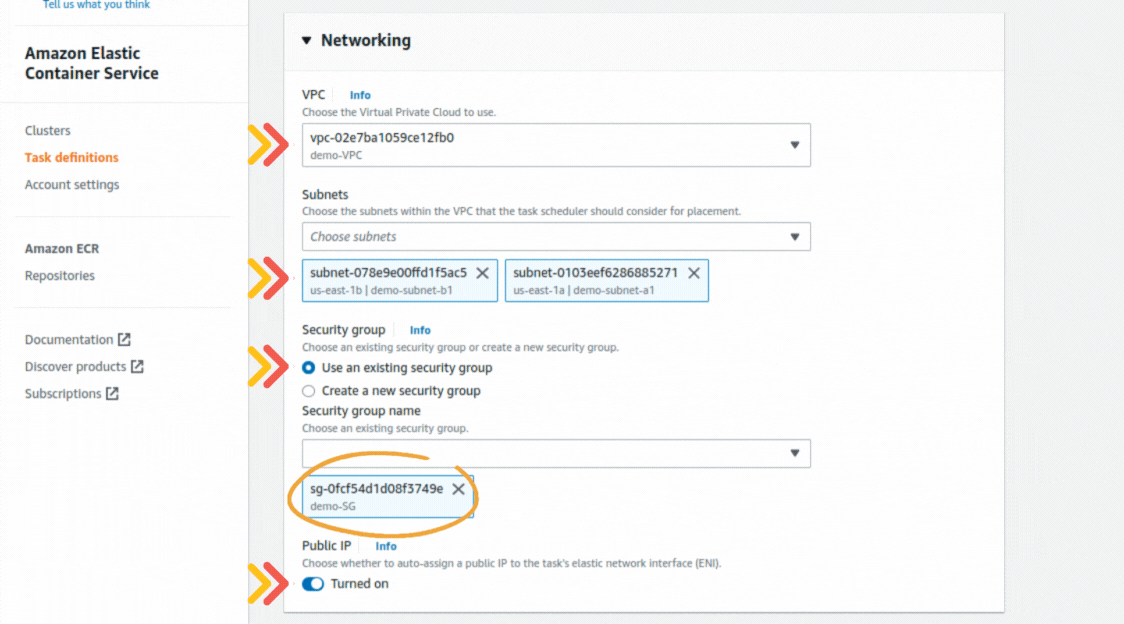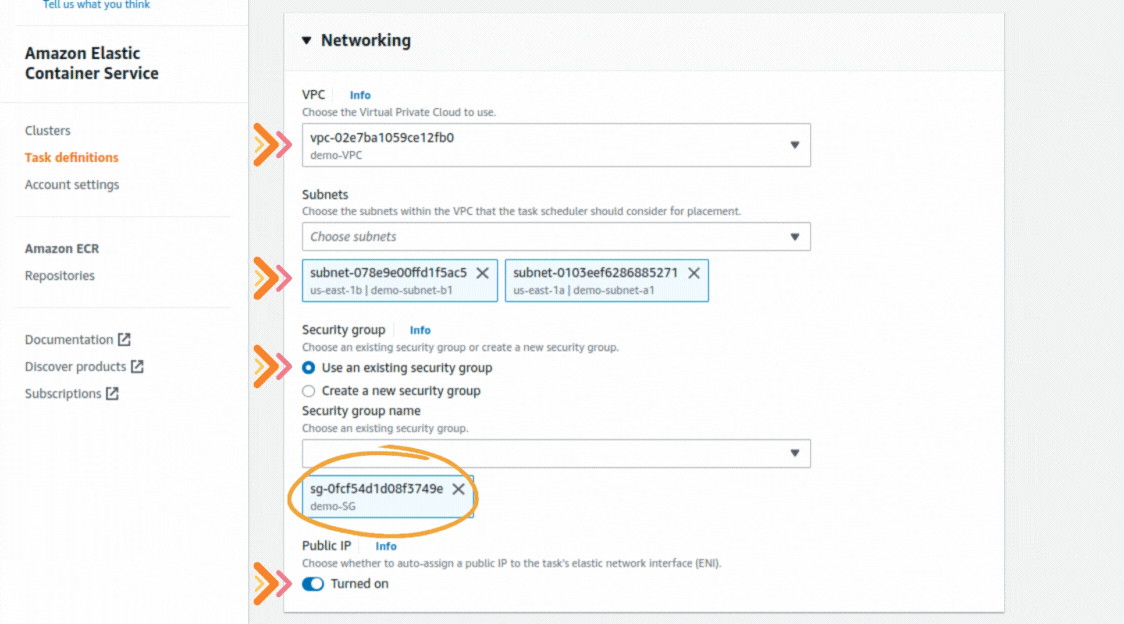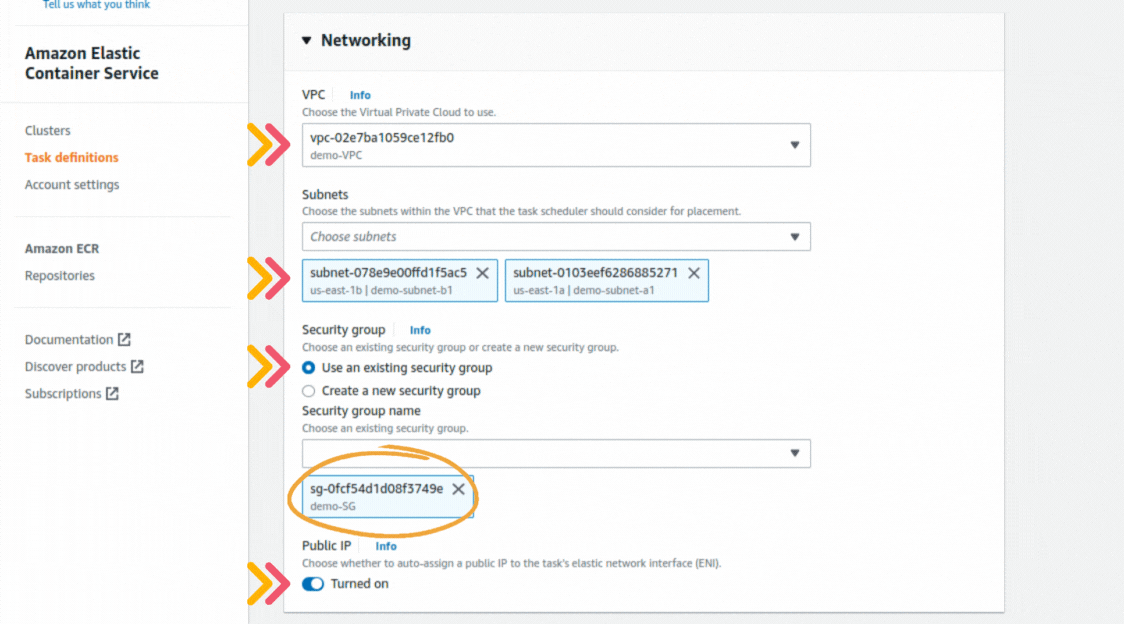
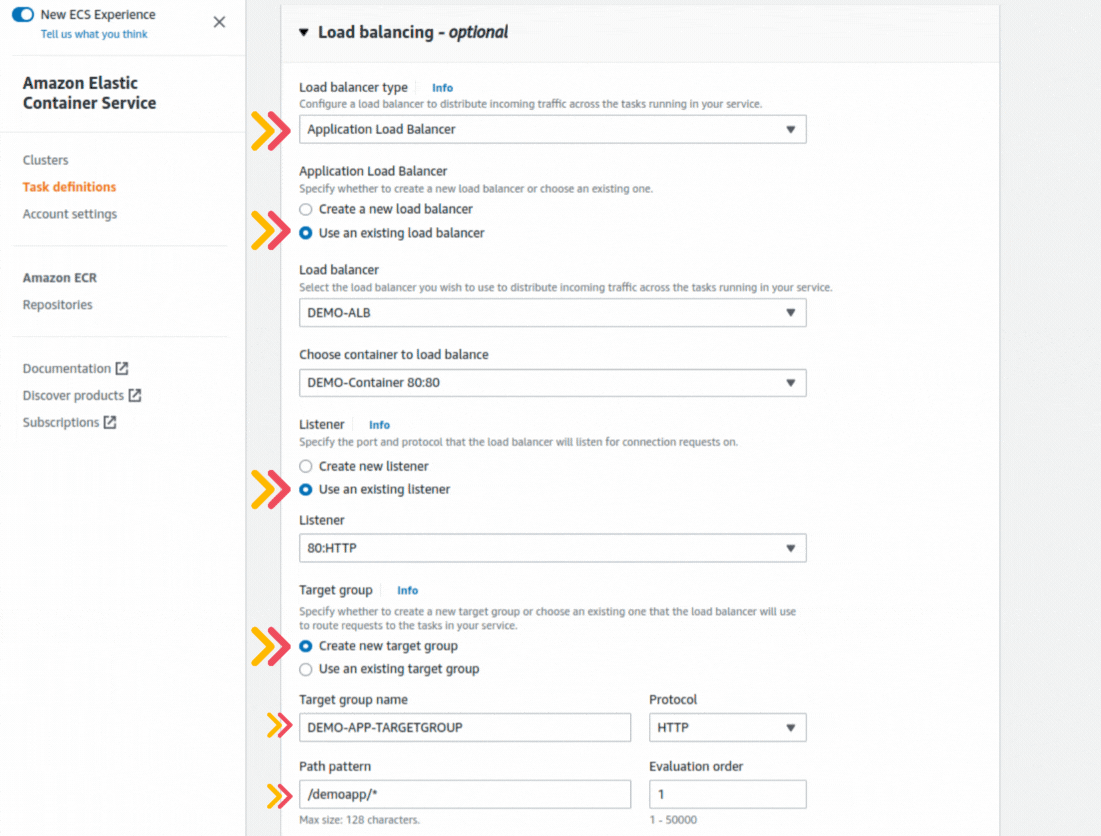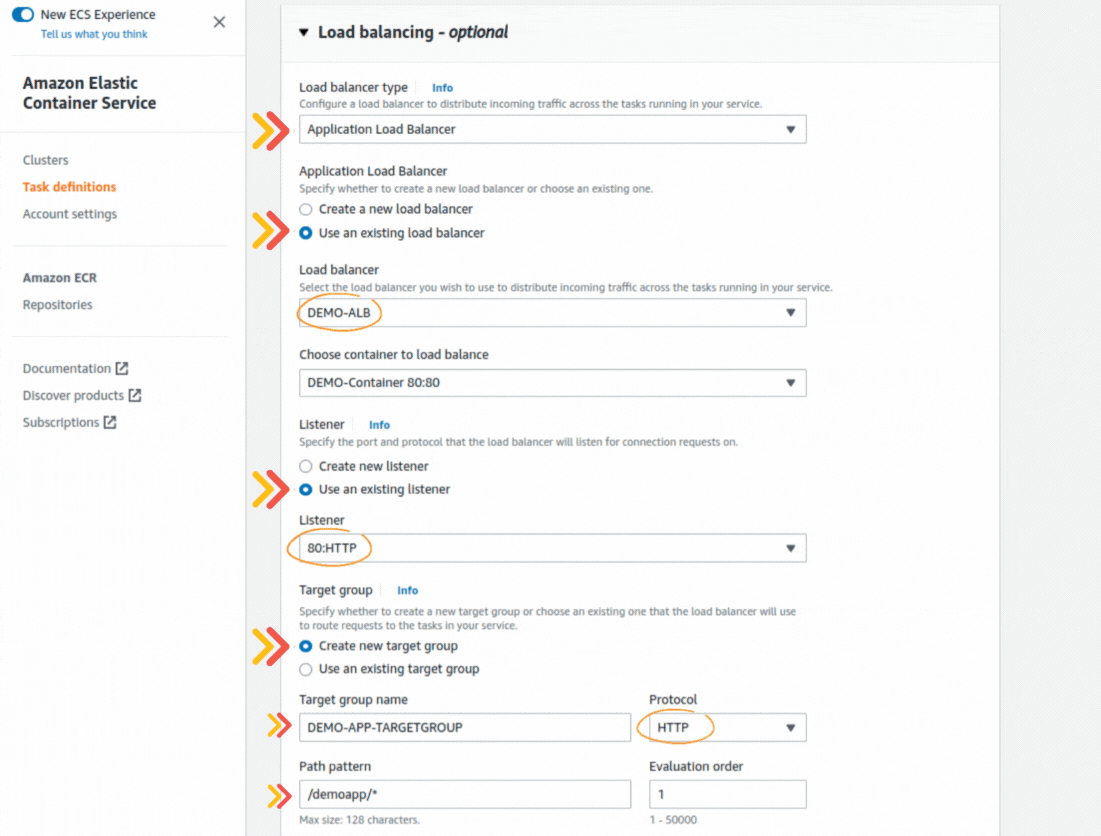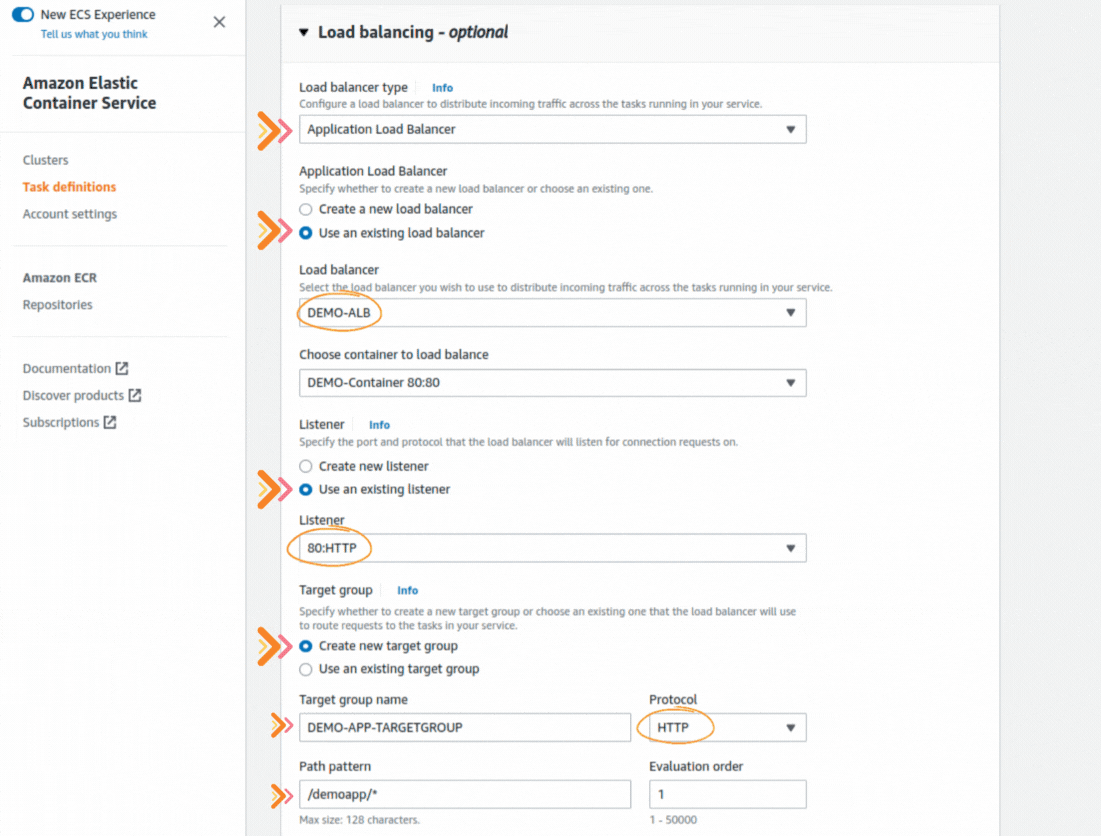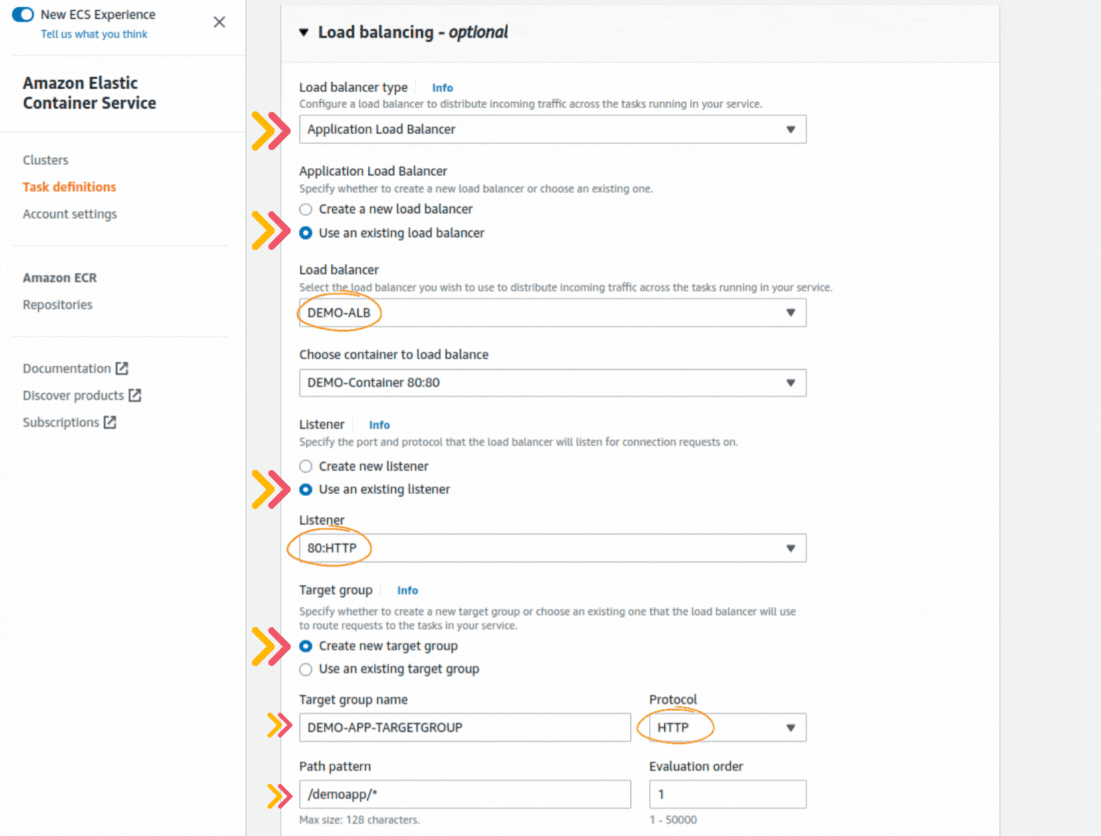
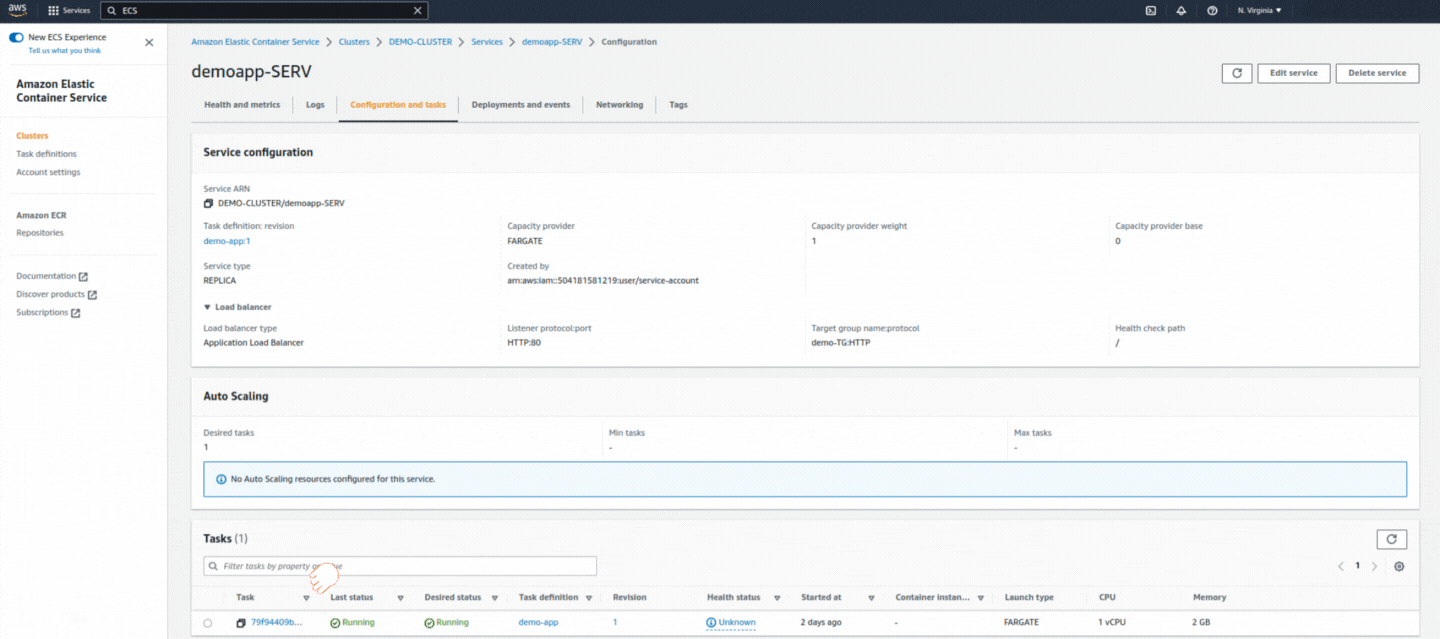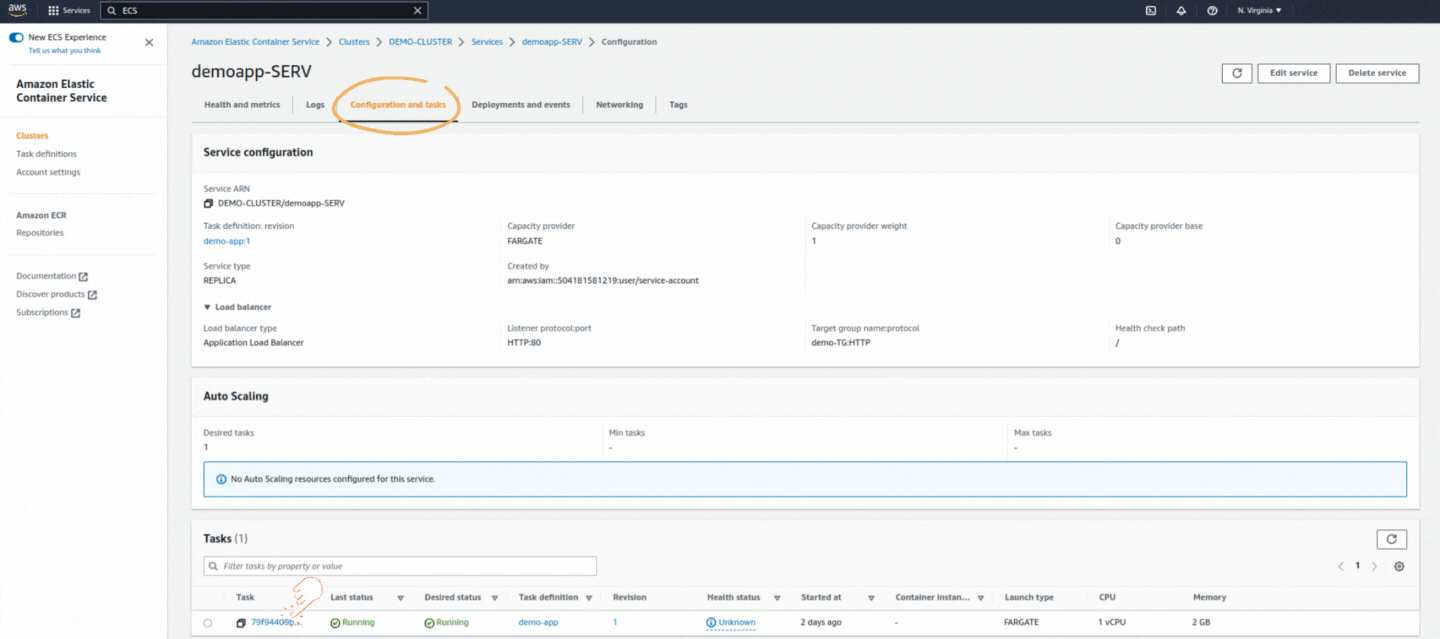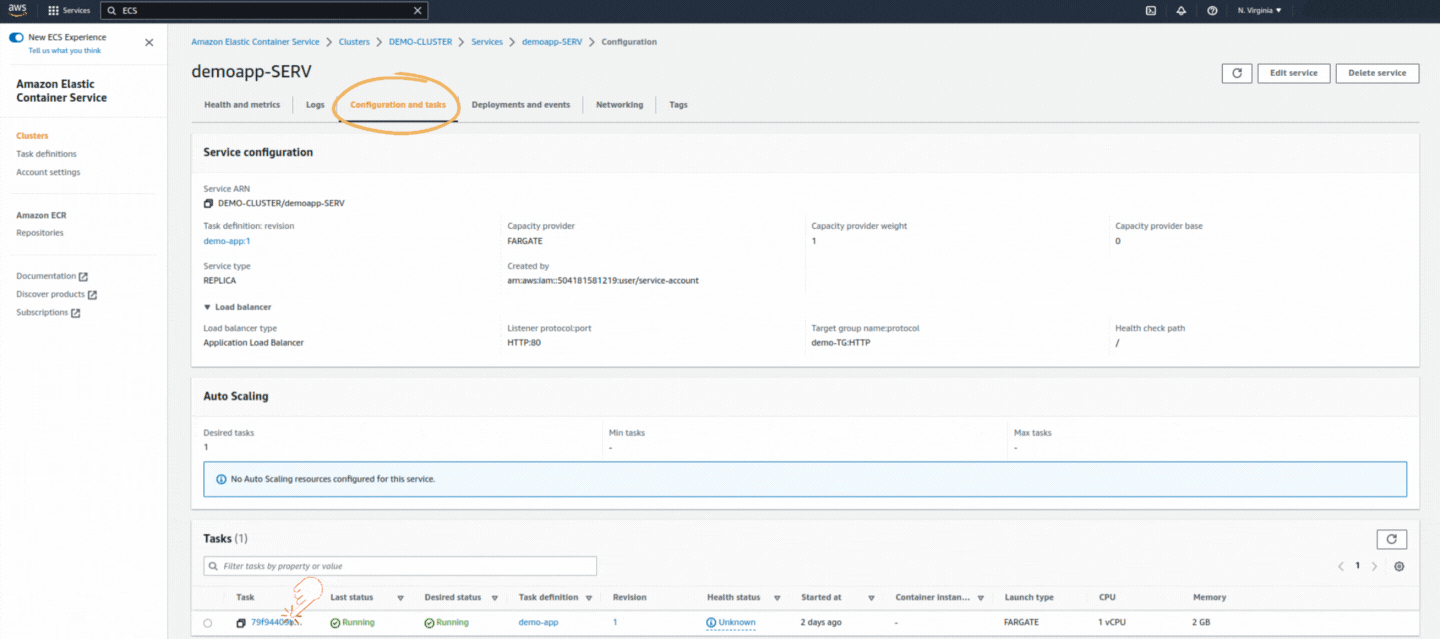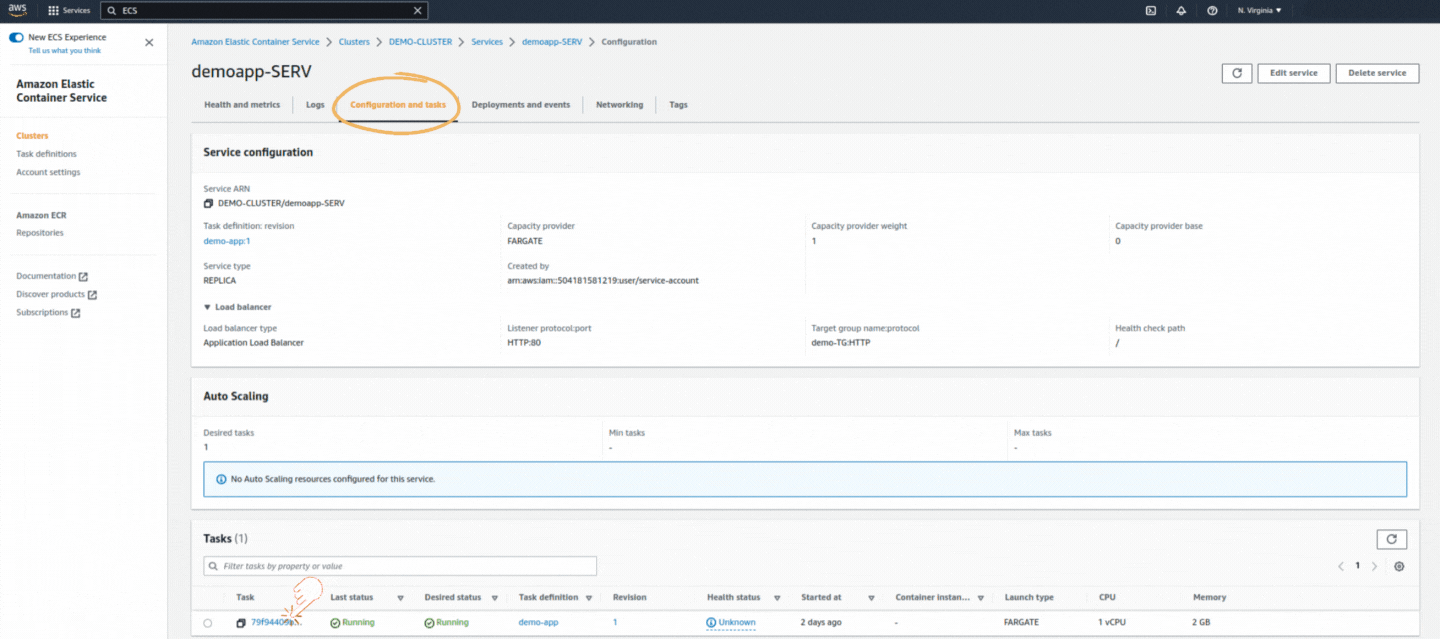
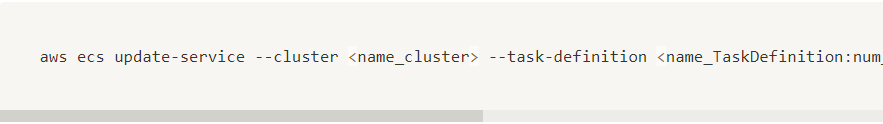
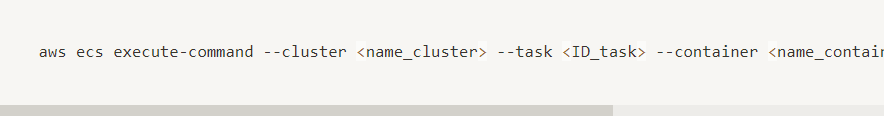
If you could not attend the Invent meeting at the end of last year, we will tell you the novelties that AWS prepared for 2023.
So let’s get started:

AWS Supply Chain:
Created to somehow solve the problems that exist with the global supply chain.
We know that Amazon has been in the market for more than 30 years. And in that period, it has been dealing with and trying to improve its logistics network and supply chain for all the products it sells.
And as they say, no one can take away what you danced! That is why Amazon has used these 30 years. And this experience was captured by creating AWS Supply Chain for all AWS customers.
The benefits offered with this are to provide your users with the ability to:
- View stock levels.
- Predictions based on machine learning.
- Risk projection and cost reduction.
- Alerts for products that will be out of stock.
- Have the parties involved have contact to resolve the problem.
It will initially be used as a preview in Northern Virginia, Oregon, and France.
AWS Clean Rooms
As we know, it is not enough with knowing about our data, but also about our biology.
That is why AWS is focusing on the analysis of biological data.
Hence, the creation of AWS Clean Rooms. This works under the concept of a clean room in a hospital and is something that has been brewing for a while and came to light in the past year.
AWS Clean Rooms will allow you to preview for forecasting, as well as share and analyze groups of data without the need to duplicate or share the underlying data itself with third parties.
All this with the intention of “taking care” of the information received and “protecting” it.
Amazon Security Lake
Security will always be important for businesses.
That is why AWS has created Amazon Security Lake to increase security policies when accessing the information handled by different companies.
This product promises is that will be able to manage, aggregate, and analyze the different records and events on the data that is being accessed throughout its entire life cycle.
In this way, threat detection is enabled, and accidents can be investigated and acted on more quickly.
 Amazon Omics
Amazon Omics
As we have said, AWS has focused on database management over the years. And raising its bar, it has now decided to analyze the biological data of human beings, which is why Amazon Omics has emerged.
Which is designed for large-scale research and analysis of “human genome” data from entire populations, it will also store and analyze these data.
For those companies such as Pfizer, and Moderna, among others, who need to know the genomic data of those with whom they have been experimenting and those who will seek to add to these experimental projects.
AWS Glue Data Quality
In the same sense of data storage and analysis, AWS creates this new service to improve the quality of data that is managed in multiple information sources and “data lakes”.
AWS Glue Data Quality’s core offering is to automatically measure, monitor, and manage data quality.
In addition to programming its periodic execution as the stored data changes to simplify the process of maintaining the quality of the information that is processed.
Amazon Athena for Apache Spark y Amazon DocumentDB Elastic Cluster
AWS builds these products for data storage and analysis.
In the case of Amazon Athena, it is created to add compatibility with this famous platform based on the open-source Apache Spark.
The benefit offered by Amazon Athena is to automate the necessary resources, and speed up the execution time and the results of the queries made on said platform.
In the case of Amazon DocumentDB Elastic Cluster, it’s able to support millions of writes per second and store up to 2 petabytes of data, for those who need to manage JSON data at scale.
Amazon DocumentDB Elastic Cluster achieves this by using a distributed storage system, which automatically partitions data sets across multiple nodes without the need for administrators to manage these complex processes.

AWS SimSpace Weaver
In another order of ideas, AWS creates SimSpace Weaver which is a service to run massive spatial simulations without the need to manage the infrastructure.
What does this mean?
This means that with AWS SimSpace Weaver you will be able to create quite complex 3D simulations and also provide models. In addition, bring your SDK toolkit so that you can assemble it yourself and the possibility of incorporating digital twins.
As if you were Bob the builder.
Amazon SageMaker
AWS has improved the popular machine learning service.
Granting 8 new capabilities to optimize, train and deploy Machine Learning models, considering that AI is growing exponentially.
Among these new capabilities is:
Access control and permissions
Documentation and review of information models throughout the machine learning life cycle.
Unify in the same interface the control and monitoring of the models.
Improve data preparation to increase its quality.
Allows data scientists to collaborate in real-time and/or validate models in an automated way, using real-time interference requests.
And if this were not enough, it will be able to support geospacial data.
What is this for?
Scientists can continue to find ways to control our weather, agriculture, and other areas that are natural and where man thinks he can continue to intervene, now using AI.
Tell us what you think of the AWS news, which ones are you interested in implementing in your business, or venture?